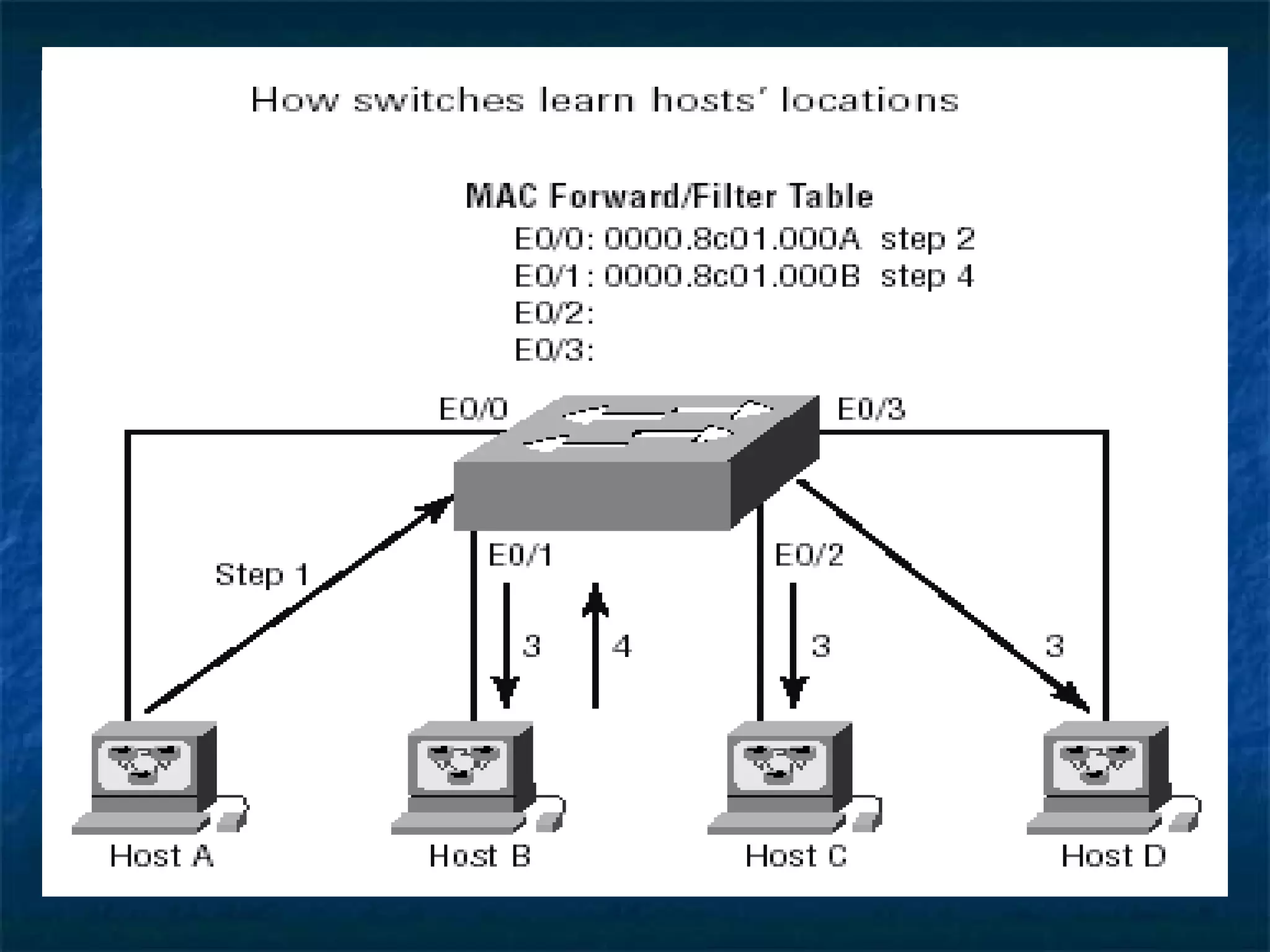
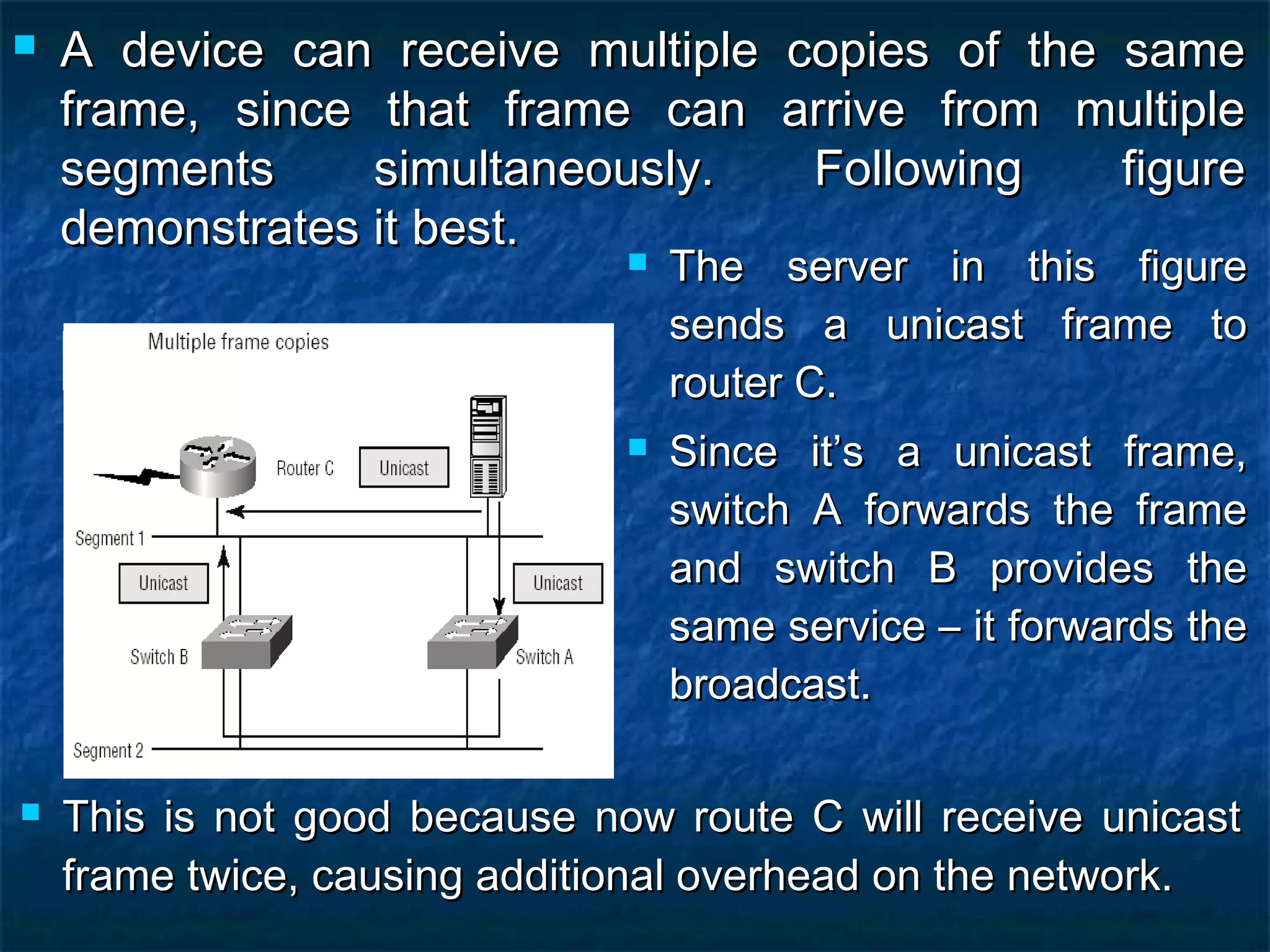
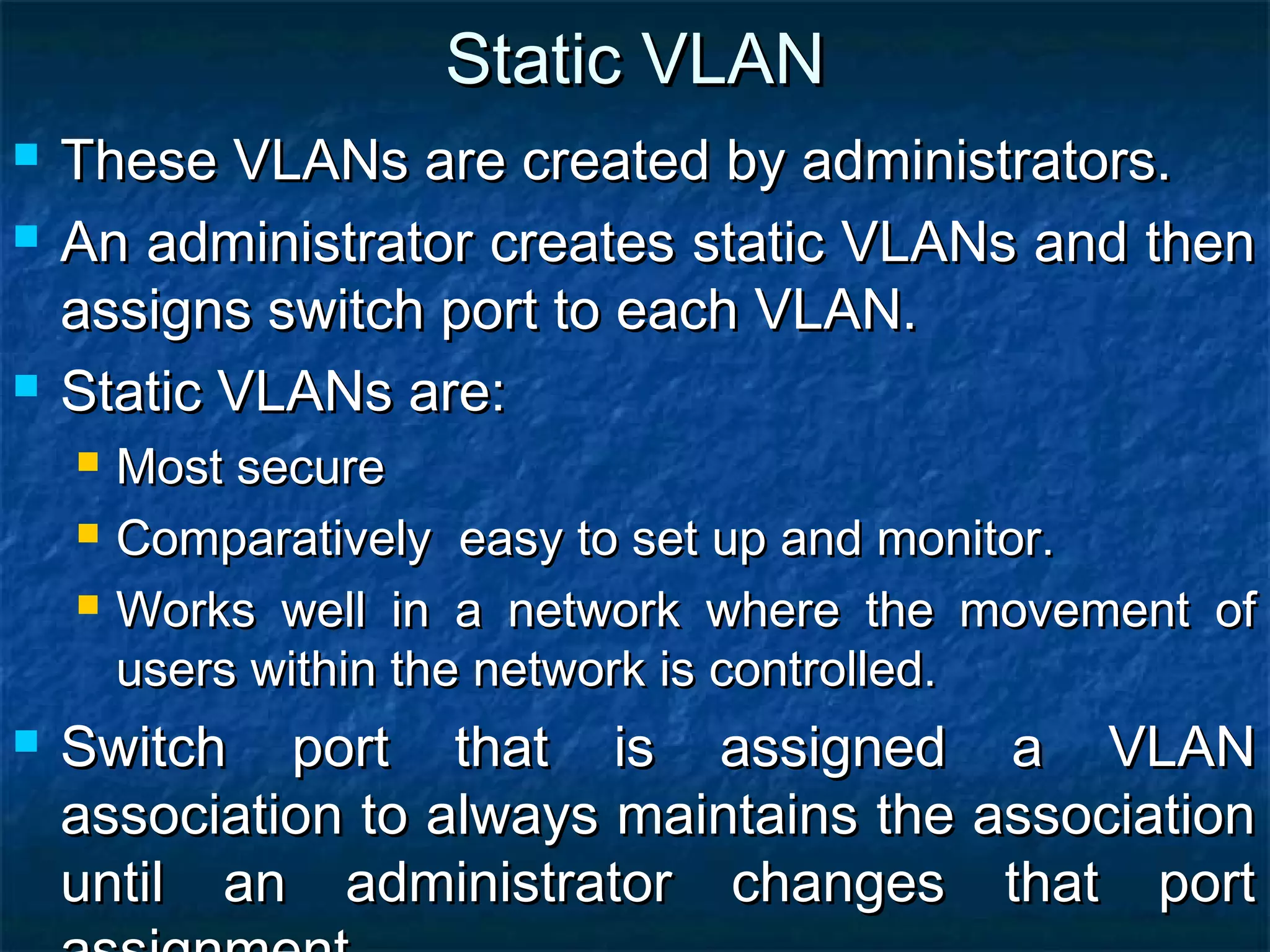
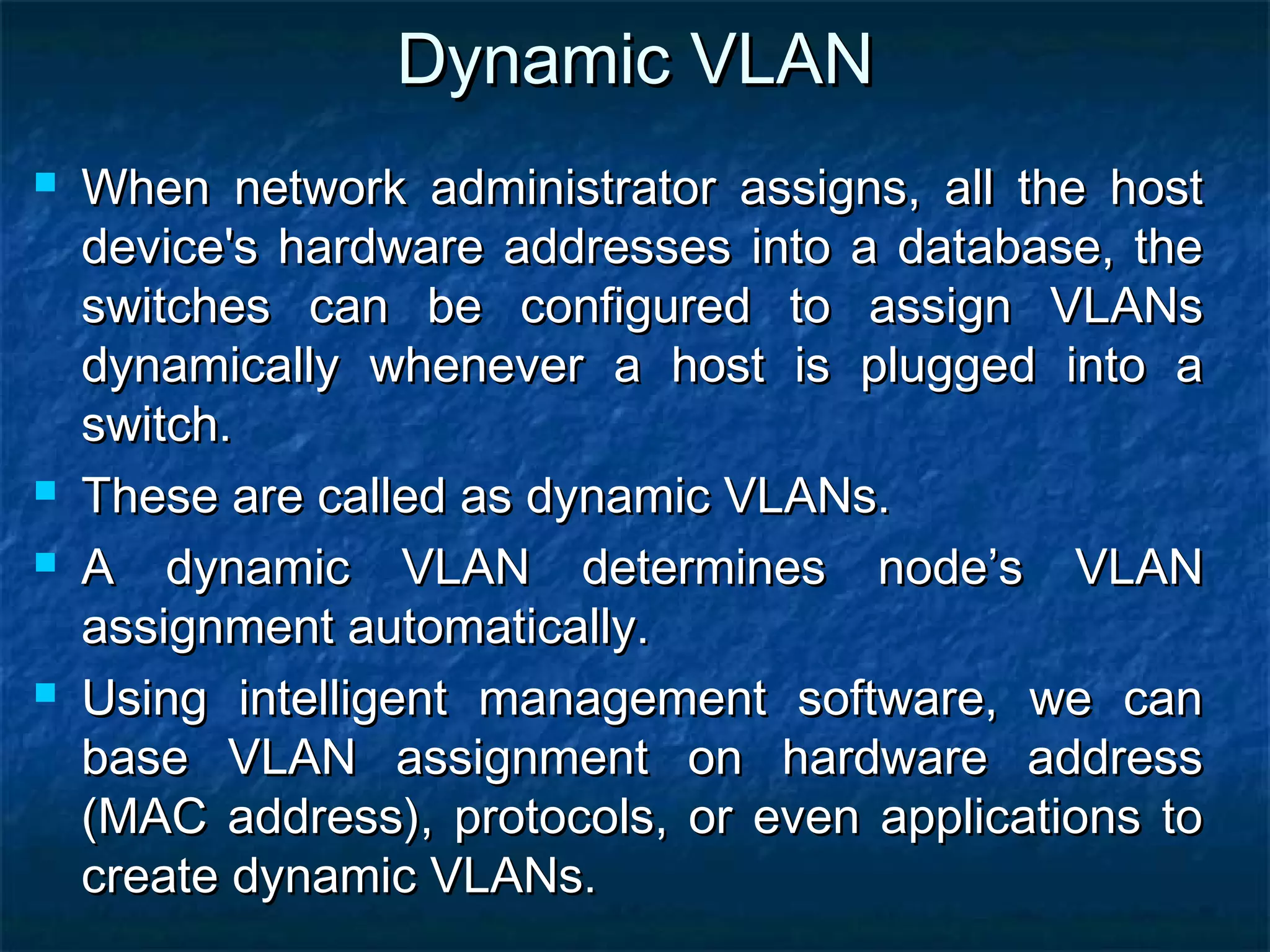
