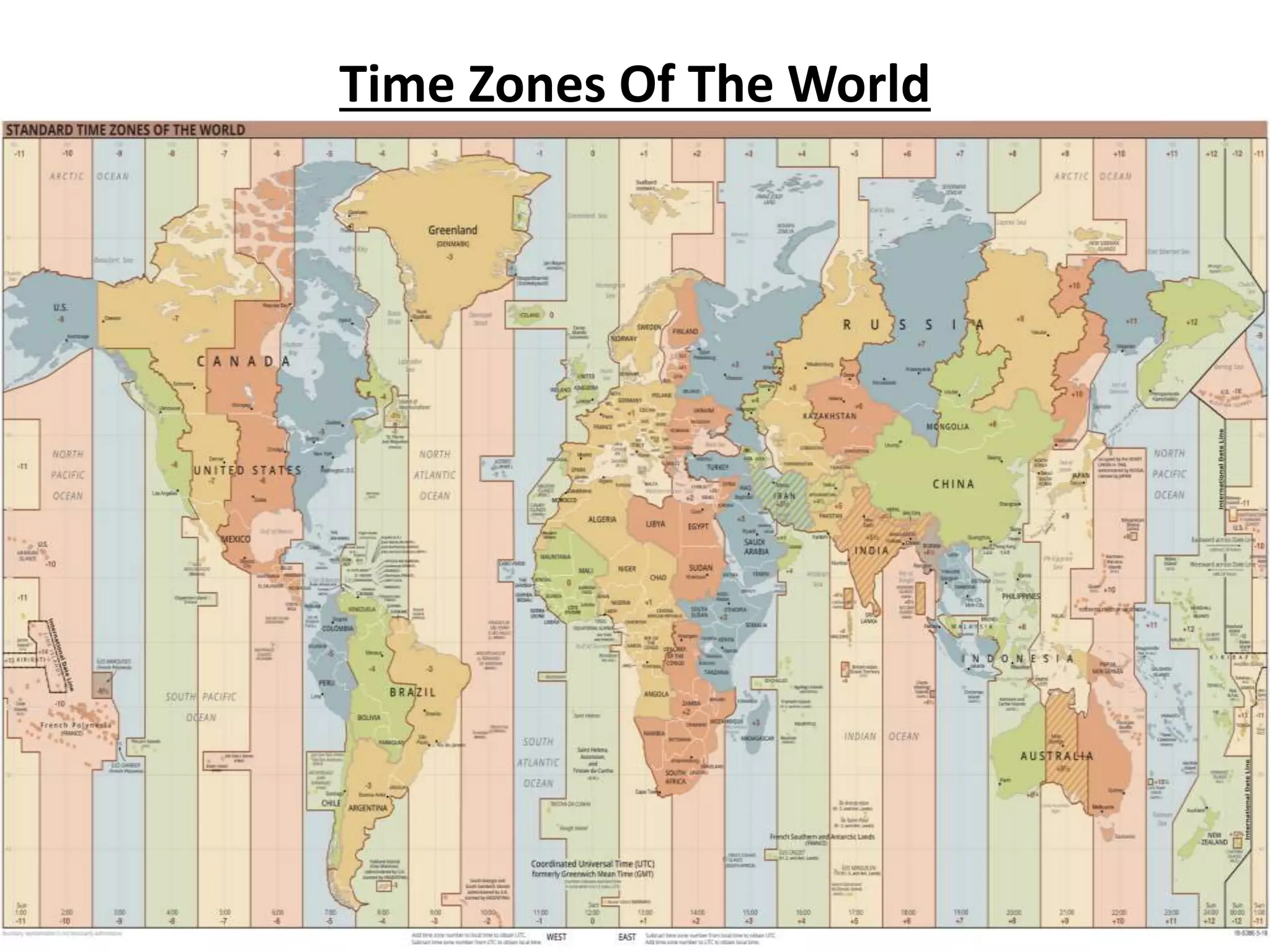
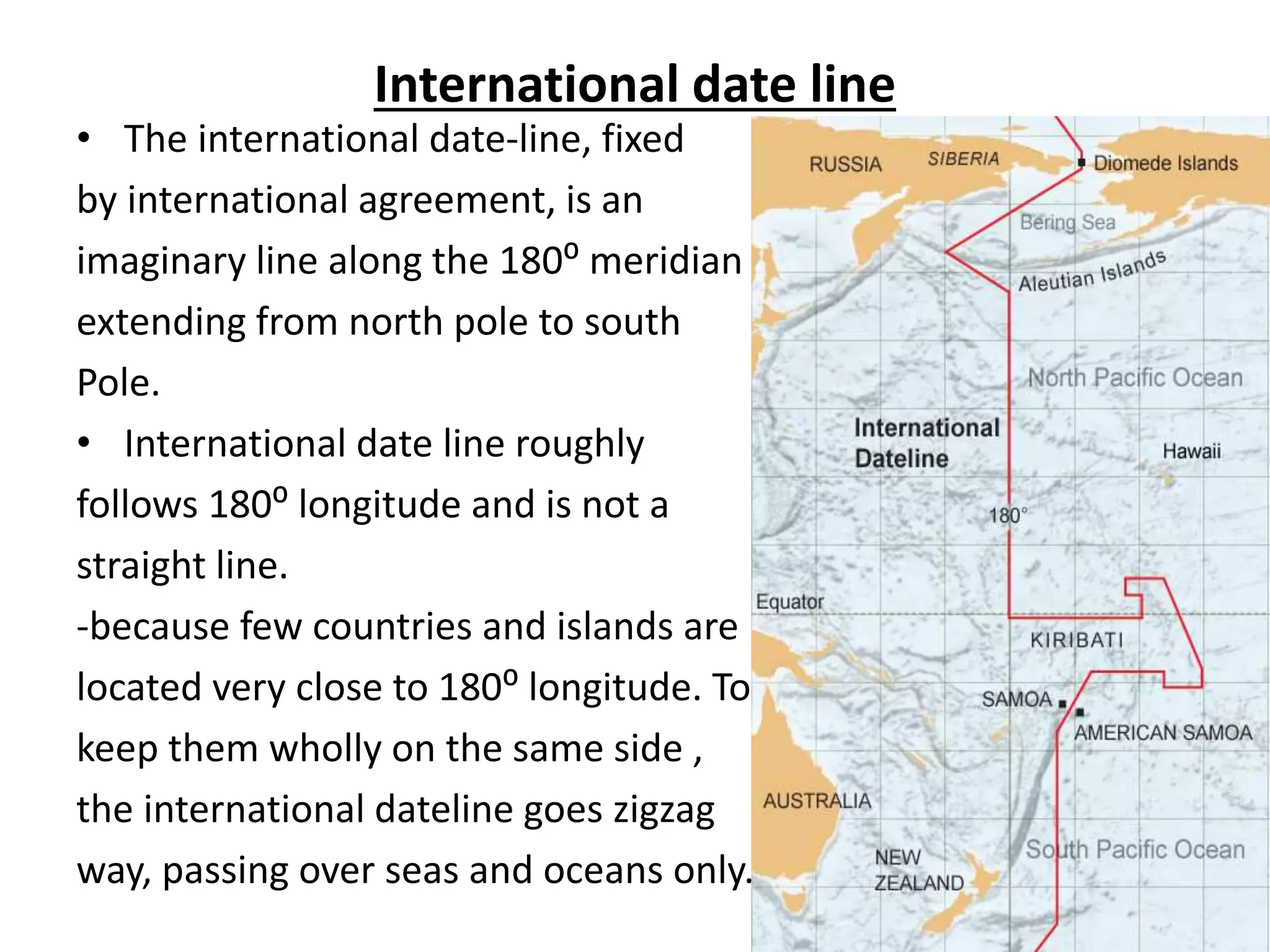
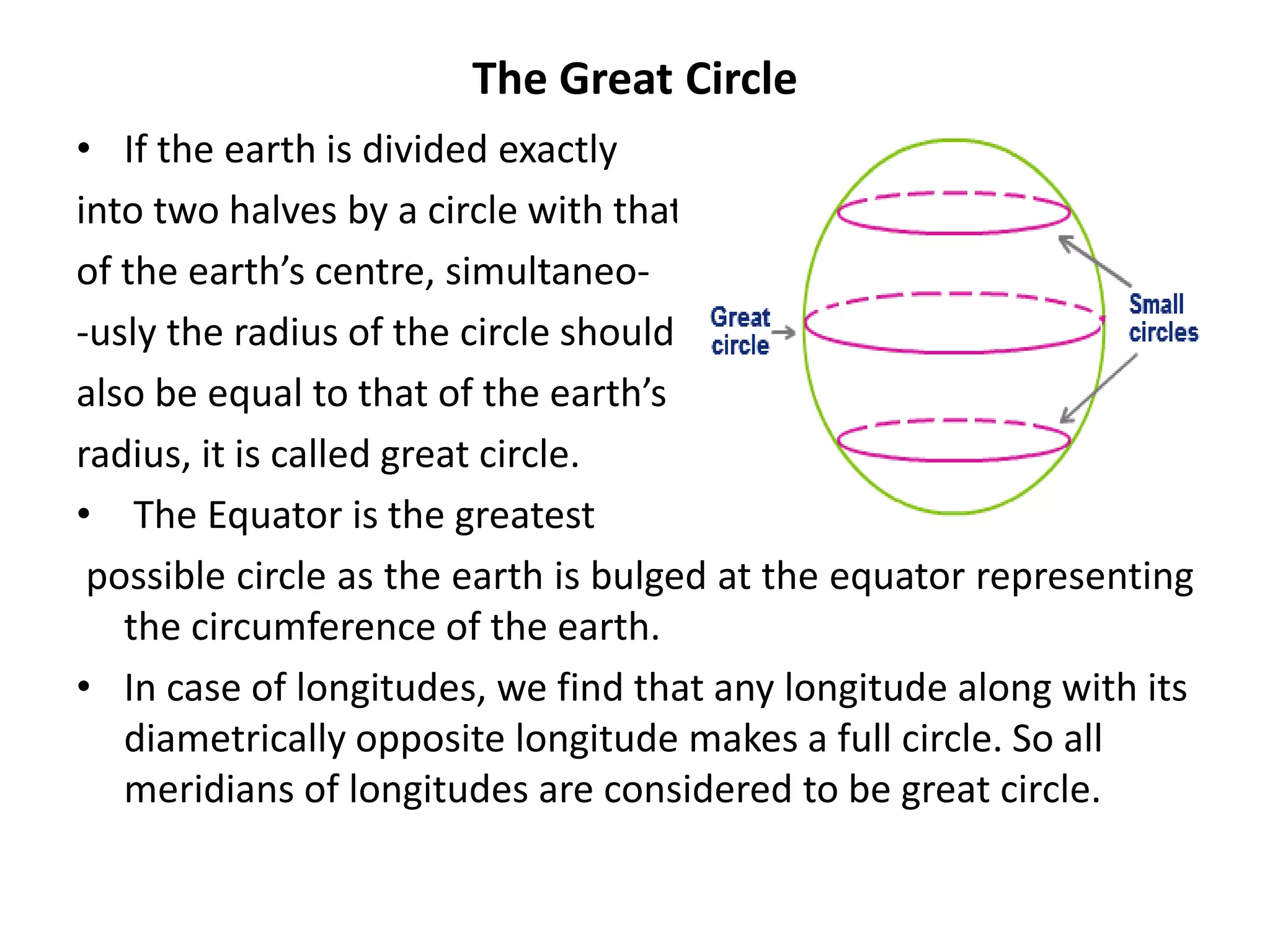
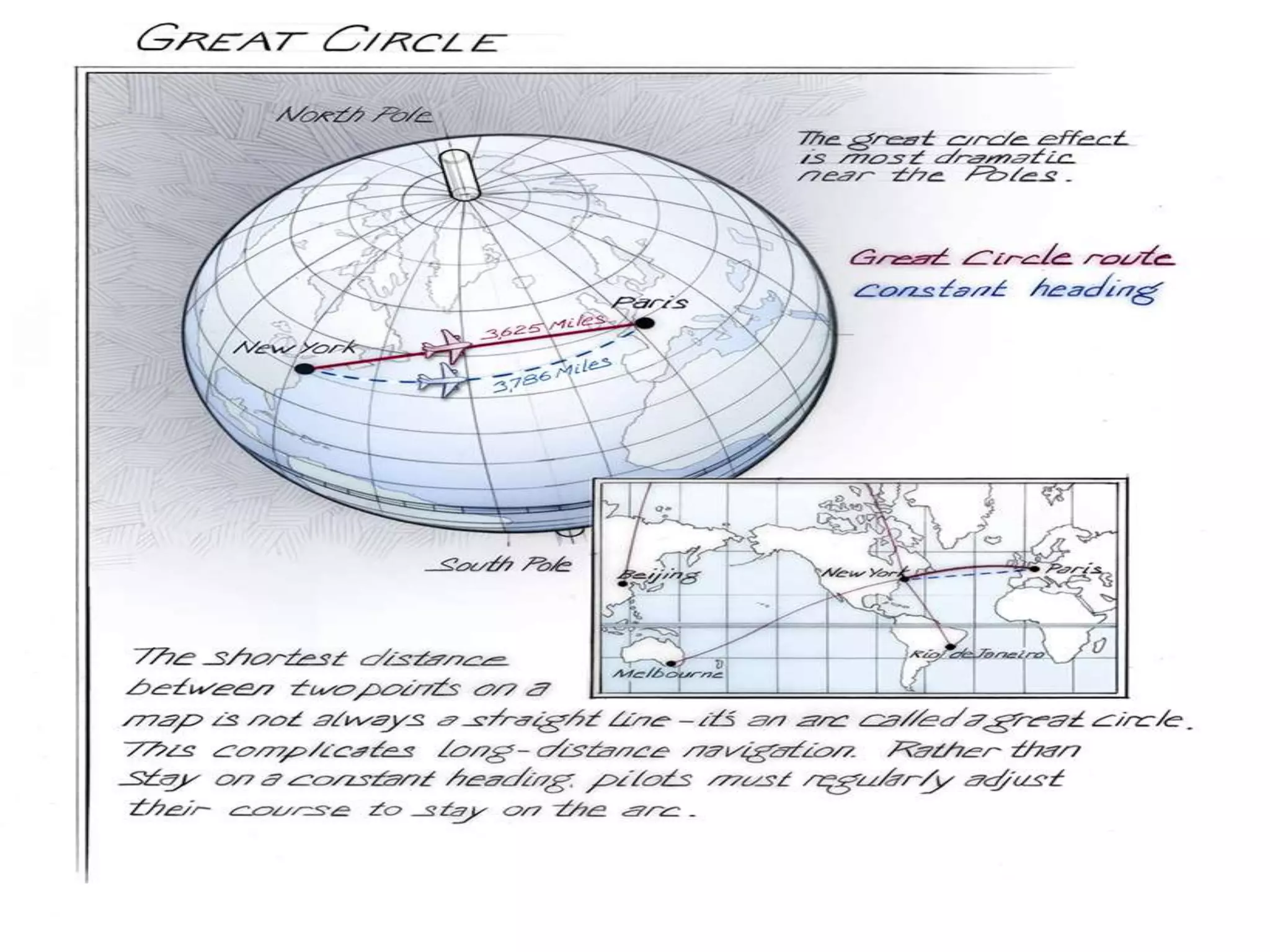
