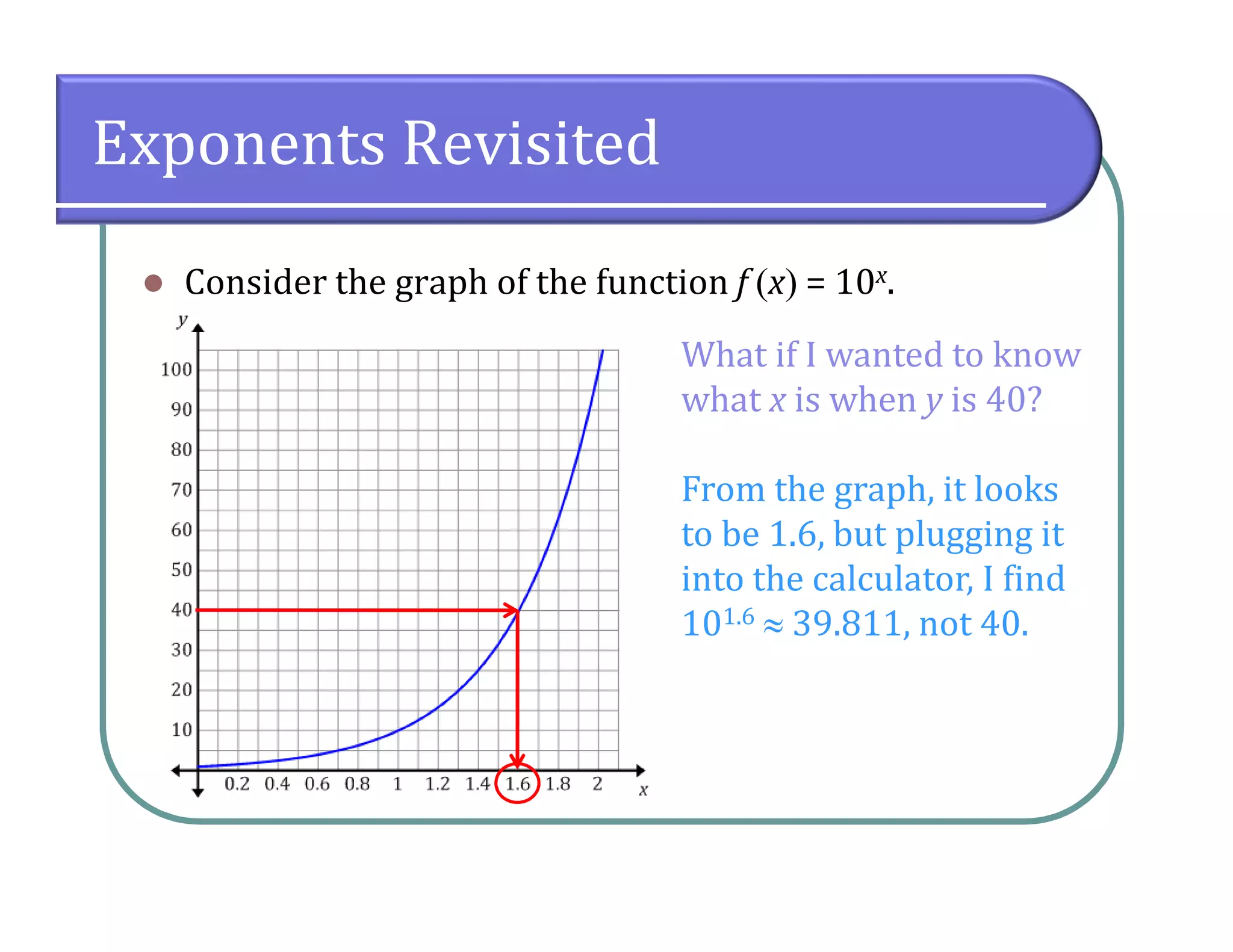
