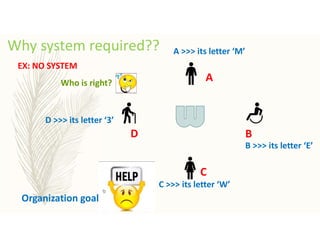
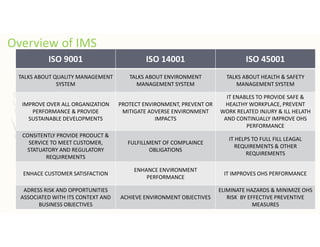
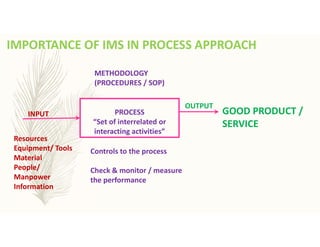
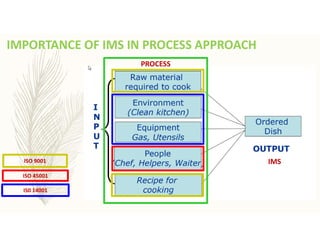
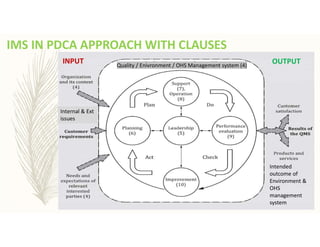
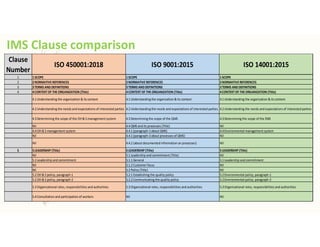
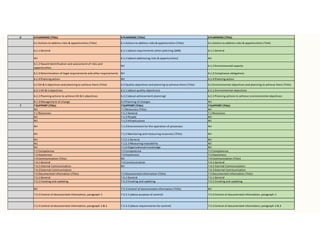
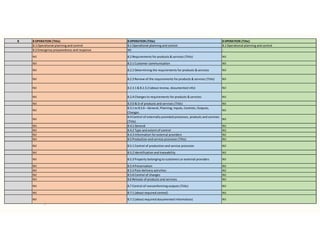
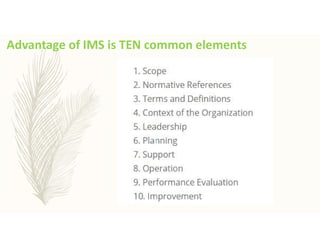
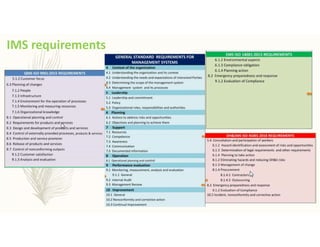
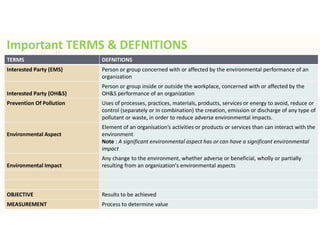
The document outlines the importance of awareness training on Integrated Management Systems (IMS) standards: ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 45001:2018. It emphasizes that the success of organizational activities and the implementation of these systems relies on employees' understanding of their roles and the systems in place. The training aims to enhance overall organizational performance, ensure compliance with legal requirements, and improve customer satisfaction through effective management practices.