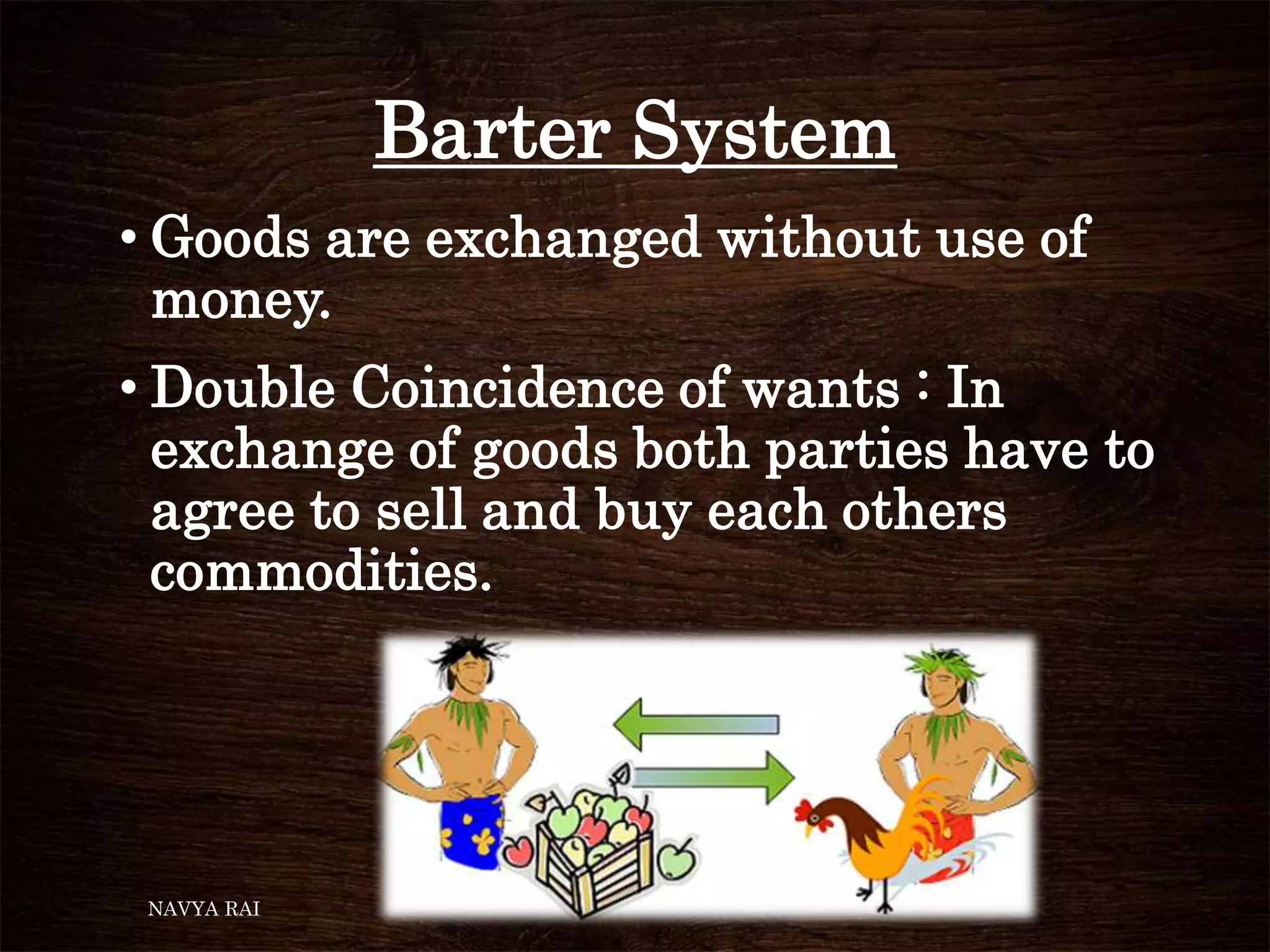
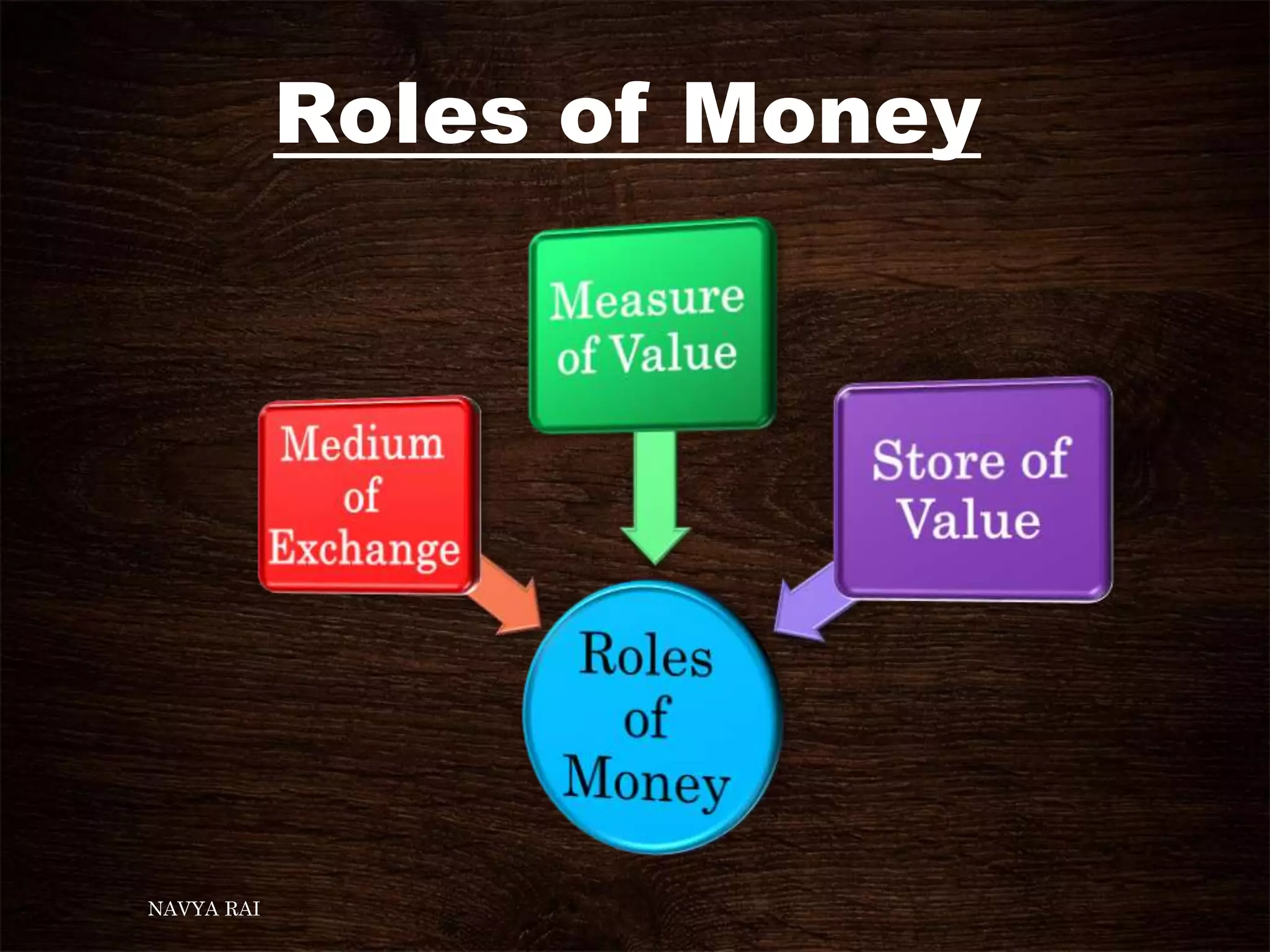
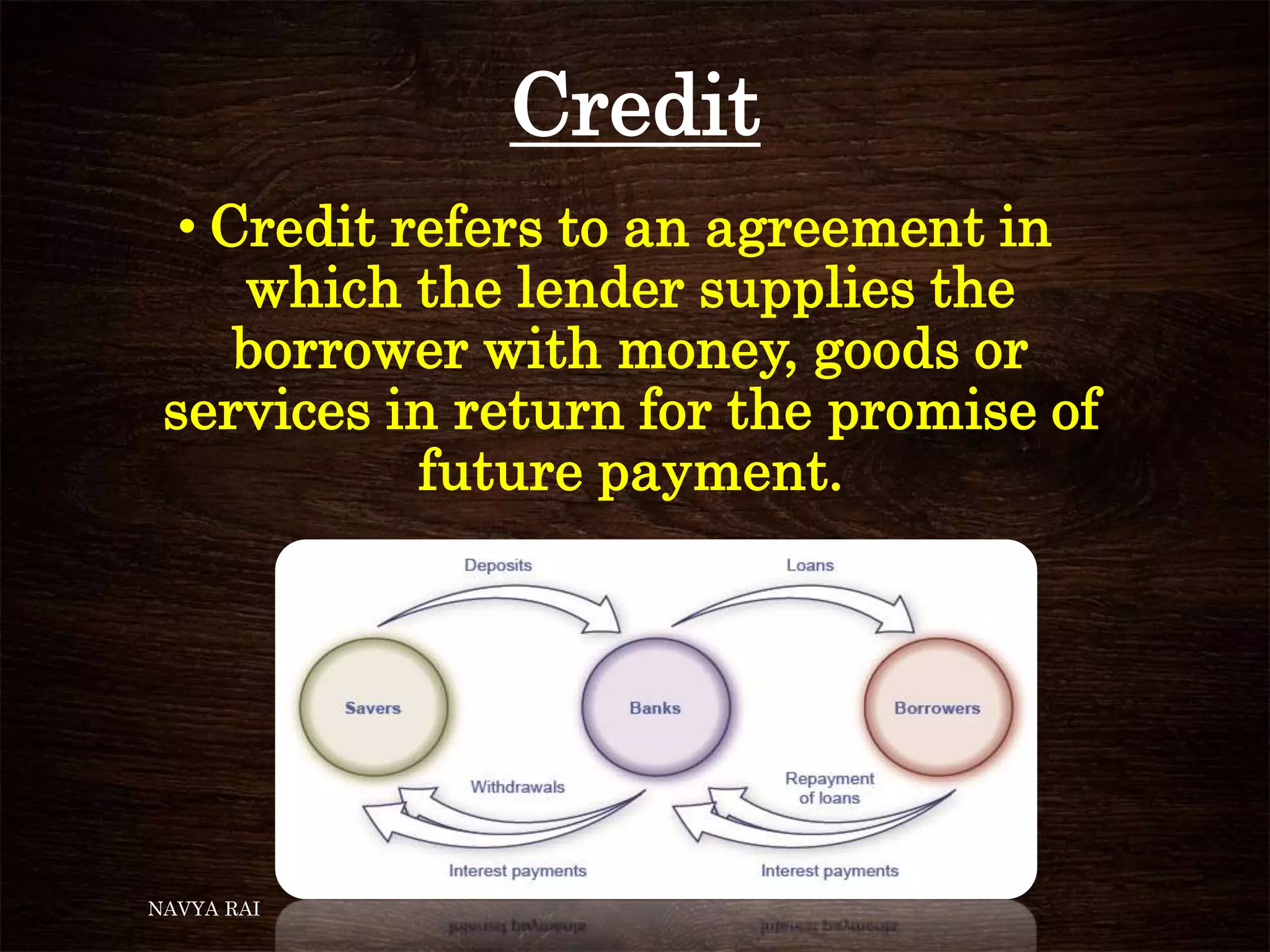