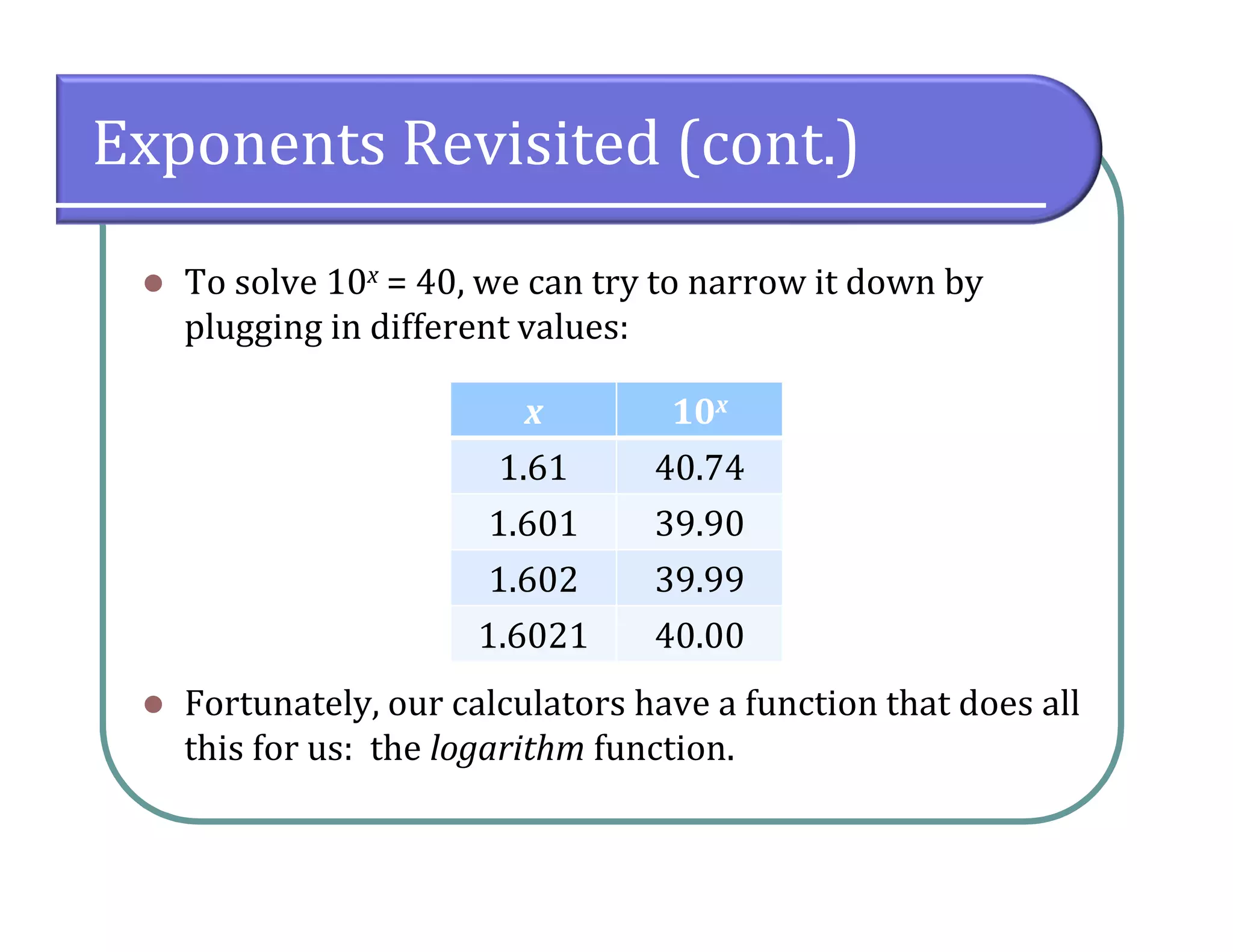
