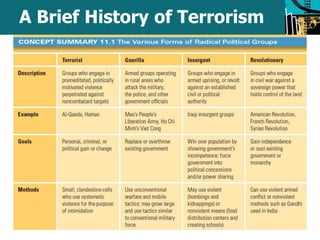
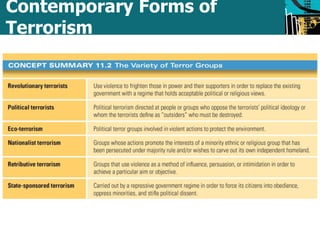
This document defines and discusses political crime and terrorism. It covers the goals of political criminals, how individuals become political criminals, categories of political crimes like election tampering, and definitions of terrorism. Terrorism is defined as using violence against innocent people for political aims. The document also provides a brief history of terrorism and discusses contemporary forms like revolutionary, nationalist, and state-sponsored terrorism. It examines motivations for terrorism and responses to terrorism like increased surveillance powers under the USA Patriot Act.