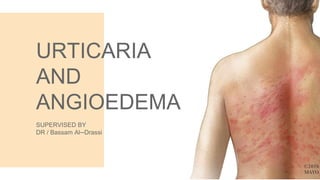
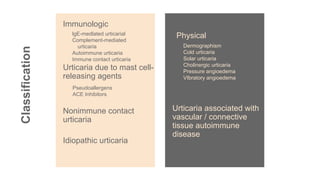
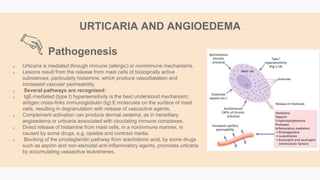
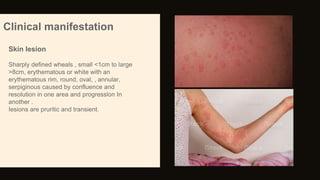
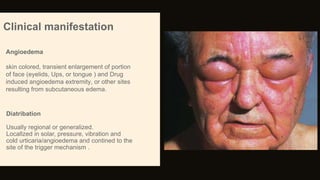
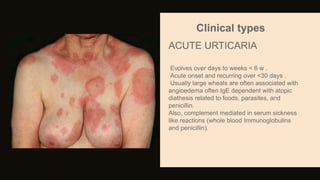
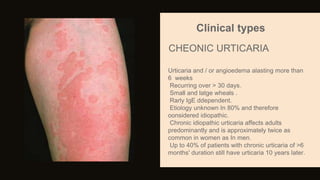
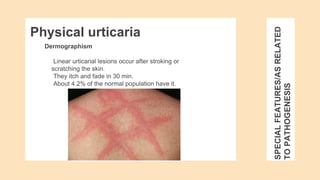
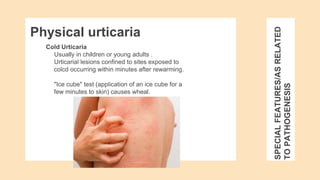
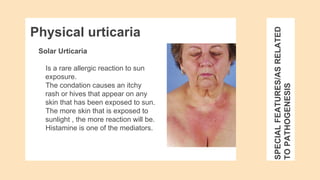
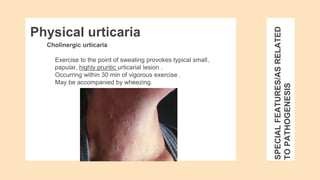
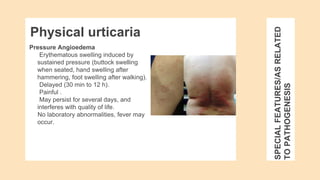
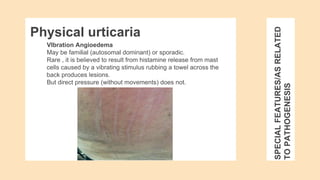
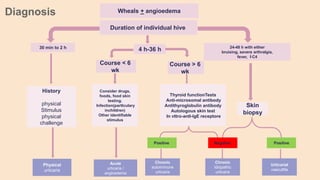
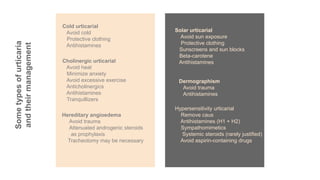
Urticaria and angioedema are conditions characterized by wheals (hives) and swelling in the skin. Urticaria involves superficial swelling in the upper dermis, while angioedema involves deeper swelling in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. They can be acute, recurrent, or chronic. Causes include allergic reactions, physical stimuli, infections, medications, foods, emotional stress, and autoimmune factors. Diagnosis involves taking a thorough history regarding triggers, medications, and associated symptoms.