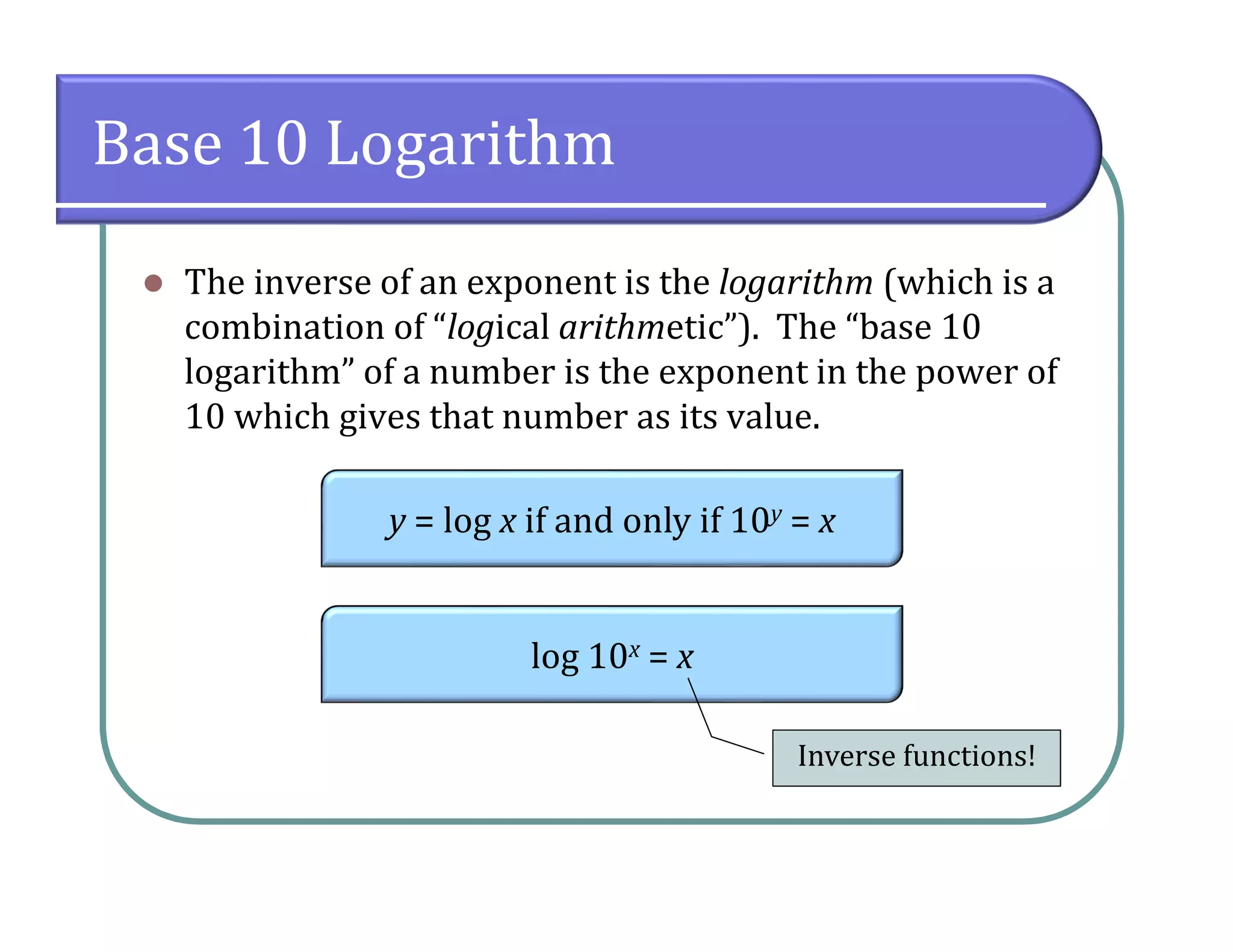
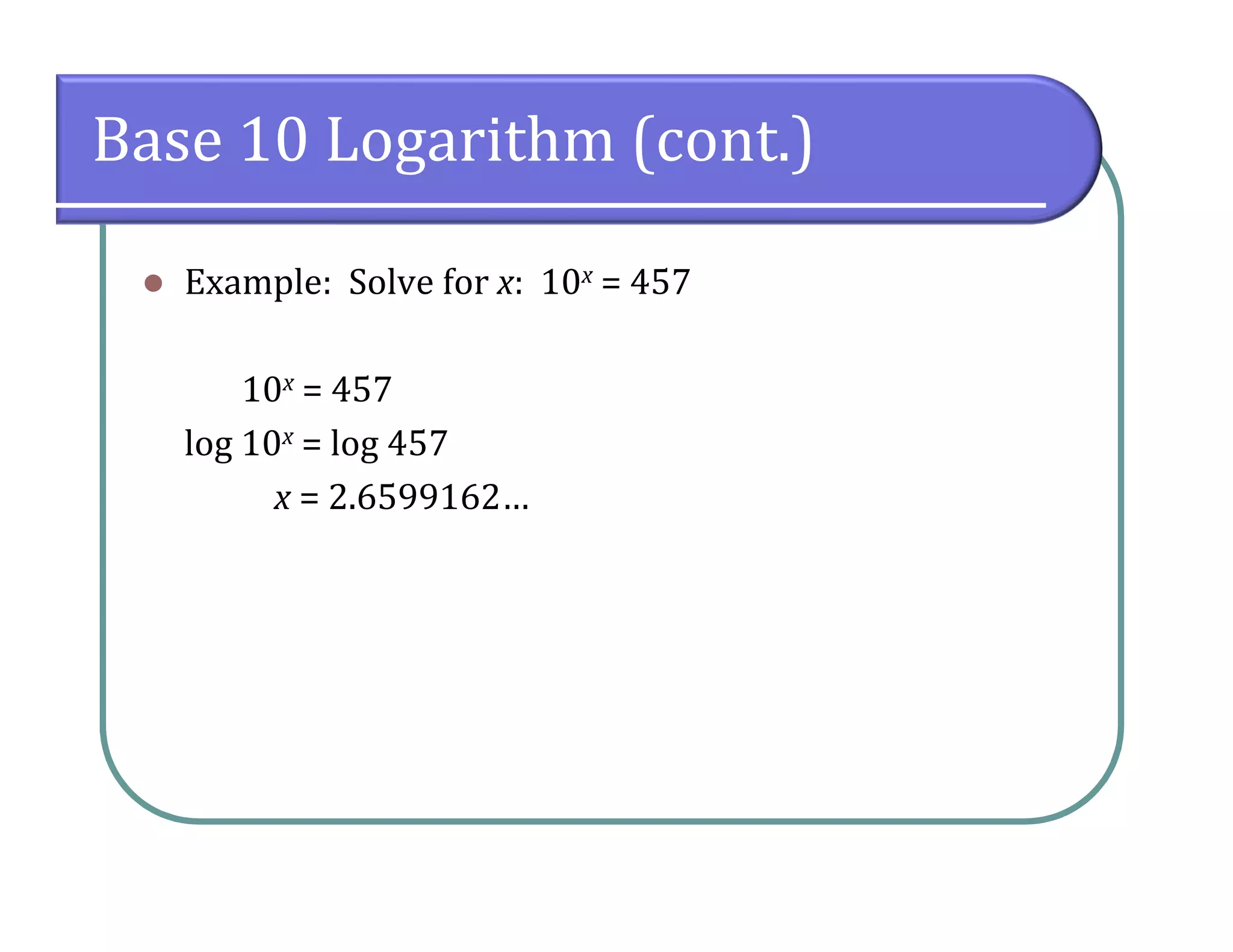
