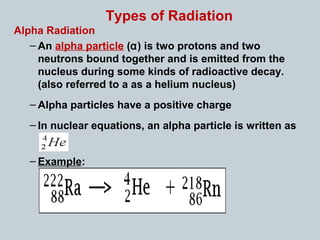
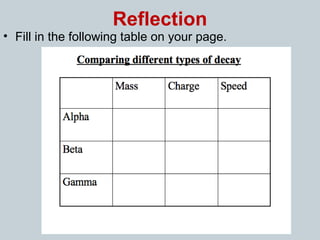
Matter can undergo physical, chemical, and nuclear changes, with nuclear changes involving transformations of an atom's nucleus. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of nuclear radiation from unstable isotopes, resulting in their decay until stable isotopes are formed, accompanied by significant energy release. There are three main types of nuclear radiation: alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays, each with distinct properties and levels of penetration.