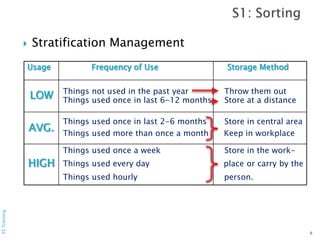
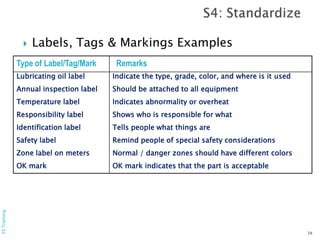
The document outlines the 5S methodology, a system originating from Toyota designed to enhance workplace organization and safety. It details the five steps: Sort, Straighten, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, emphasizing their implementation and benefits, such as increased productivity and reduced waste. Additionally, it covers the importance of safety and the role of audits in maintaining these practices.