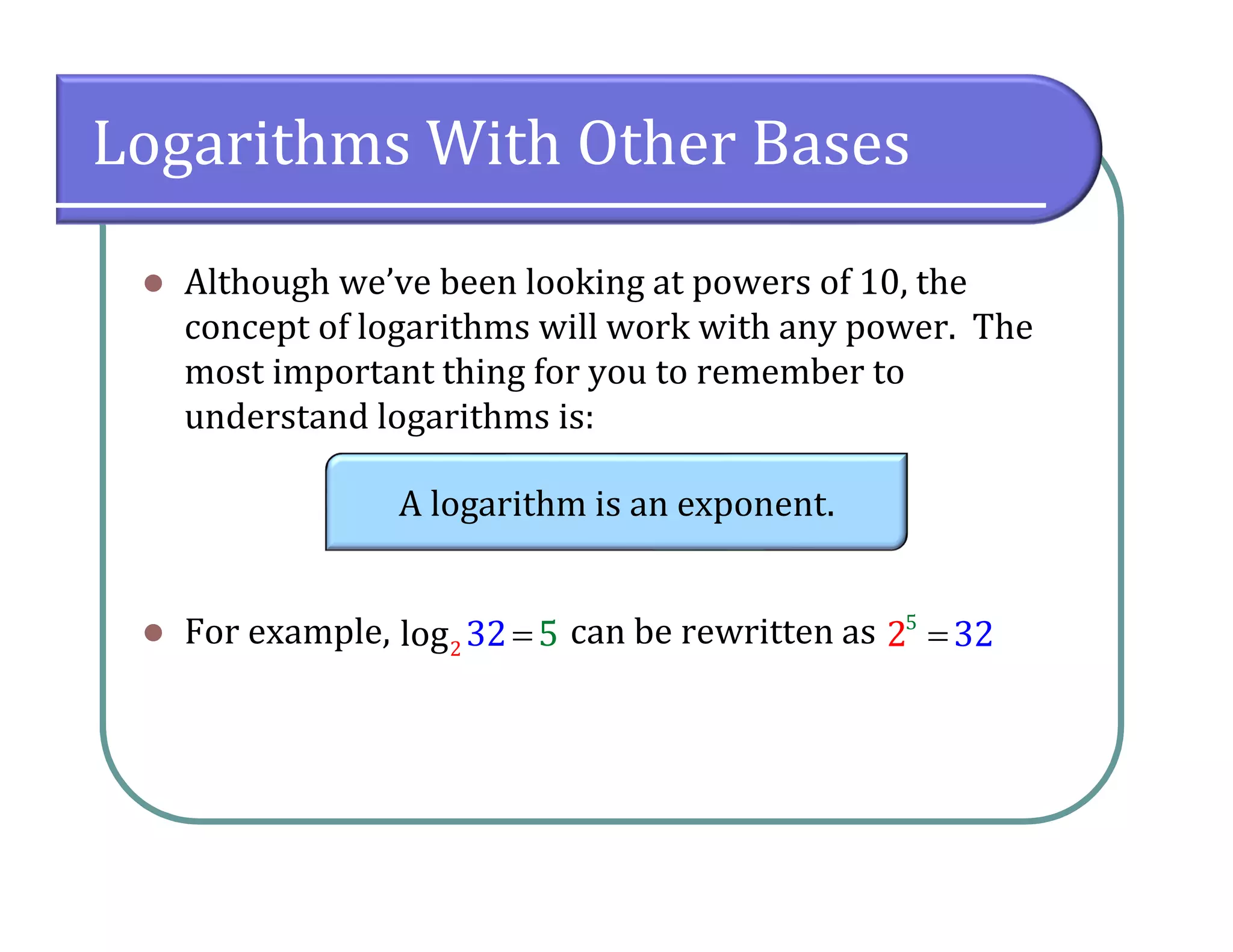