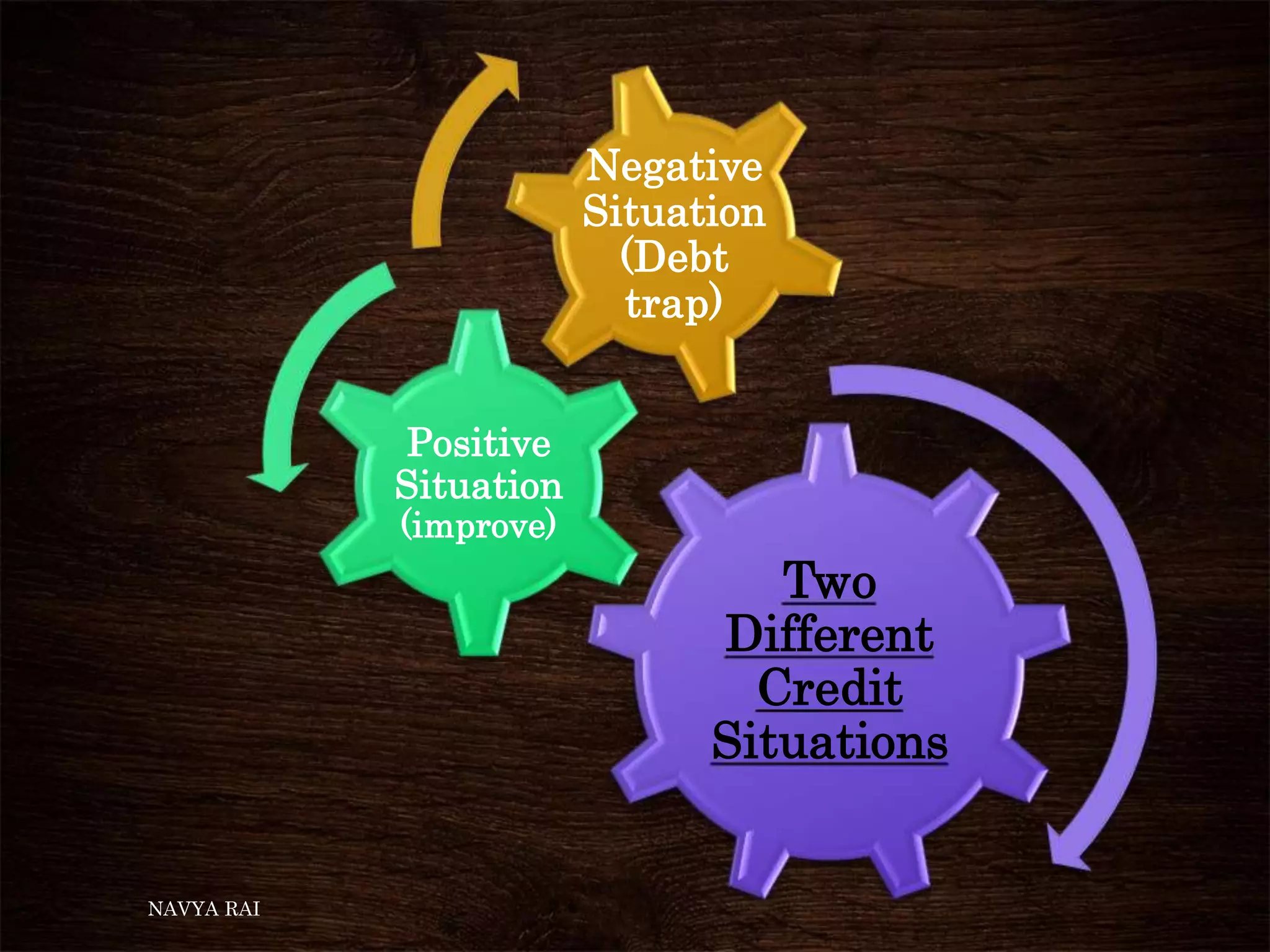
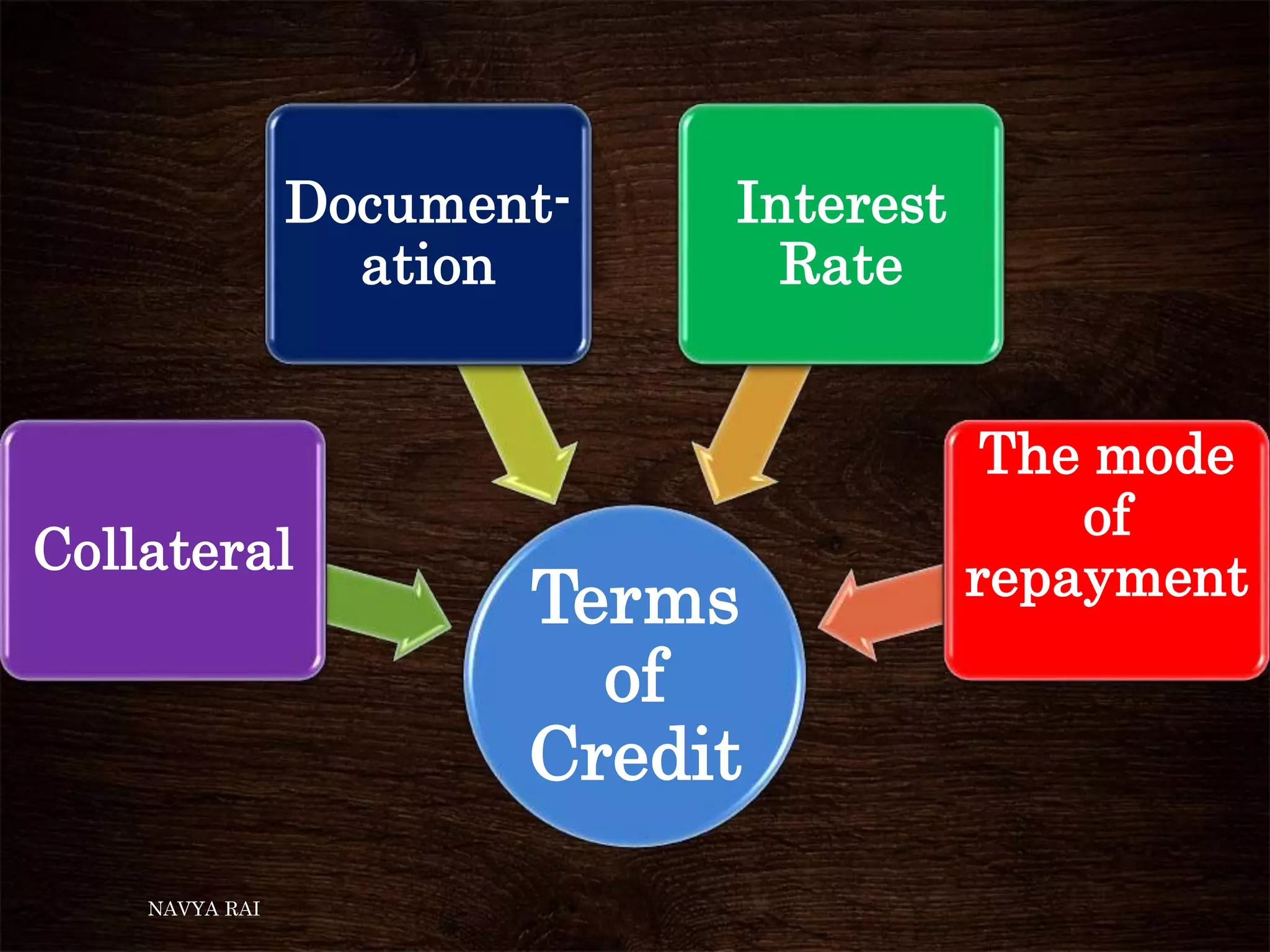
