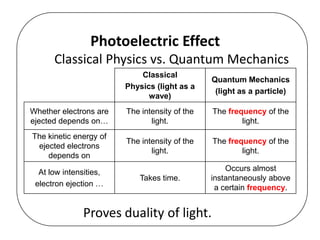
This document discusses evidence for both the wave and particle nature of light. For the wave nature, it mentions phenomena like reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference that were observed in experiments. For the particle nature, it discusses observations that supported Planck's quantization of energy and Einstein's model of light as discrete photon particles, including the photoelectric effect, atomic spectra, and blackbody radiation. The photoelectric effect in particular provided strong evidence that light behaves as a particle by instantaneously ejecting electrons from metals above a threshold frequency, rather than depending on intensity as waves were thought to. This helped establish the dual wave-particle nature of light.