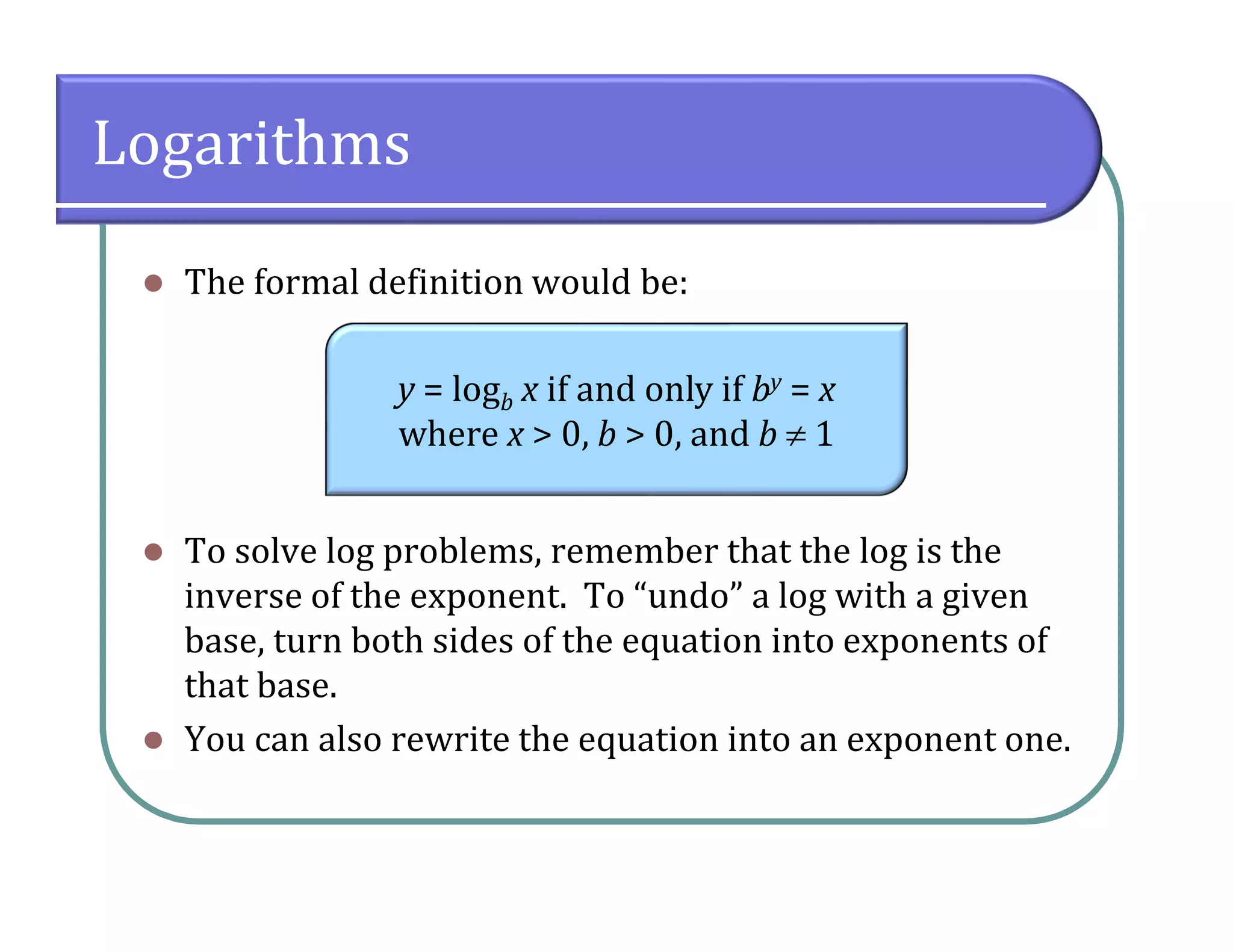
