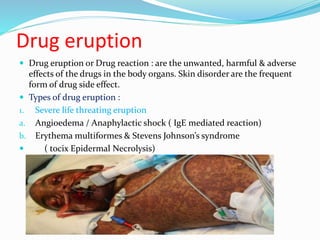
1) Drug eruptions are unwanted, harmful skin effects caused by drugs and can include rashes, blisters, and hives.
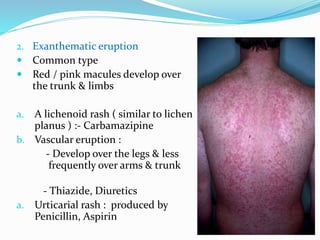
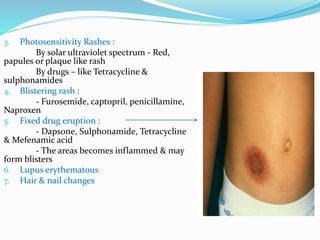
2) There are several types of drug eruptions such as severe life-threatening eruptions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exanthematous eruptions which cause red macules on the body, and photosensitivity rashes caused by drugs like tetracycline.
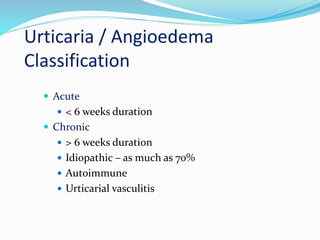
3) Urticaria, commonly known as hives, causes wheals or swollen bumps on the skin that are usually itchy and come and go rapidly, and can sometimes involve angioedema which is swelling under the skin of the face, lips, tongue, and