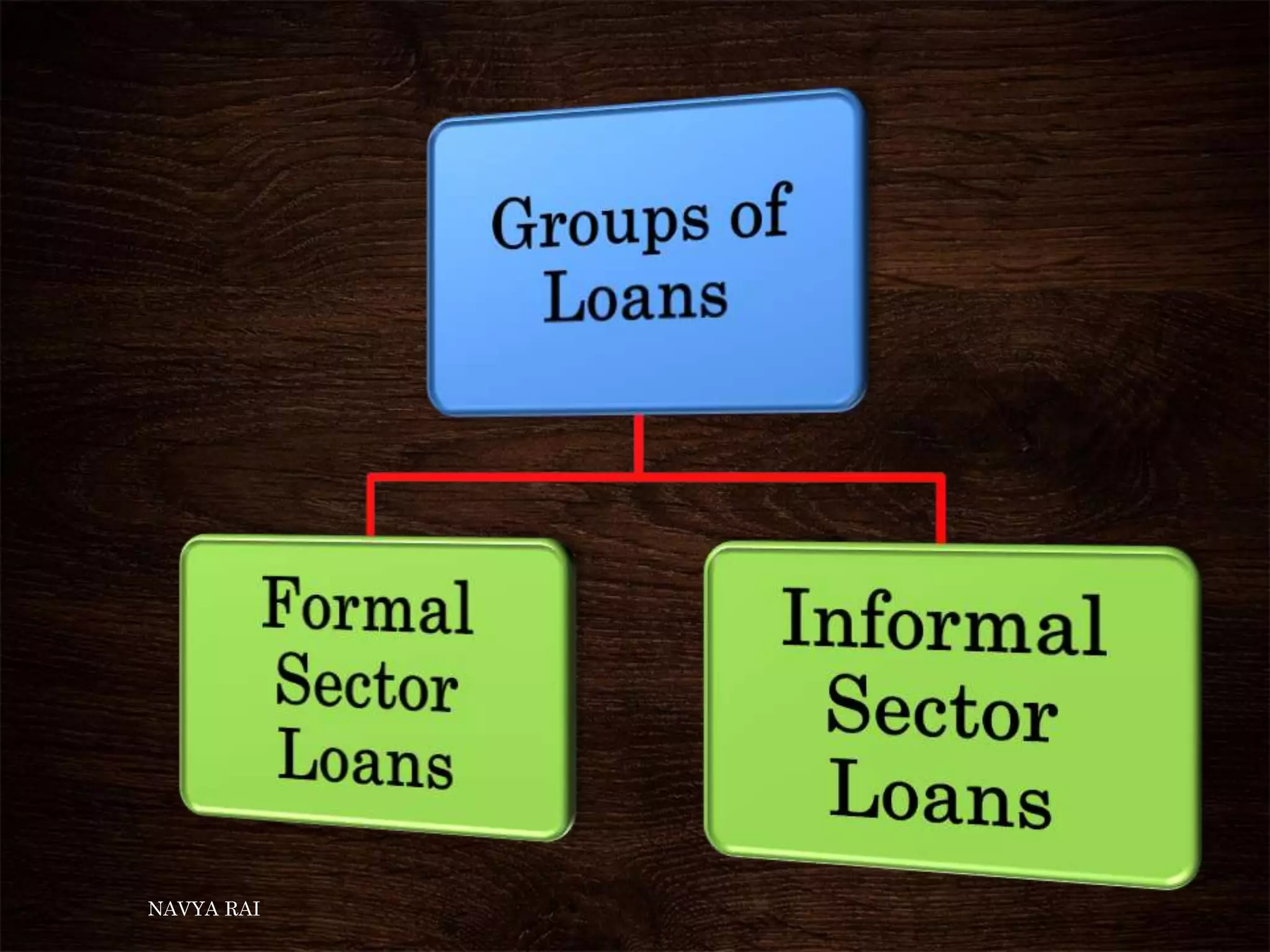
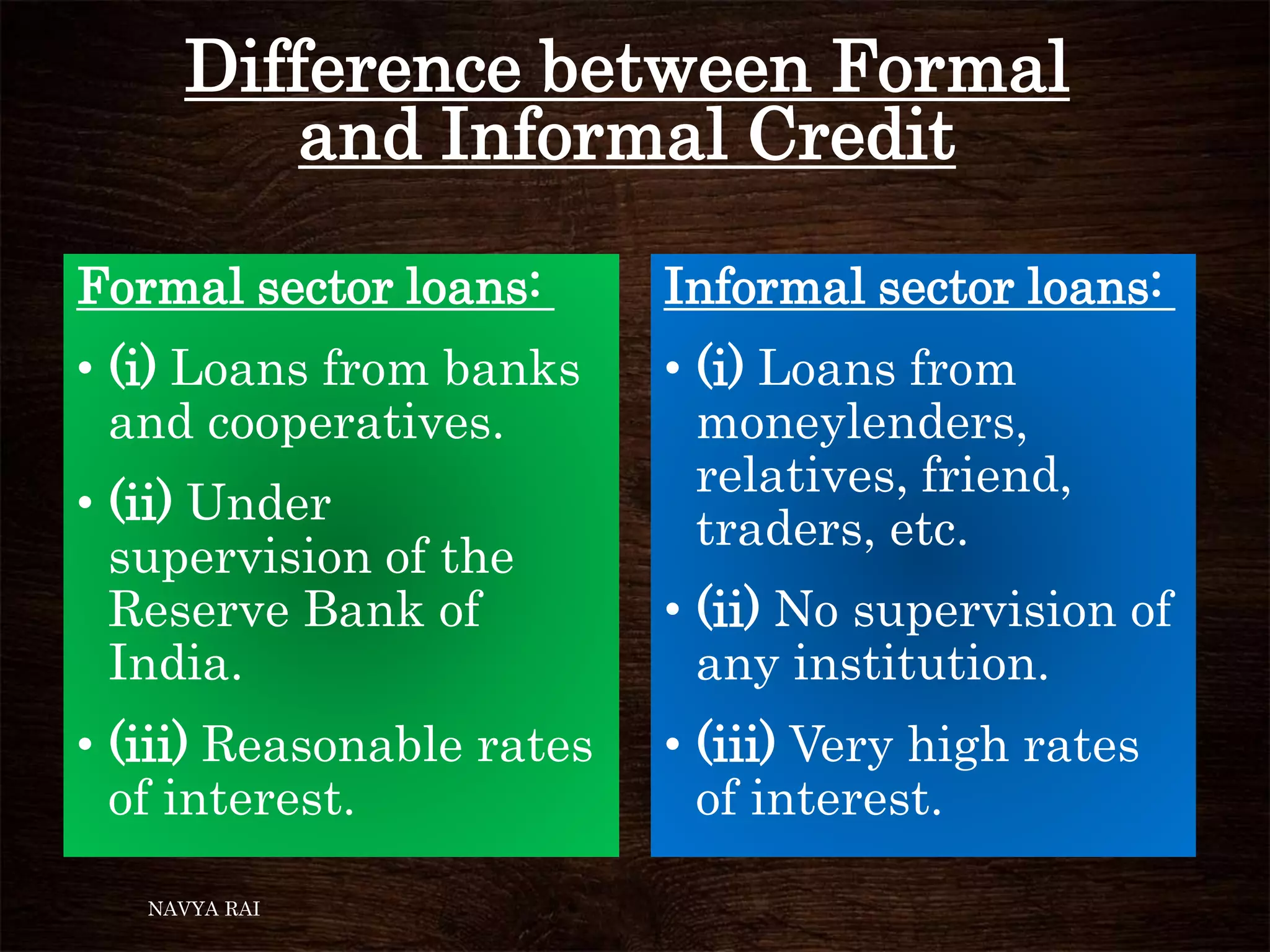
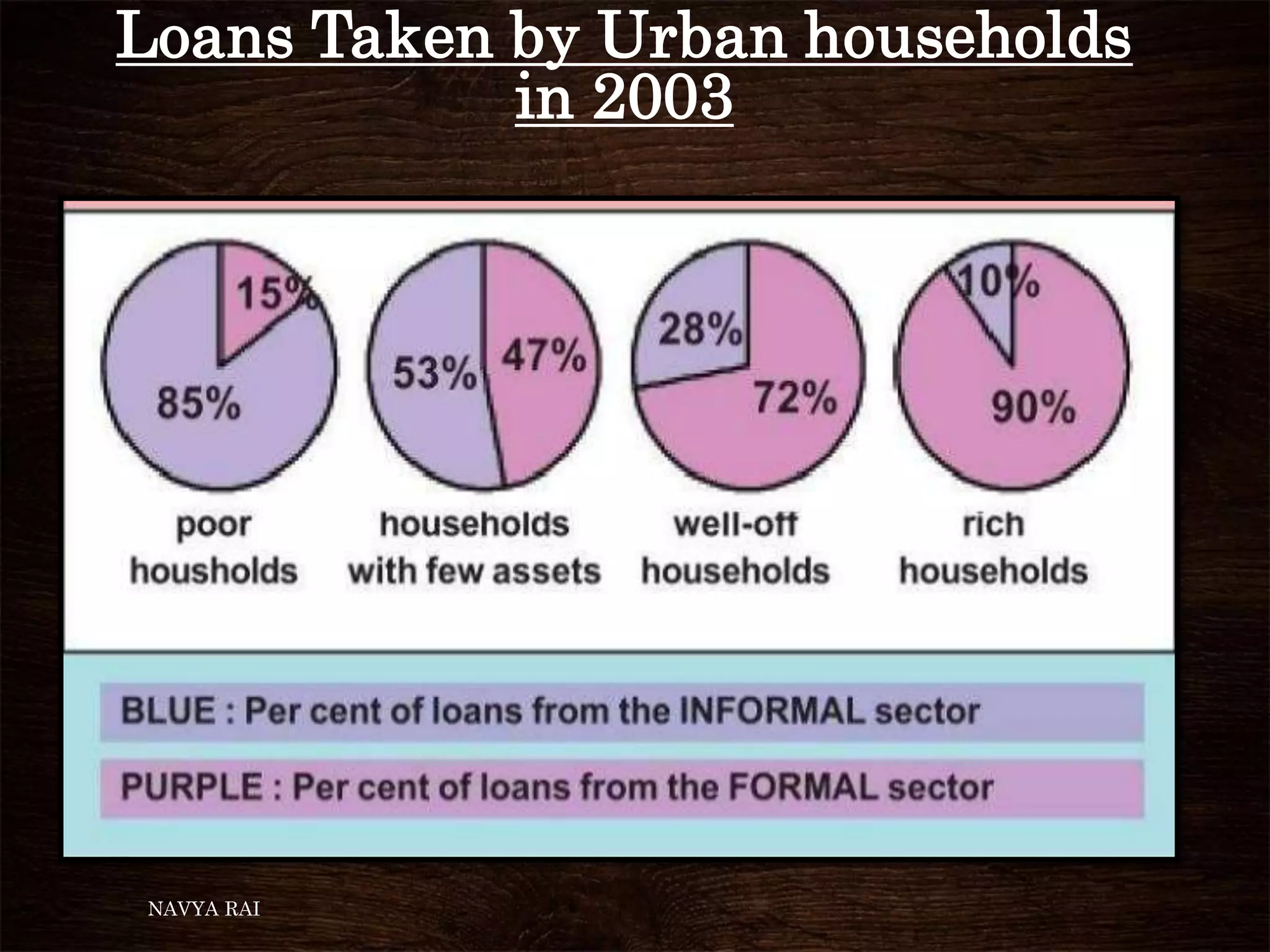