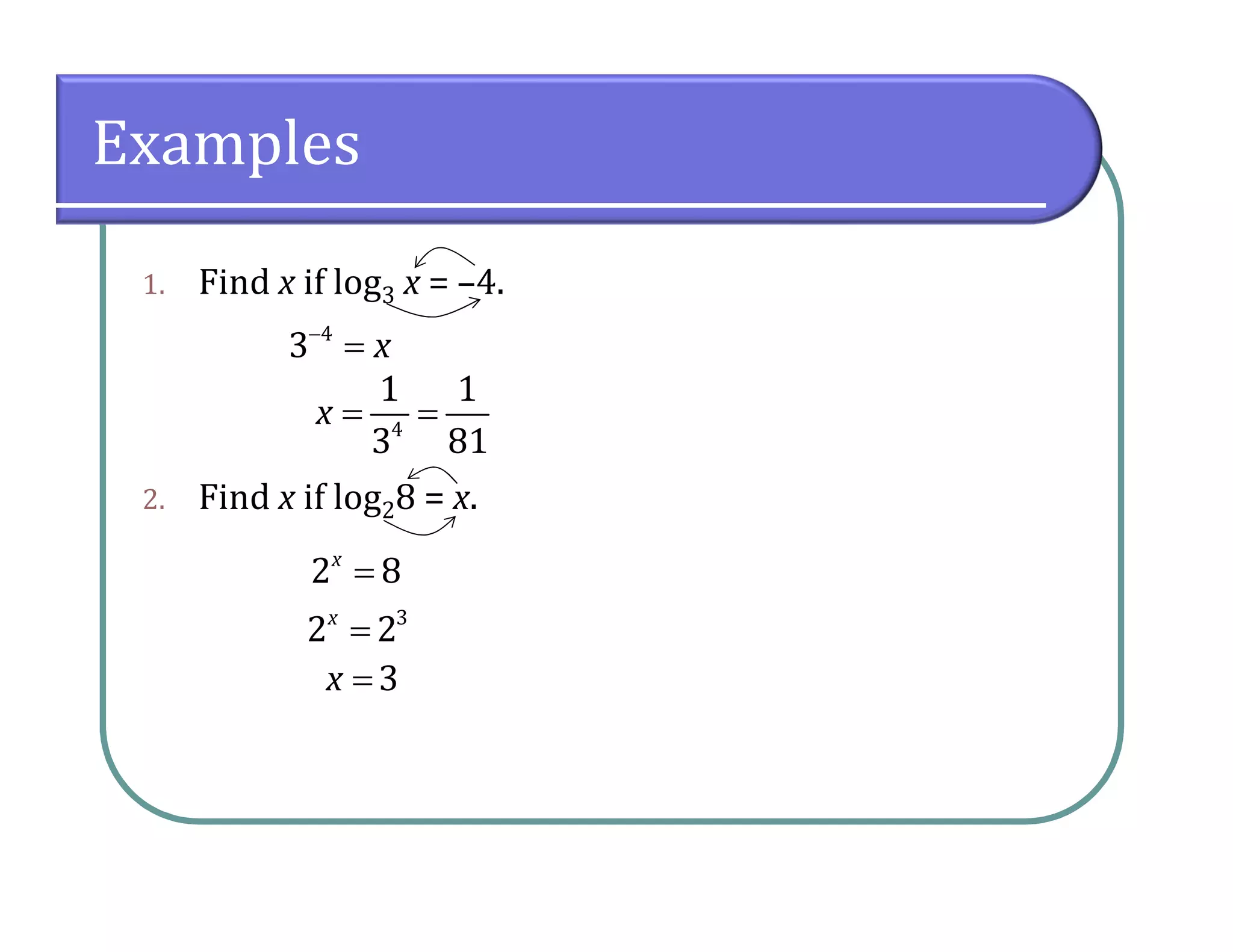
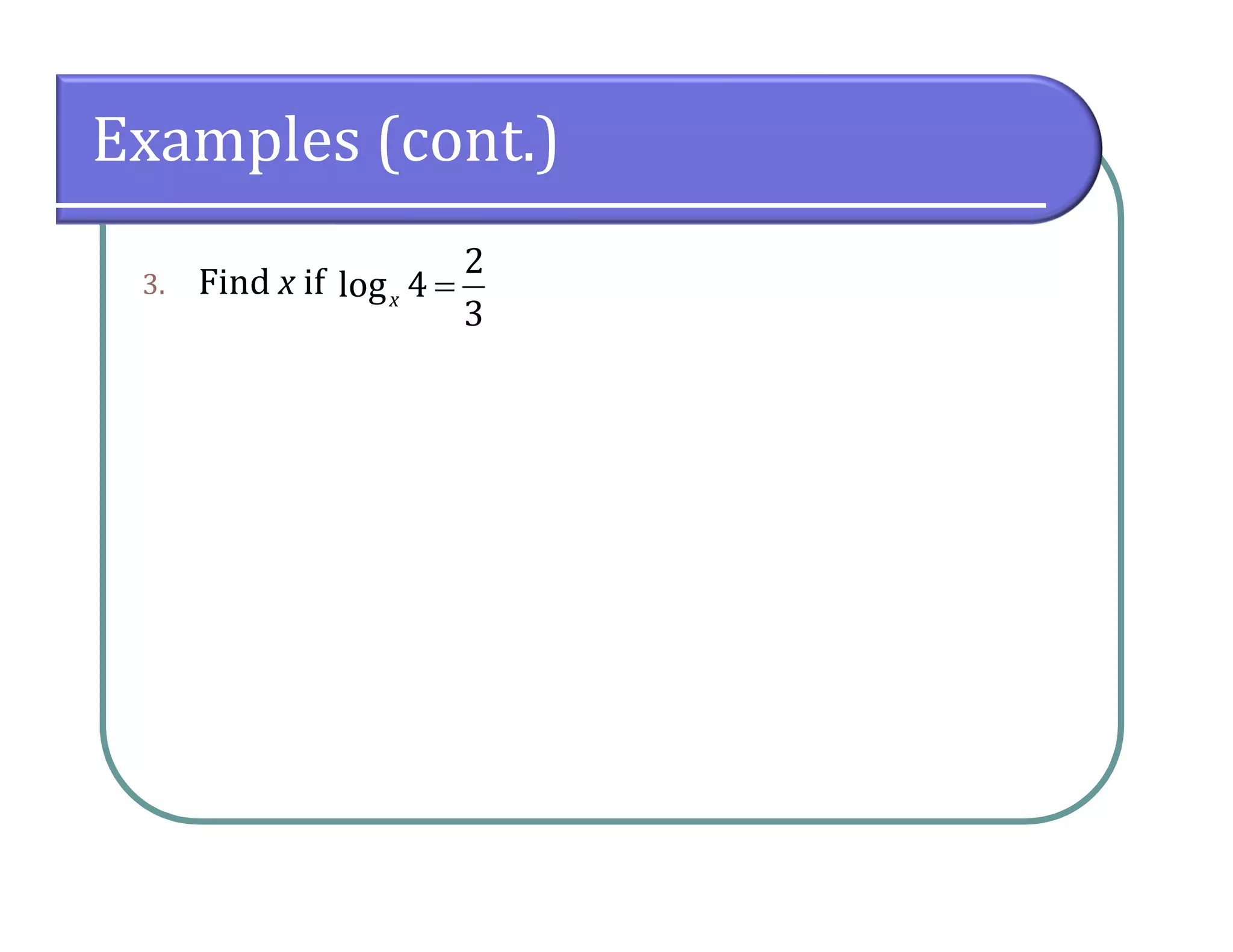
