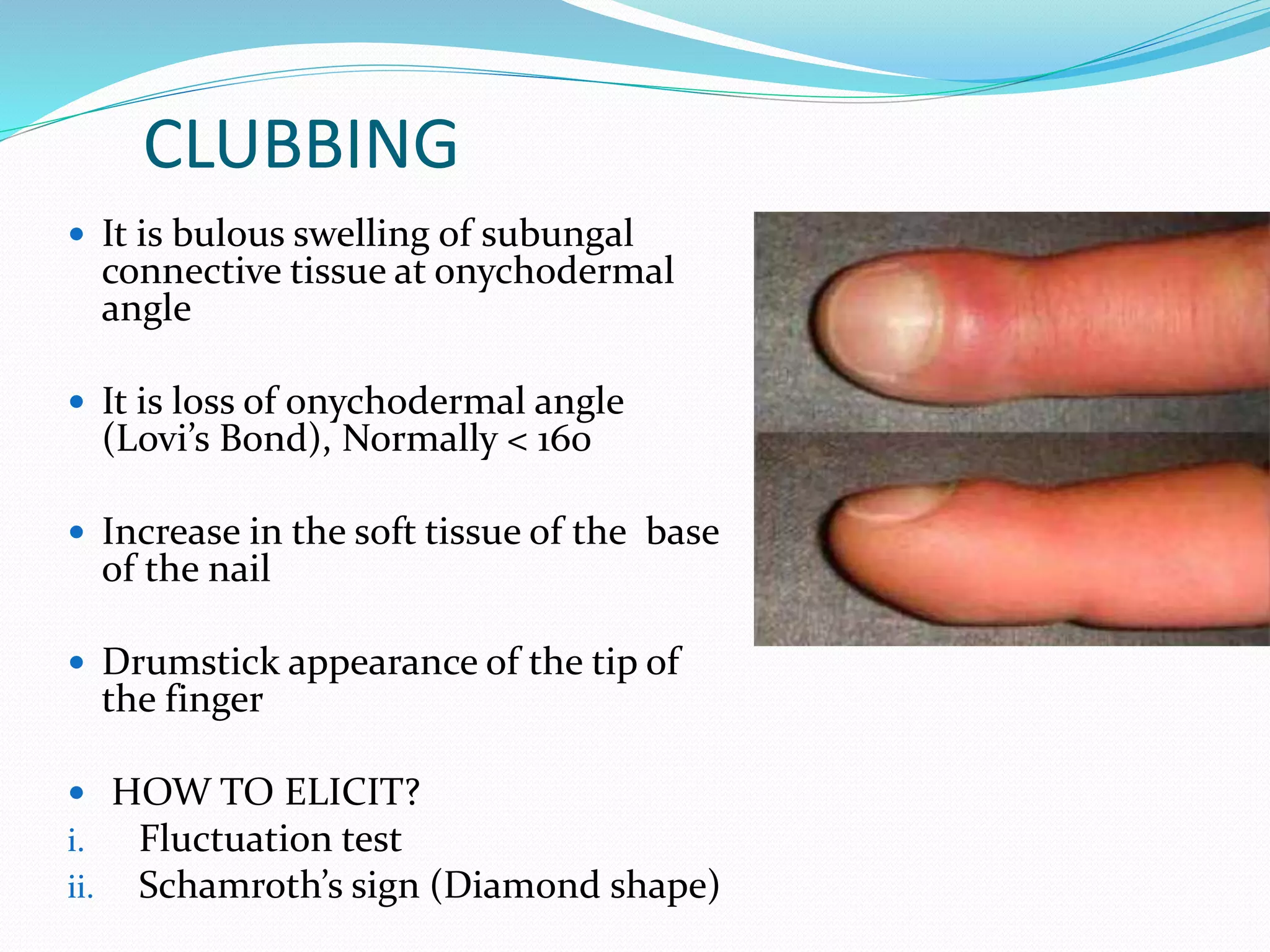
The document outlines the general principles and techniques of physical examination, including vital signs assessment (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, and respiratory rate). It provides detailed information on the significance of various abnormal findings, such as pallor, icterus, cyanosis, clubbing, lymphadenopathy, oedema, and dehydration, including their causes and examination techniques. Additionally, it covers the normal ranges for vital signs and the classifications of blood pressure, emphasizing the importance of thorough and relevant patient assessment.