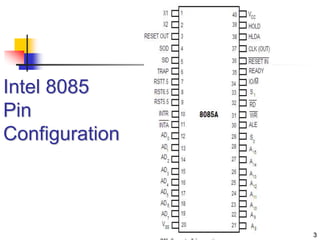
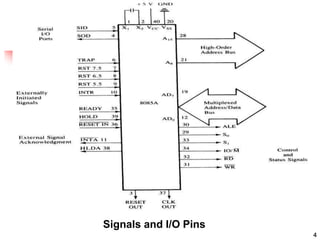
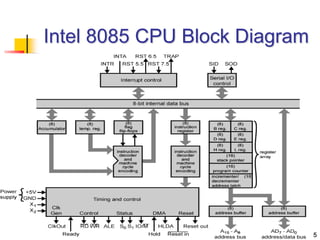
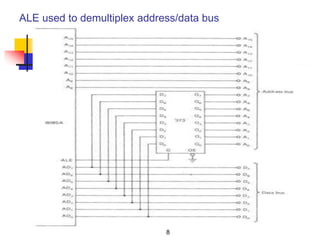
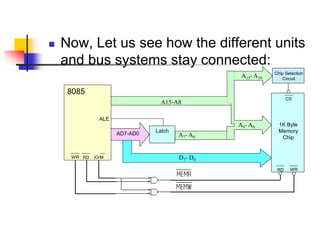
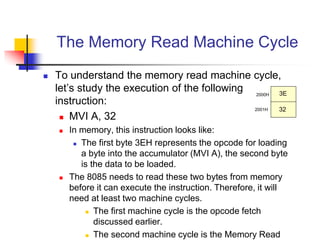
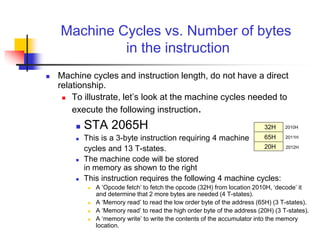
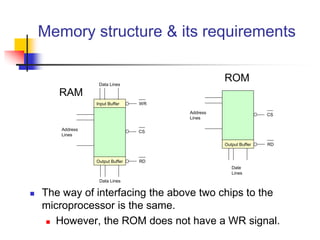
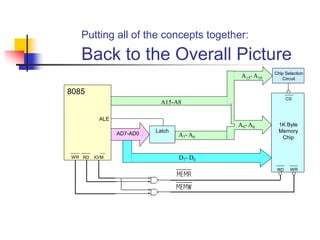
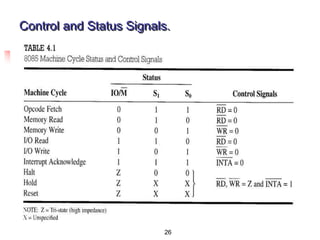
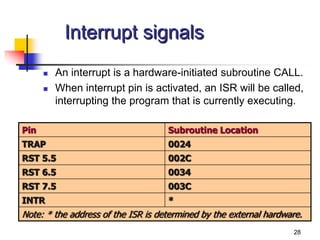
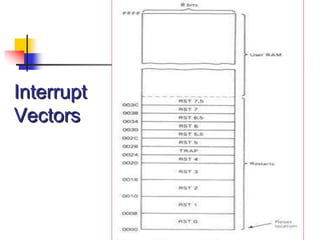
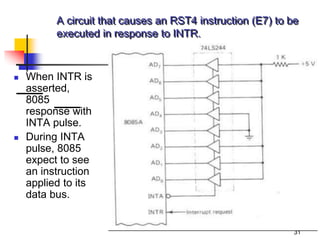
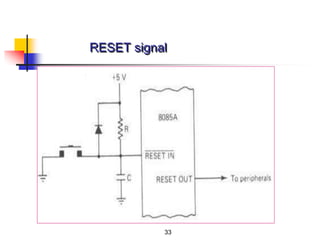
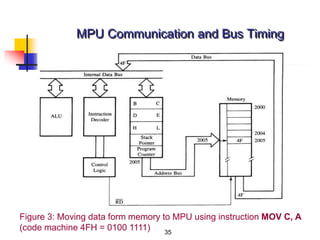
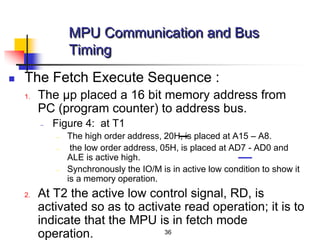
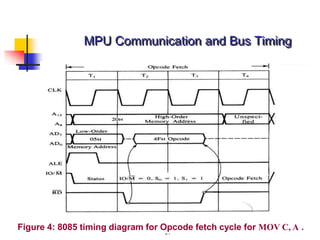
The document provides an introduction to the Intel 8085 microprocessor. It discusses that the 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor that can address 64KB of memory using a 40-pin chip. It operates at a maximum of 3MHz and its pins can be grouped into address bus, data bus, control signals, power and clock, externally initiated signals, and serial I/O ports. The document also describes the address and data bus systems, control signals, interrupts, reset signals, direct memory access, and timing diagrams for opcode fetch cycles.