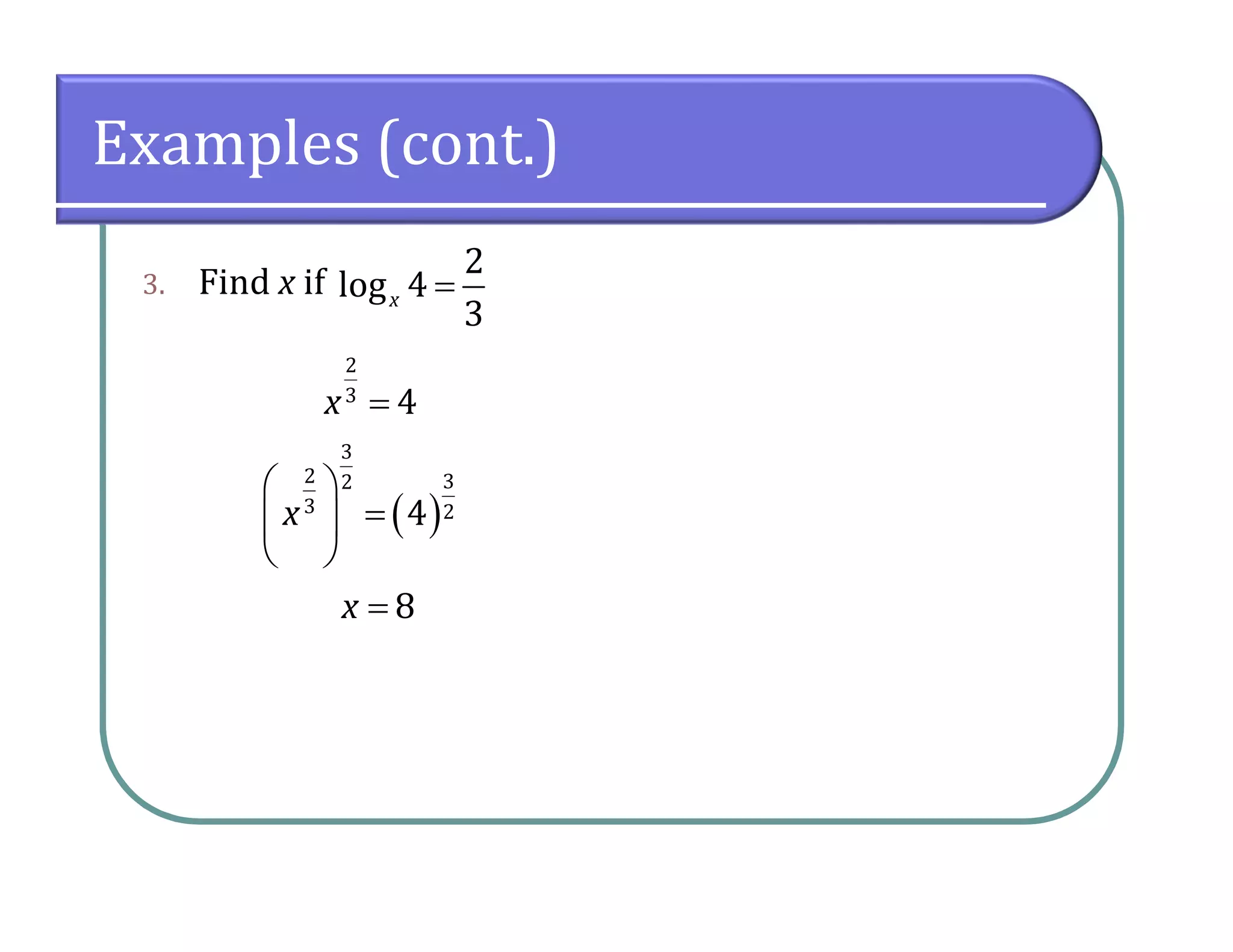
