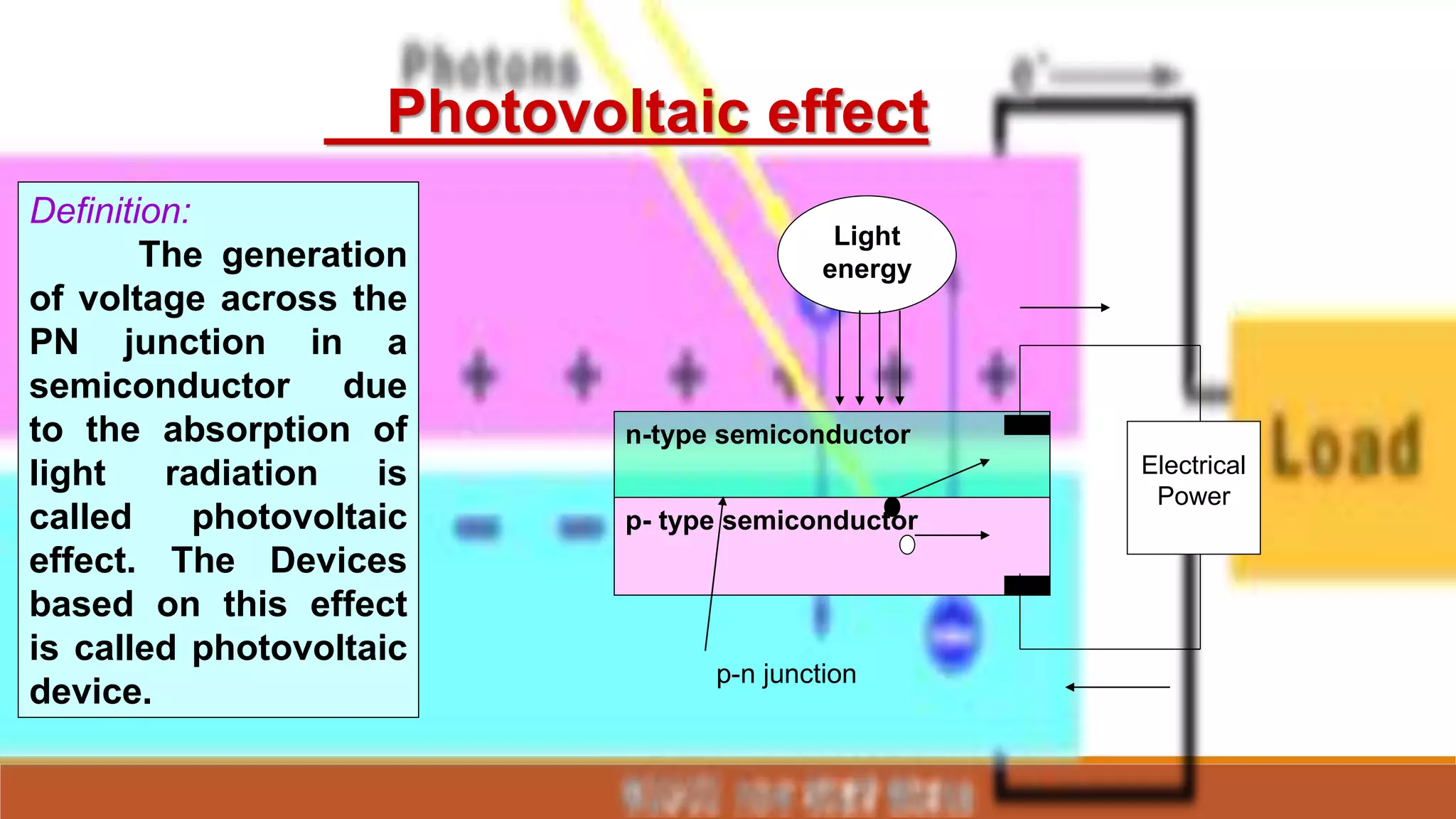
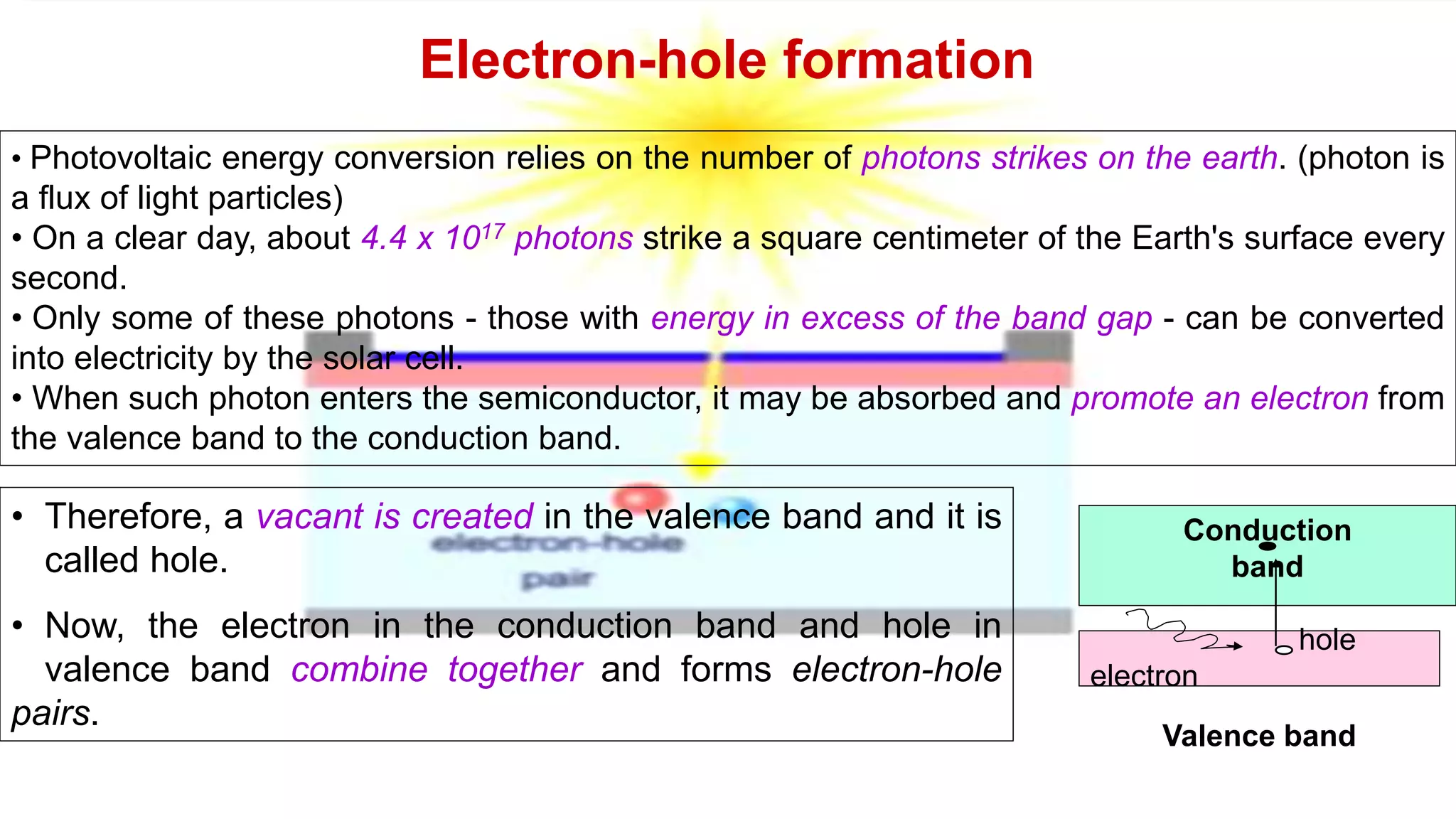
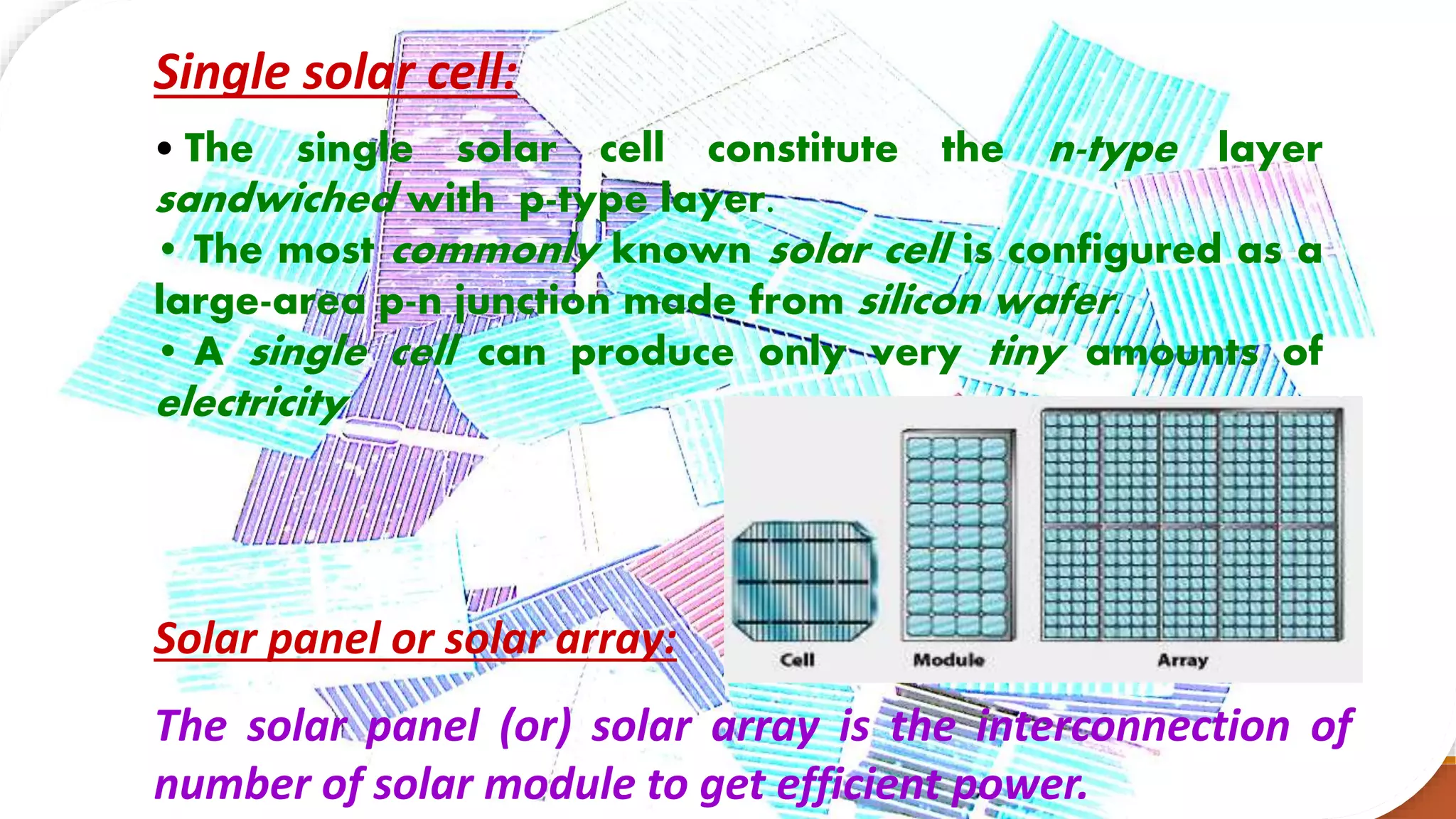
Solar cells convert light energy from the sun into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. They have increased in efficiency over time from early cells with 4-6% efficiency to over 50% efficiency today. Solar cells are made of semiconductor materials like silicon, cadmium telluride, or gallium arsenide. When light hits the p-n junction between positive and negative layers of semiconductor, electrons gain energy and move, creating an electric current. Multiple solar cells are connected into solar panels to produce usable amounts of electricity with applications like powering homes, satellites, and remote equipment.