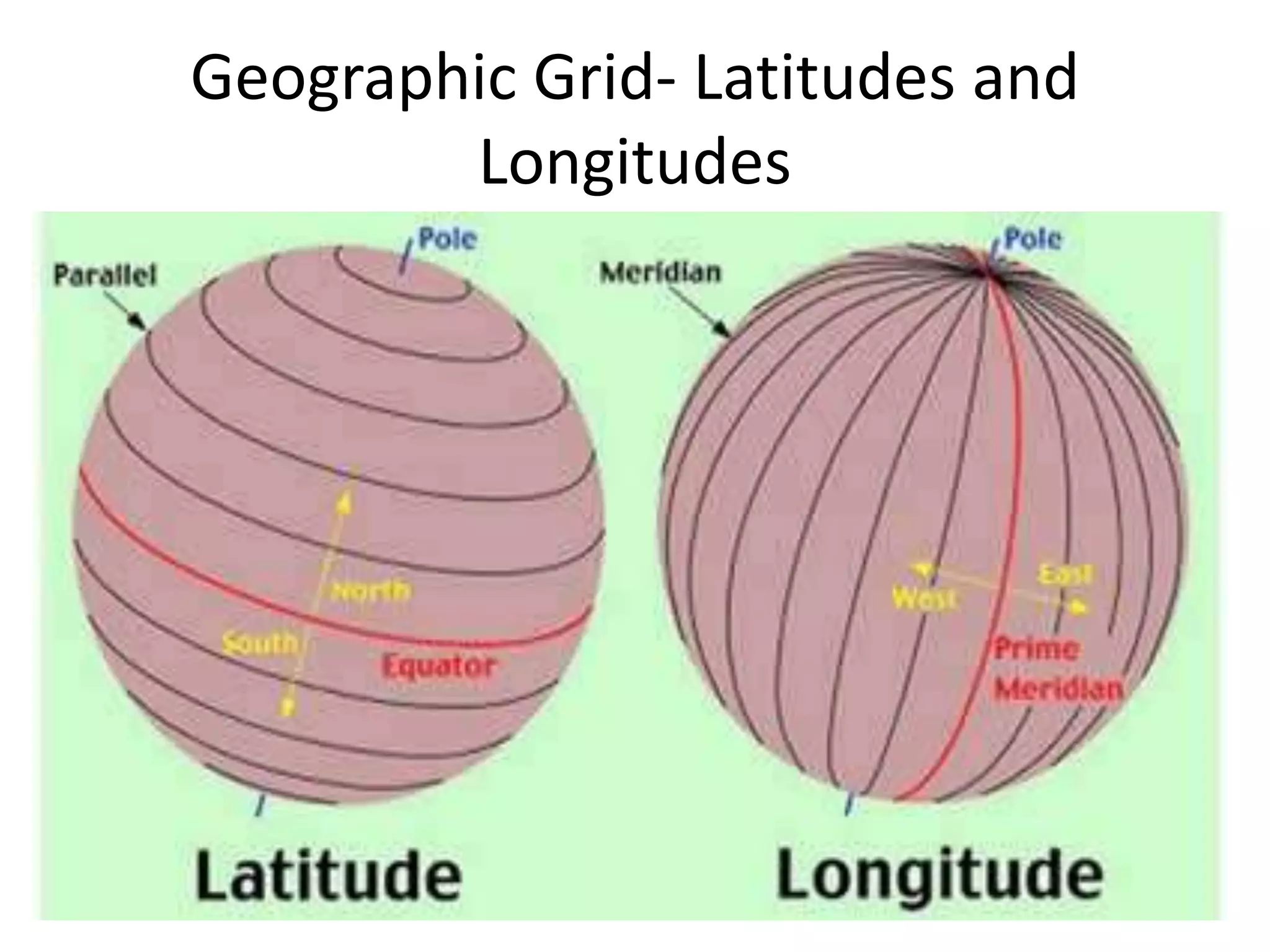
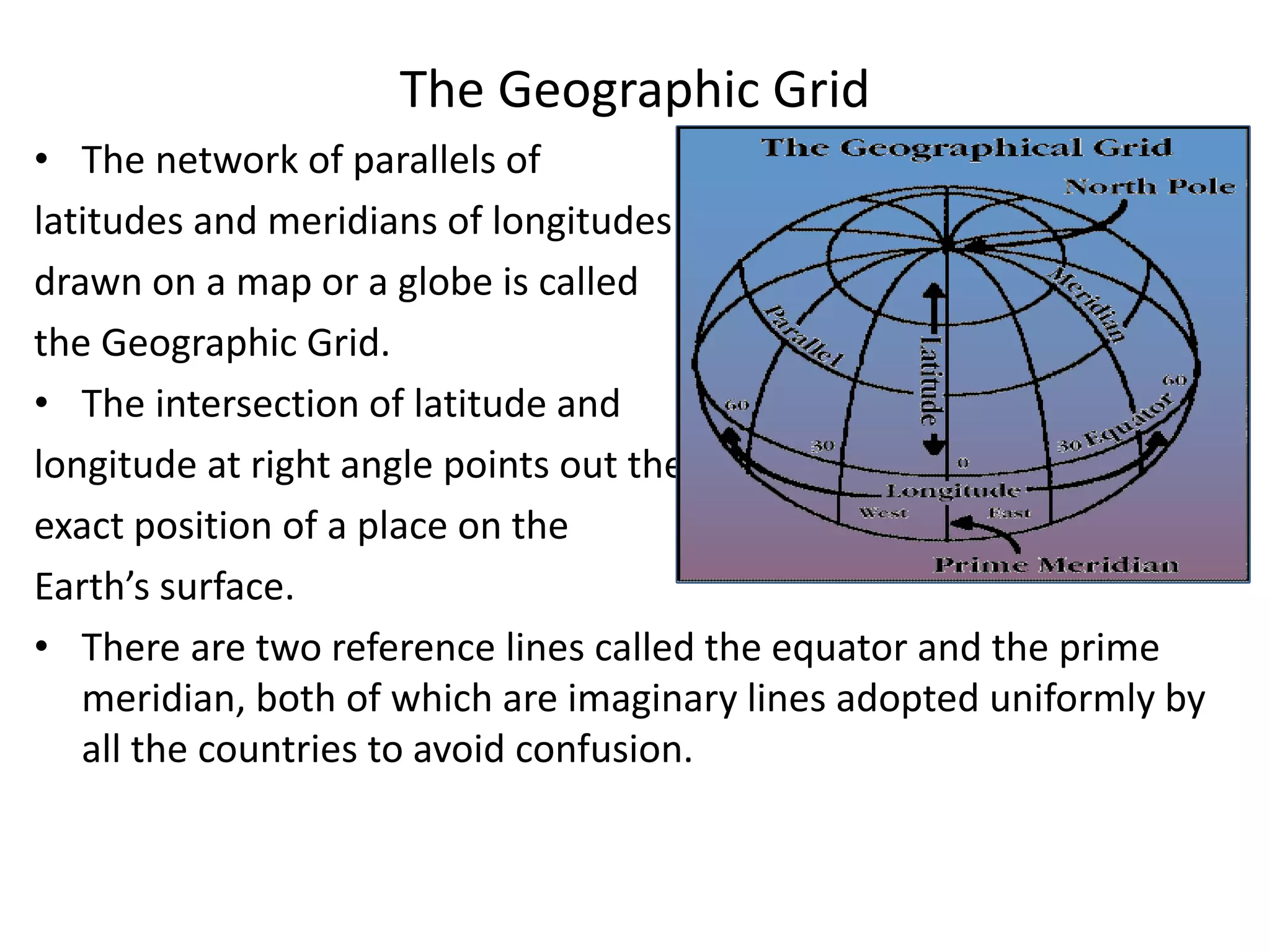
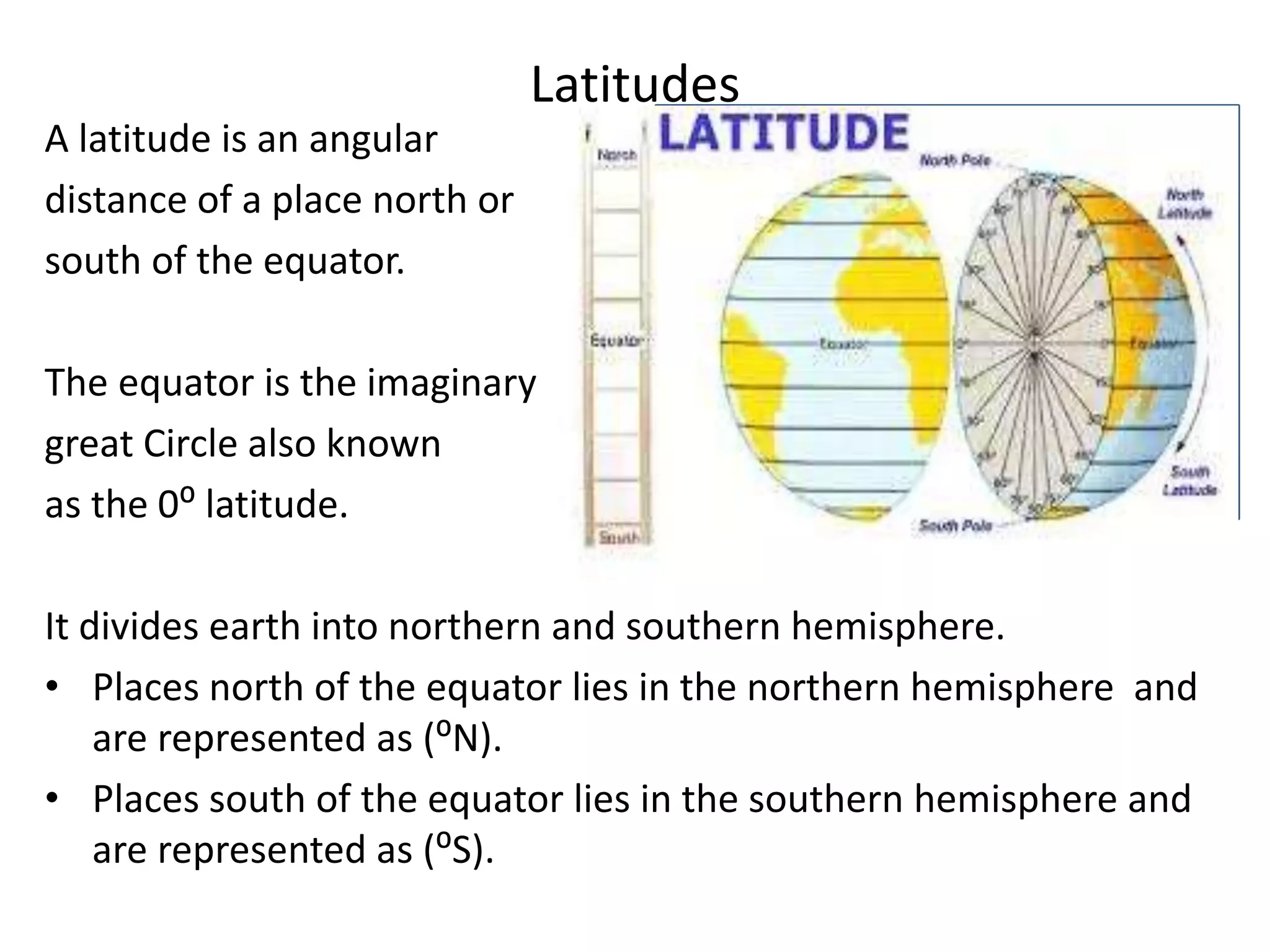
