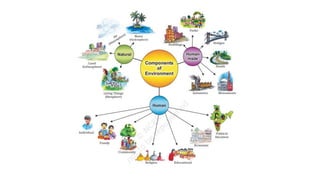
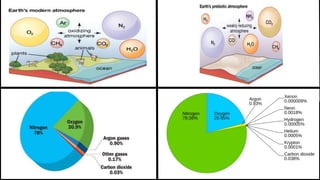
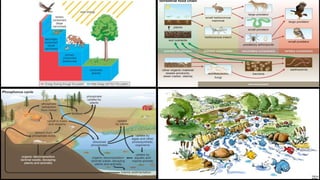
The document defines environment as everything that surrounds living organisms, including both natural and human-made elements. It notes that the natural environment comprises land, water, air, plants, and animals, while the human environment includes permanent settlements, transportation systems, and other infrastructure created by humans. It also outlines several components of the environment, including the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere, and explains how human activity has modified the natural environment through activities like agriculture, industry, and transportation.