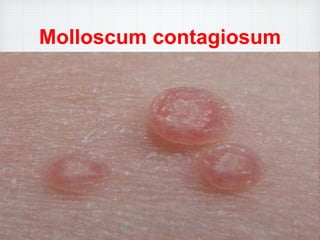
Molluscum contagiosum is a common, harmless skin infection caused by a poxvirus that spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact. It presents as small, flesh-colored bumps with a dimpled center that contain a white, curdy core. While generally asymptomatic, the bumps can occasionally itch or cause a skin rash. Diagnosis is made through visual examination of characteristic lesions, and treatment options range from natural resolution to cryotherapy, curettage, laser surgery, or topical medications depending on severity. Left untreated in healthy individuals, molluscum contagiosum will usually clear up on its own within months without scarring.