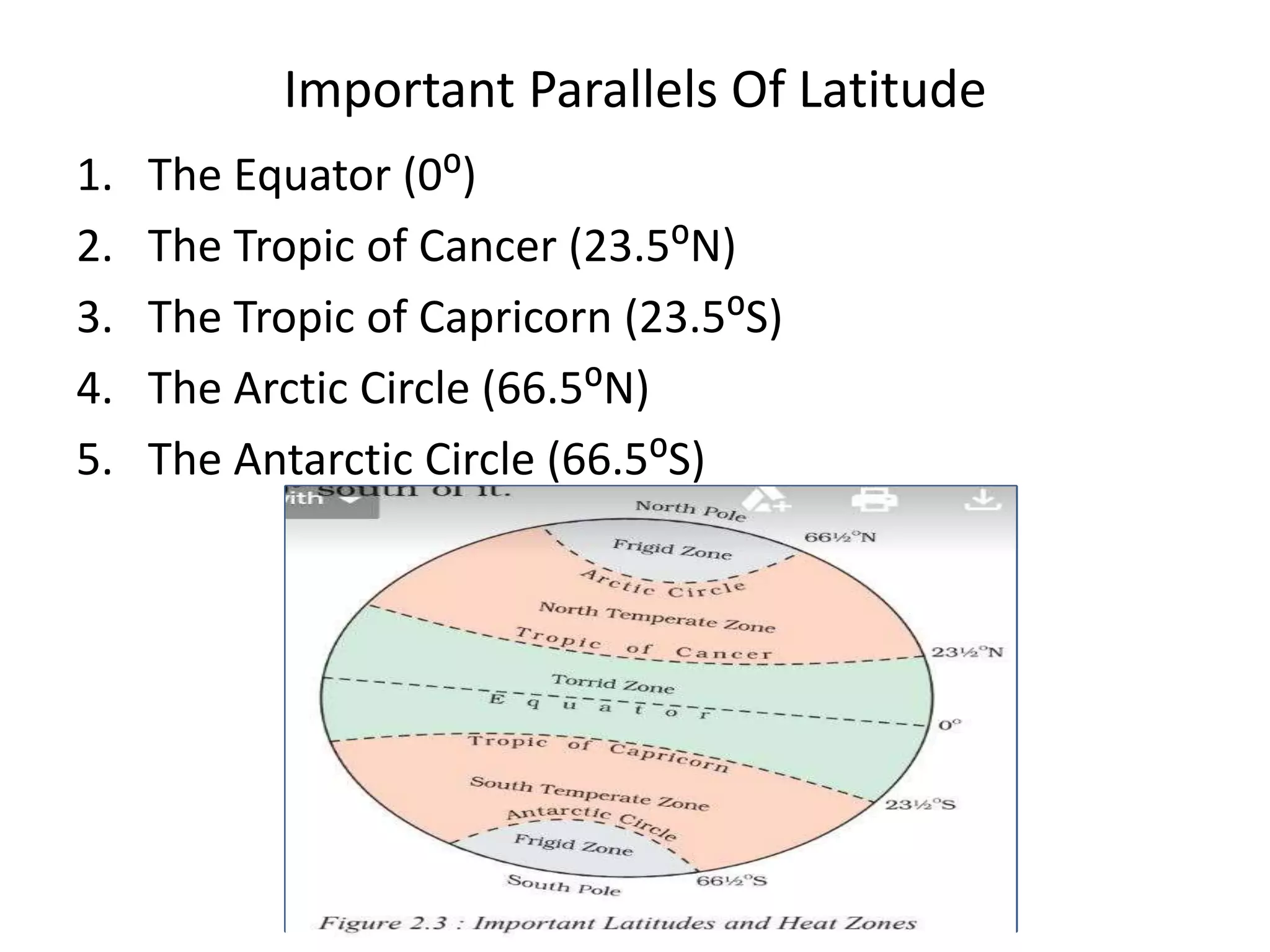
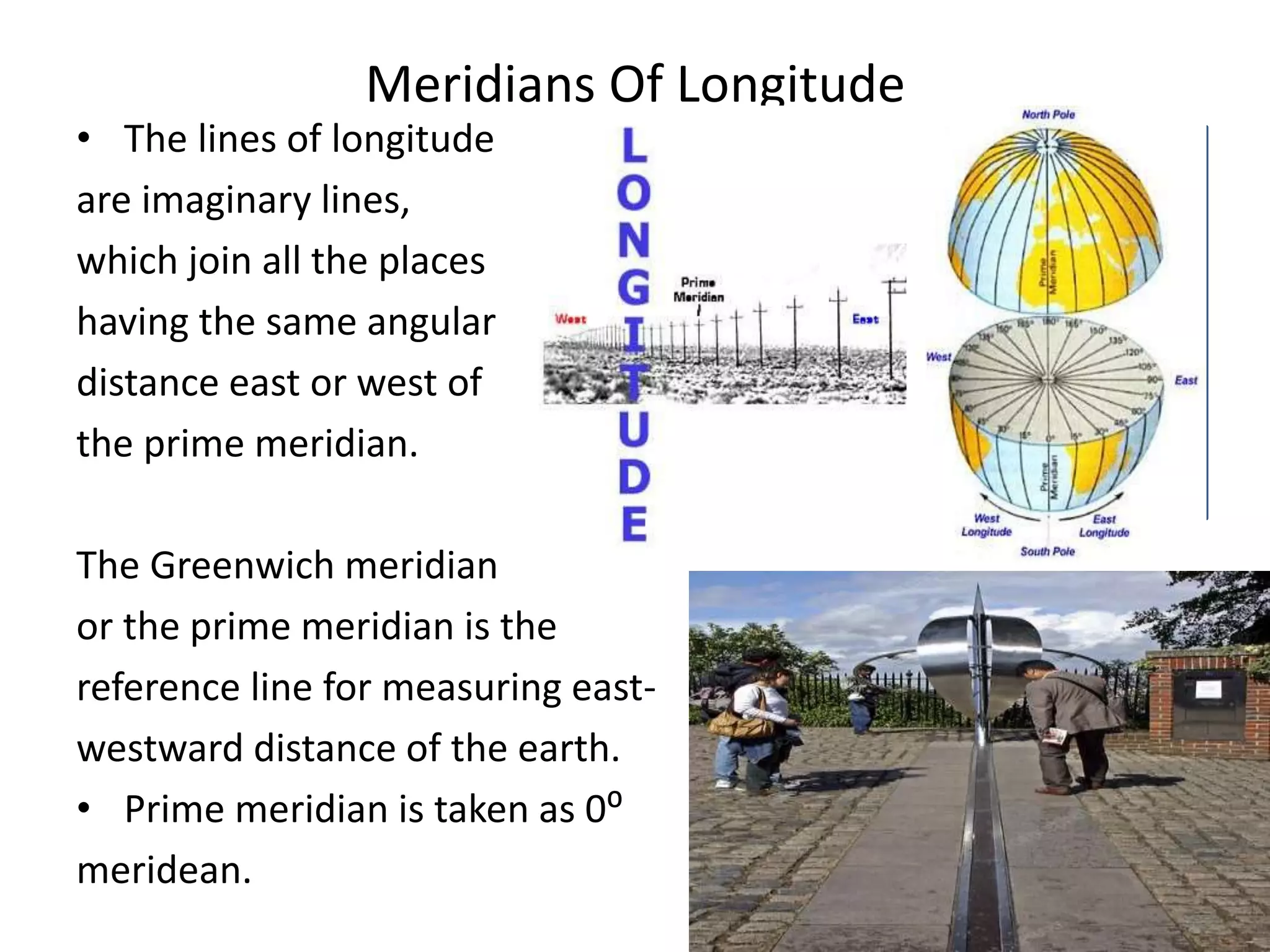
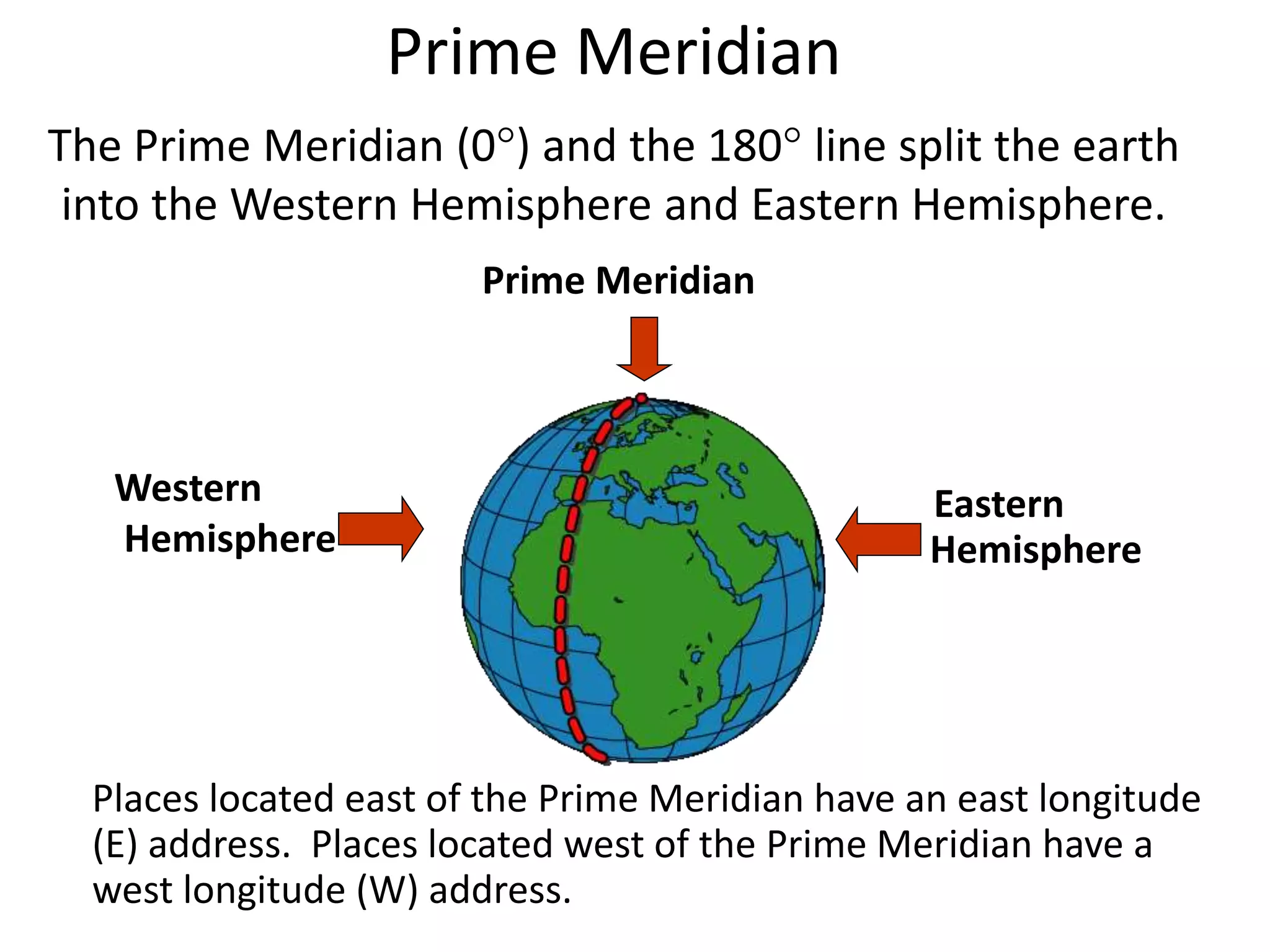
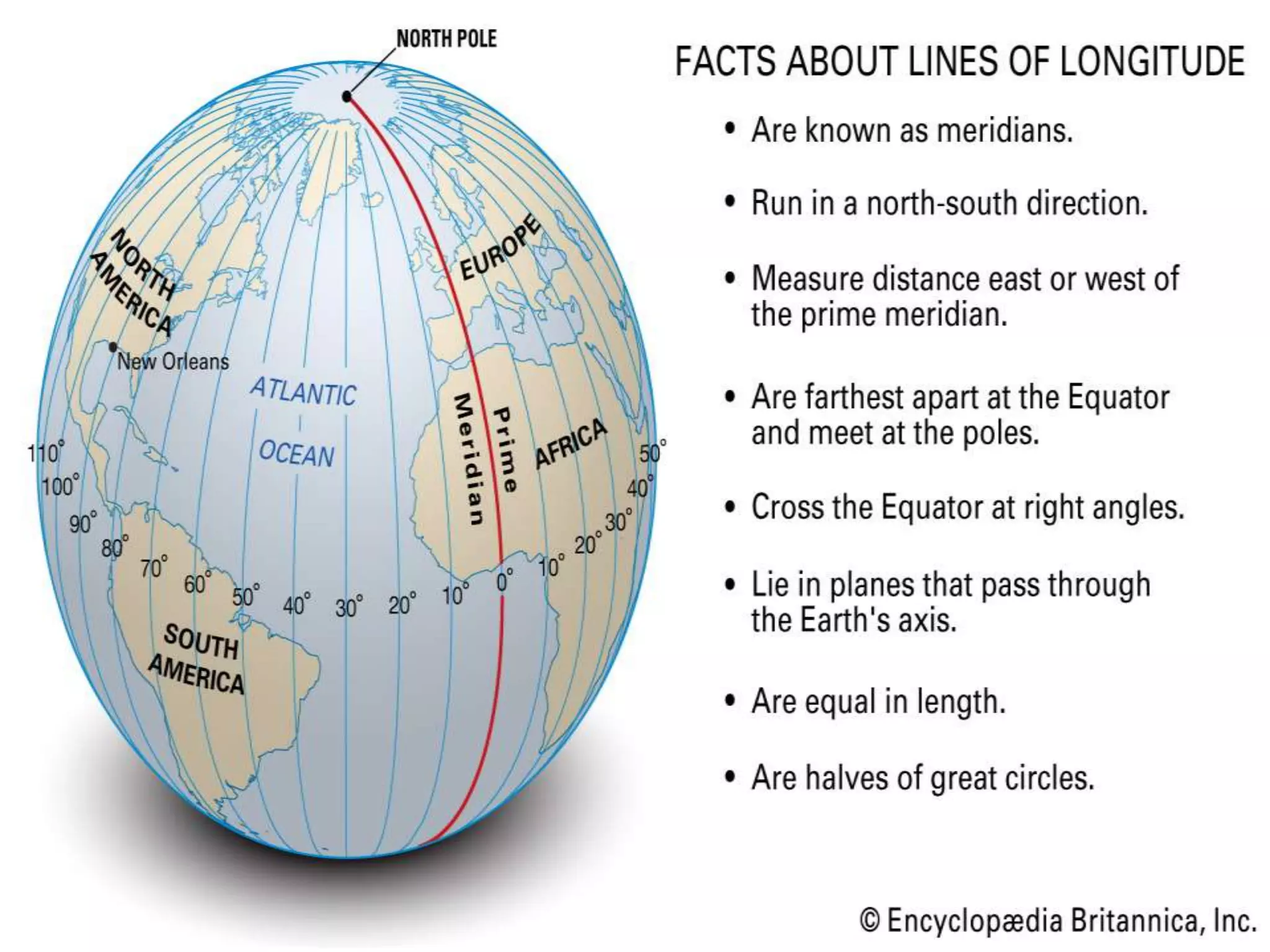
