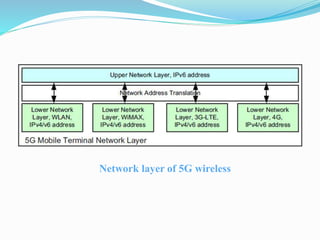
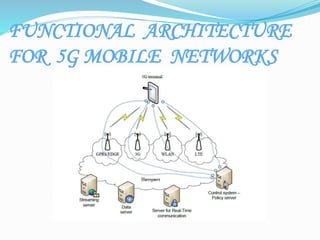
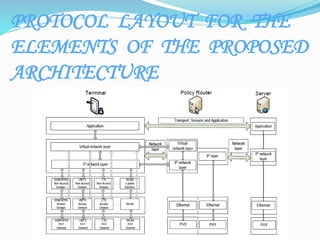
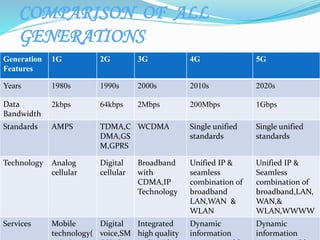
This document provides an overview of wireless technologies from 0G to 5G. It discusses the evolution and key features of each generation including the underlying technologies, data speeds, and applications. The 5G section describes its architecture, hardware/software components, features, applications, and how it represents an improvement over previous generations with speeds up to 1Gbps and the ability to support new technologies like wearables and IoT.