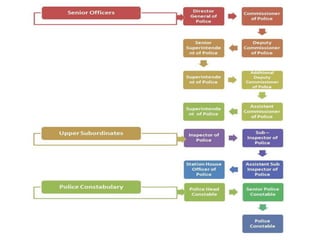
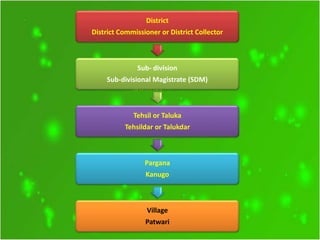
The document discusses rural administration in India, highlighting the role of local government in managing village needs and addressing issues such as law enforcement and land record maintenance. It details the hierarchy of police and land record management, including the responsibilities of various officials like the district collector and patwari. Additionally, it notes the change in inheritance laws due to the Hindu Succession Act of 2005, which granted equal rights to daughters in agricultural property.