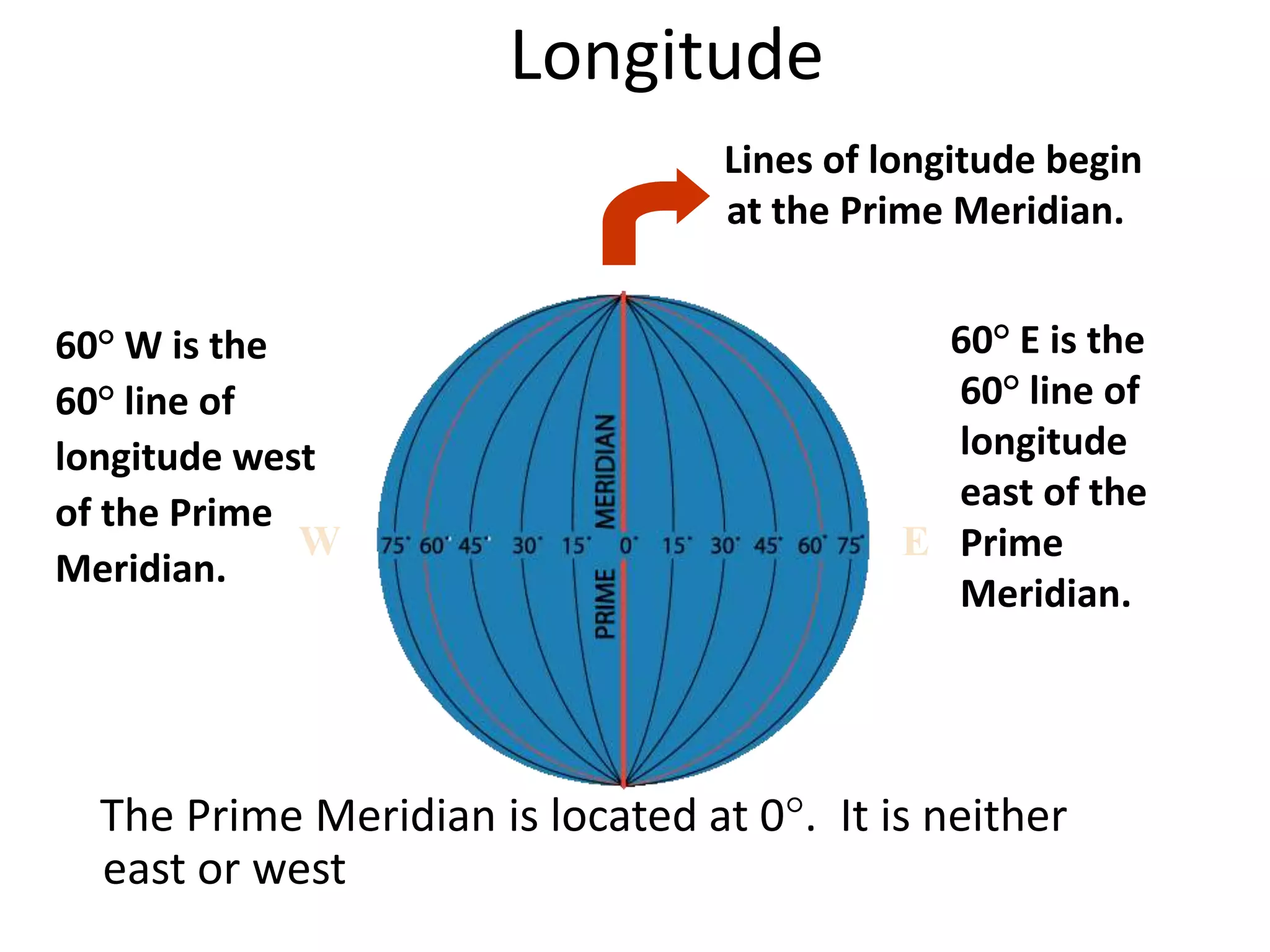
The document explains the geographic grid, consisting of latitude and longitude lines that help determine the exact positions of places on Earth. It describes the significance of the equator and prime meridian, the numbering of latitude from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles, and how longitude is measured east and west of the prime meridian. Additionally, it covers time zones, the concept of local versus standard time, and the role of great circles in navigation for the shortest travel routes.
