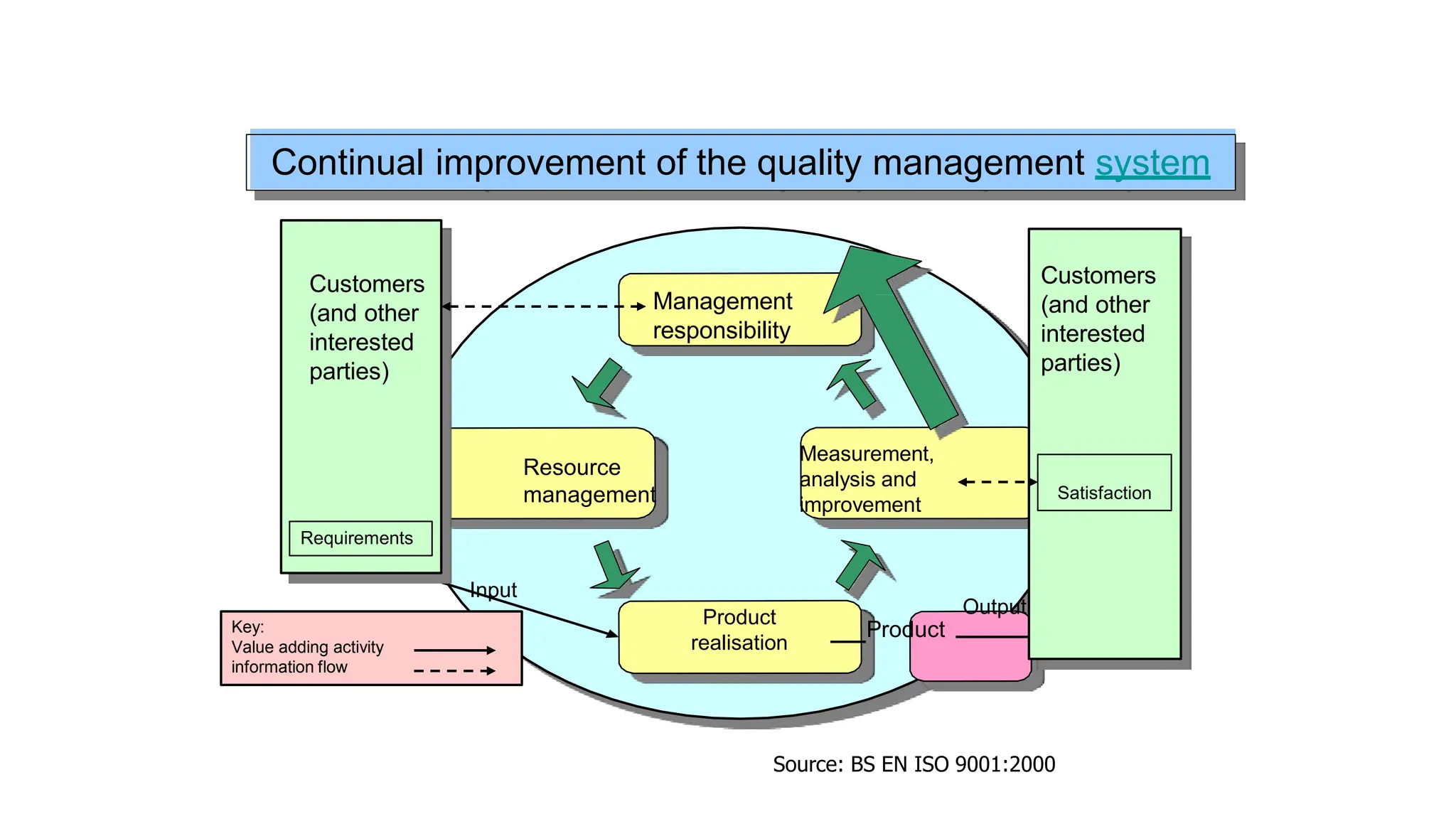
The document outlines the importance of integrated management systems (IMS) and the standards that guide them, primarily ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. It emphasizes the benefits of implementing IMS, such as improved efficiency, unified policies, and compliance with legal requirements, while detailing the process standards rather than specific product or service standards. Additionally, it highlights the need for coordinated efforts across multiple management systems to address overlapping responsibilities and enhance overall organizational performance.