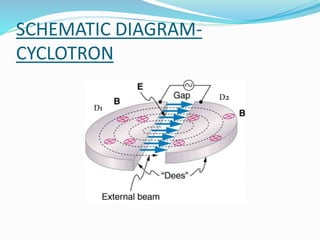
This document describes the working of a cyclotron particle accelerator. It explains that a cyclotron uses a magnetic field to curve the path of charged particles into a circular orbit, while an alternating electric field accelerates the particles at each half orbit. As the particles accelerate, they travel along spiraling paths of increasing radius. The document provides details on the construction of a cyclotron, including its dees and vacuum chamber between magnets. It also gives the mathematical expression for the cyclotron frequency that determines the electric field frequency needed for resonance acceleration. Limitations of the cyclotron are that particle mass may change at high speeds and it is difficult to accelerate low-mass particles like electrons.



![MATHEMATICAL EXPRESSION
The Lorentz force in the circular orbit, qv B , provides the centripetal
acceleration to maintain the circular motion at an instantaneous
radius ‘r ‘. Thus,
F = qv B = mv² ∕ r
v = q Br / m
the time taken for a semicircular orbit is,
time=distance/velocity
t = ∏r ∕ v = m∏ ∕ q B ; it shows that time is independent of radius and velocity.
The condition for resonance is half the period of the accelerating potential of
the oscillator should be ’ t’. (i.e., T∕2 = t). Hence the period of AC
T=2t
T=2∏m ∕q B [ since t = ∏m ∕q B ]
But we know frequency, ν = 1 ∕ T
therefore , Resonance frequency, ν = qB /2∏m
Which is often called “cyclotron frequency”
or “cyclotron resonance frequency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyclotronparticleaccelerators-170109080255/85/Cyclotron-5-320.jpg)