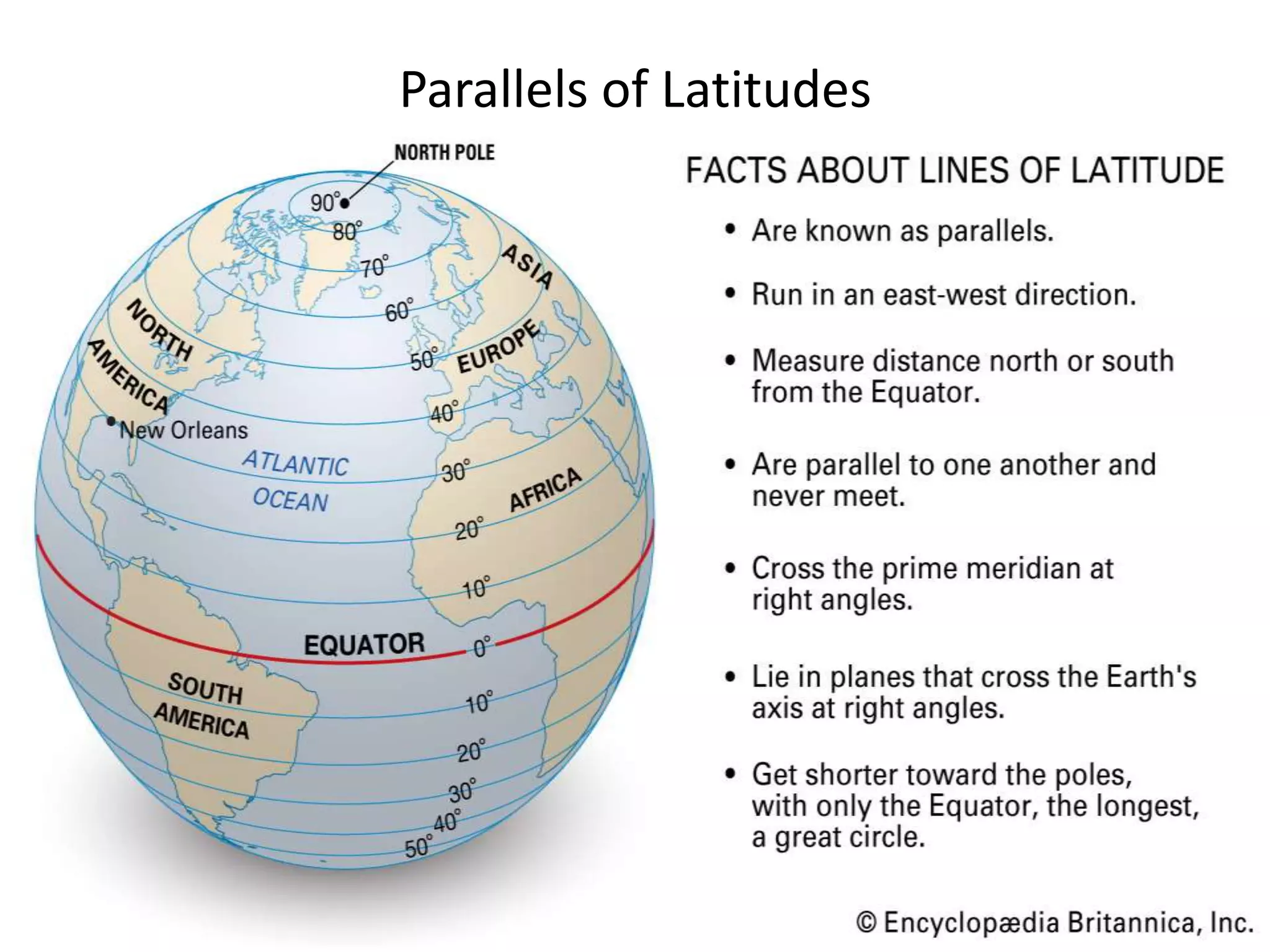
![Latitude
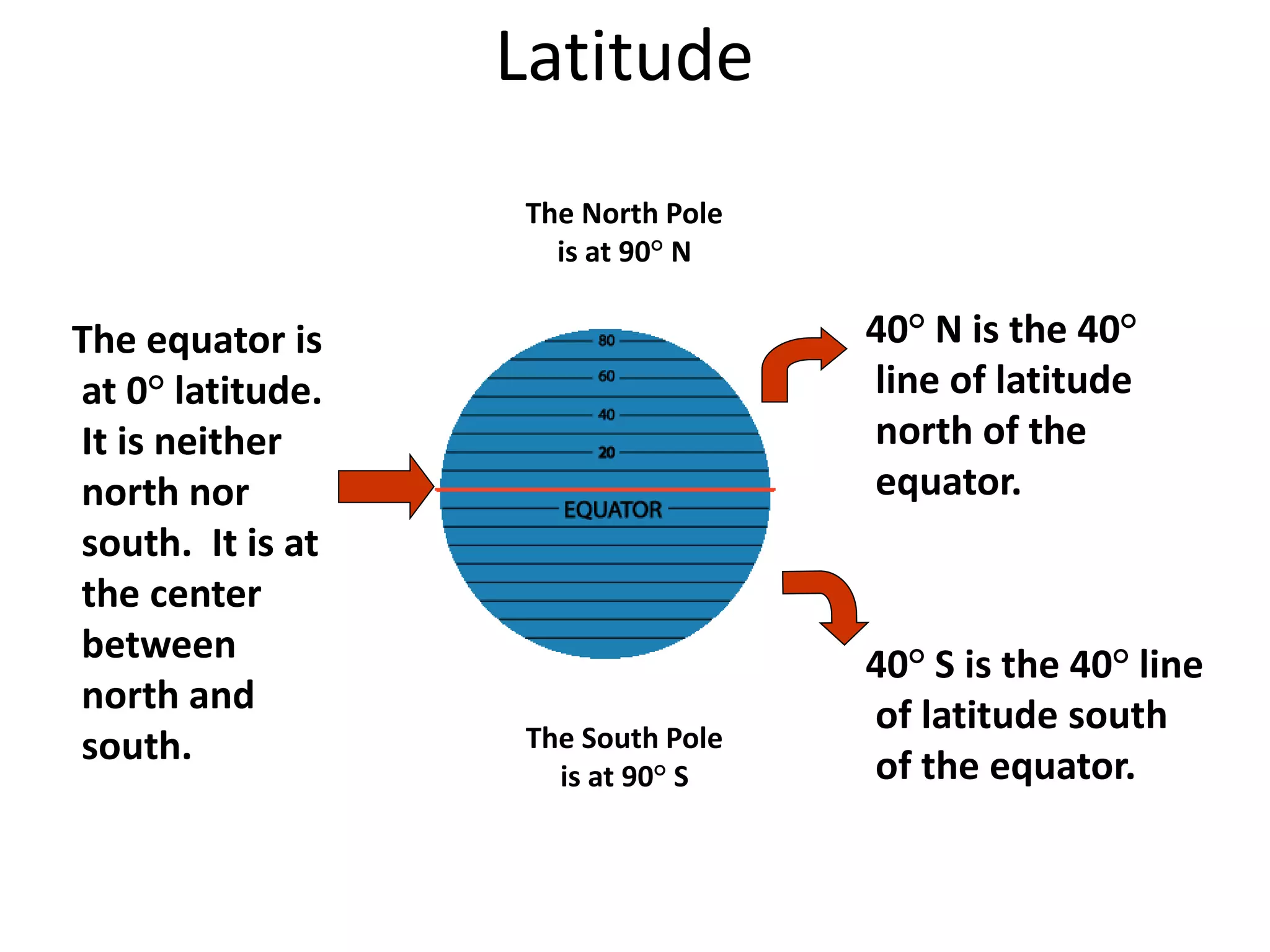
North Pole
South Pole
Lines of
latitude are
numbered
from 0° at the
equator to
90° N.L. at the
North Pole.
Lines of
latitude are
numbered
from 0° at
the equator
to 90° S.L. at
the South
Pole.
]
[
90 80
70
60
50
40
20
30
10
90
80
70
60
50
40
20
10
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geographicgrid-latitudesandlongitudesravi-200417081250/75/Geographic-grid-latitudes-and-longitudes-made-by-Ravi-Bharti-5-2048.jpg)


![• The earth takes 24 hrs to complete one rotation of 360⁰. This
gives rise to a time difference of [(24*60)/ 360] = 4min for one
degree of longitude.
• Therefore ,
1. A time difference of four min has to be added for each 1⁰ of
longitude towards the east.
2. A time difference of four min has to be subtracted for each 1⁰ of
longitude towards west.
Local time:
the time of a place recognized by the mid-day sun is called the loca’
time. All the places located along a particular longitude (from
north pole to south pole) face the overhead sun at the same
time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geographicgrid-latitudesandlongitudesravi-200417081250/75/Geographic-grid-latitudes-and-longitudes-made-by-Ravi-Bharti-14-2048.jpg)