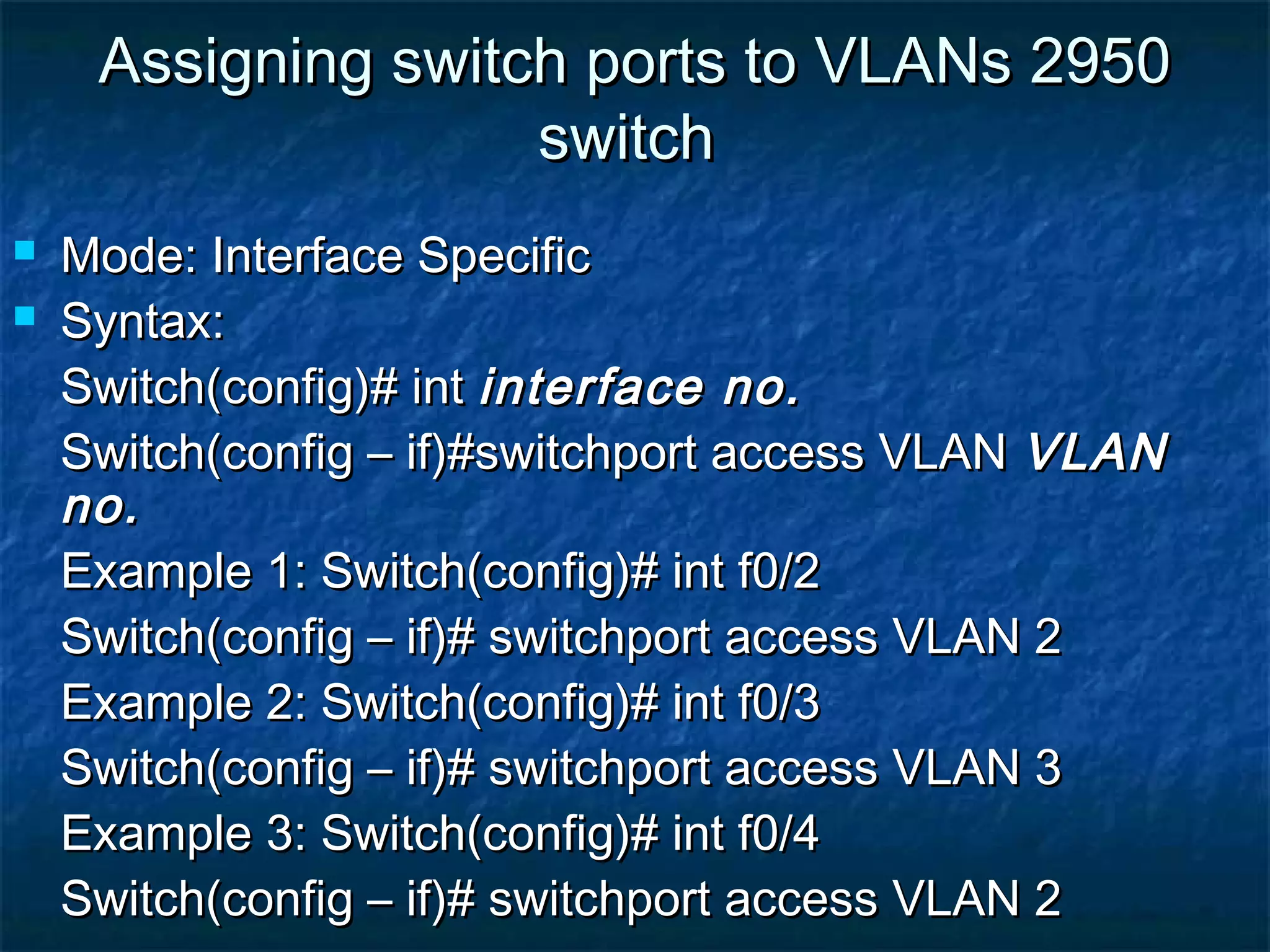
This document provides an overview of switch functionality within networking, explaining the roles and advantages of switches compared to routers, including their ability to create multiple collision domains, independent bandwidth for each port, and low latency. It details the processes of address learning, forwarding decisions, and loop avoidance, emphasizing the importance of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent loops in redundant link scenarios. Additionally, it covers different switching modes, such as cut-through, fragment-free, and store-and-forward, and outlines the basic configuration tasks for Catalyst 1900 and 2950 switches.