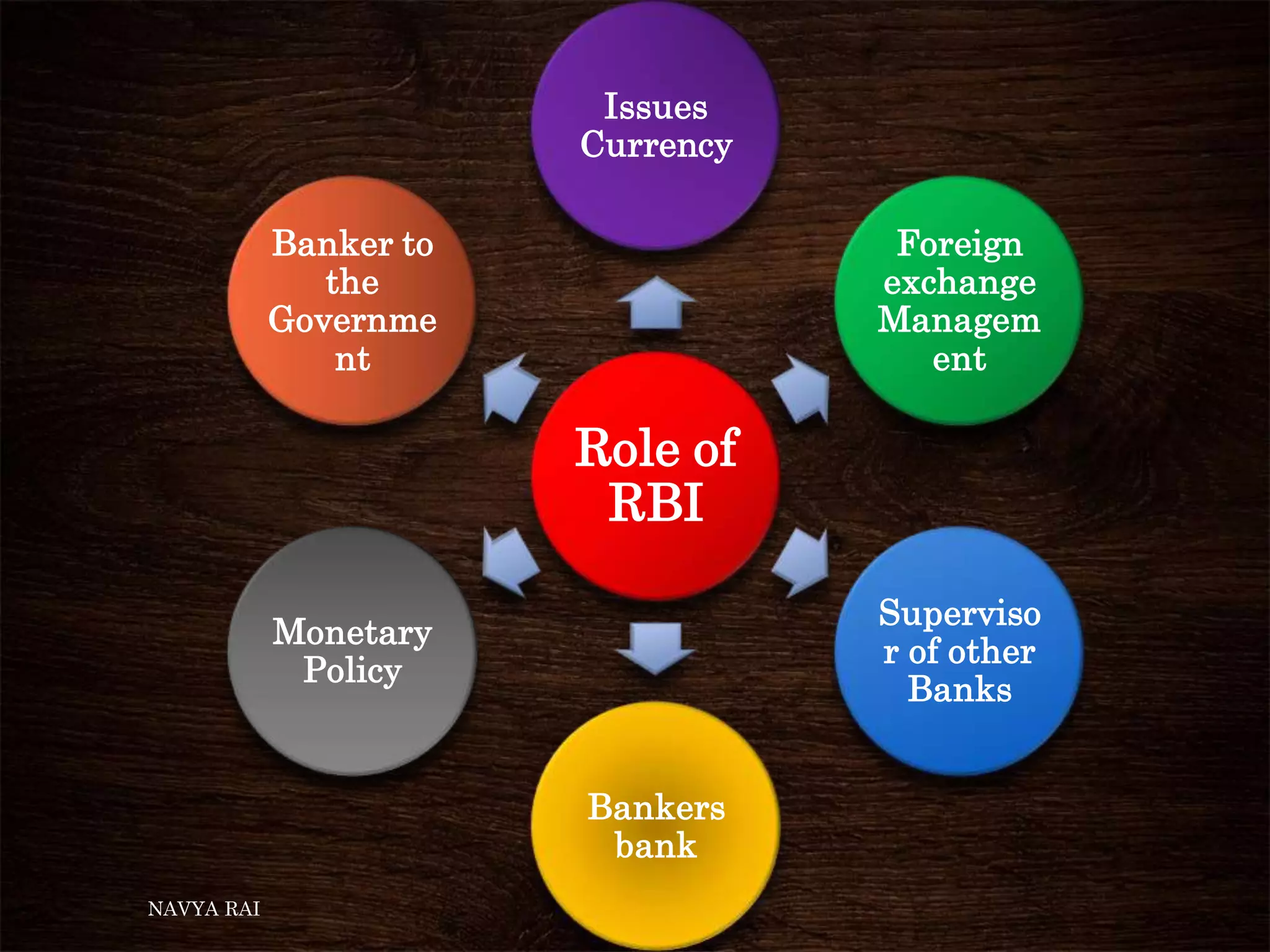
The document discusses the concepts of money, credit, and the banking system, explaining the transition from a barter system to the use of money as a medium of exchange. It highlights the roles of banks, types of credit, and the differences between formal and informal lending, as well as the benefits of self-help groups for the poor. Additionally, it mentions the Grameen Bank in Bangladesh as a model for providing small loans to impoverished individuals.