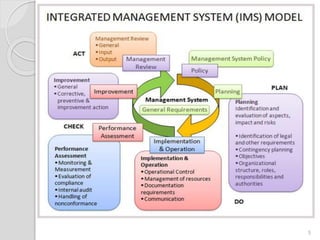
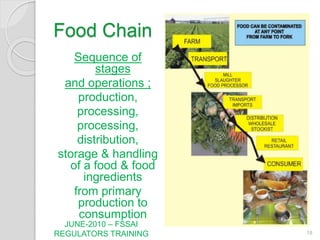
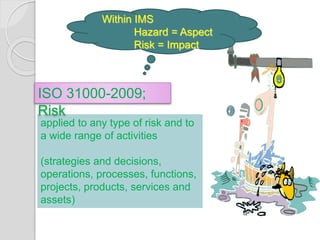
The document discusses integrated management systems (IMS) and provides an overview of several key standards. It defines IMS as the organizational structure and processes for developing, implementing, and maintaining policies across multiple standards. The three major IMS discussed are ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and ISO 18001 for occupational health and safety management. Popular additional standards covered include ISO 22000 for food safety management and ISO 31000 for risk management. The conclusion states that integrated standards can facilitate consistent auditing and ease of use when multiple standards are adopted.