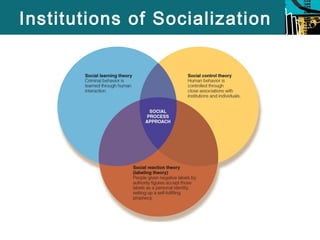
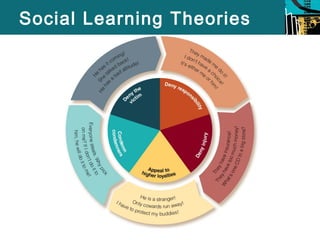
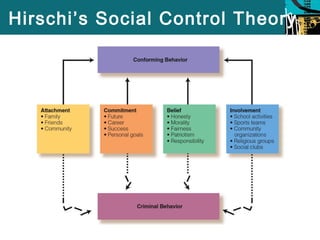
This document summarizes several social process theories of criminology. It discusses social learning theory, which posits that criminal behavior is learned through relationships with criminal peers. Social control theory argues that social bonds keep criminal behavior in check. Labeling theory suggests that people become criminals when labeled as such by others. The document also examines differential association theory and neutralization theory under the umbrella of social learning theory. It analyzes social control theory and the role of attachment, commitment, and beliefs. Finally, it discusses labeling theory and the consequences as well as critiques of these major social process theories of crime.