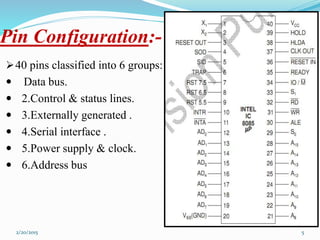
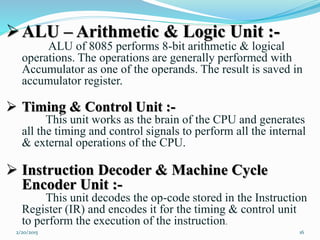
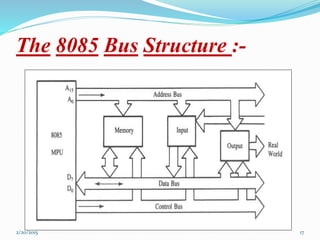
The document discusses the 8085 microprocessor. It presents information about its features, pin configuration, architecture, registers, bus structure, advantages, and disadvantages. The 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 8 data lines, 16 address lines, and a clock frequency of 3MHz. It has features like 8-bit operations, 64KB memory capacity, and 74 instructions with 5 addressing modes. The document concludes that while the 8085 had benefits like a 5V power supply, it also had limitations like low speed and small memory that led to later versions like the 8086.