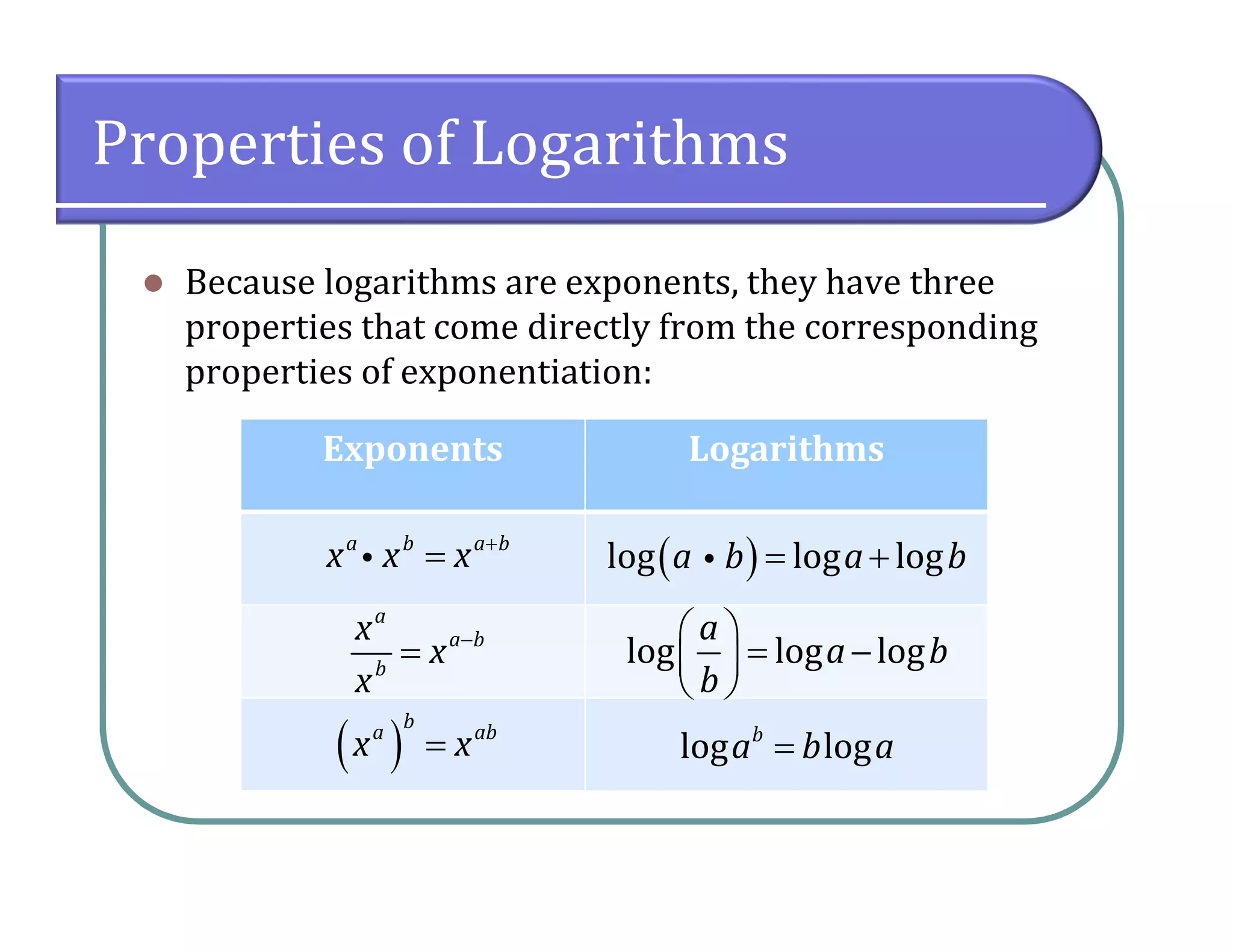
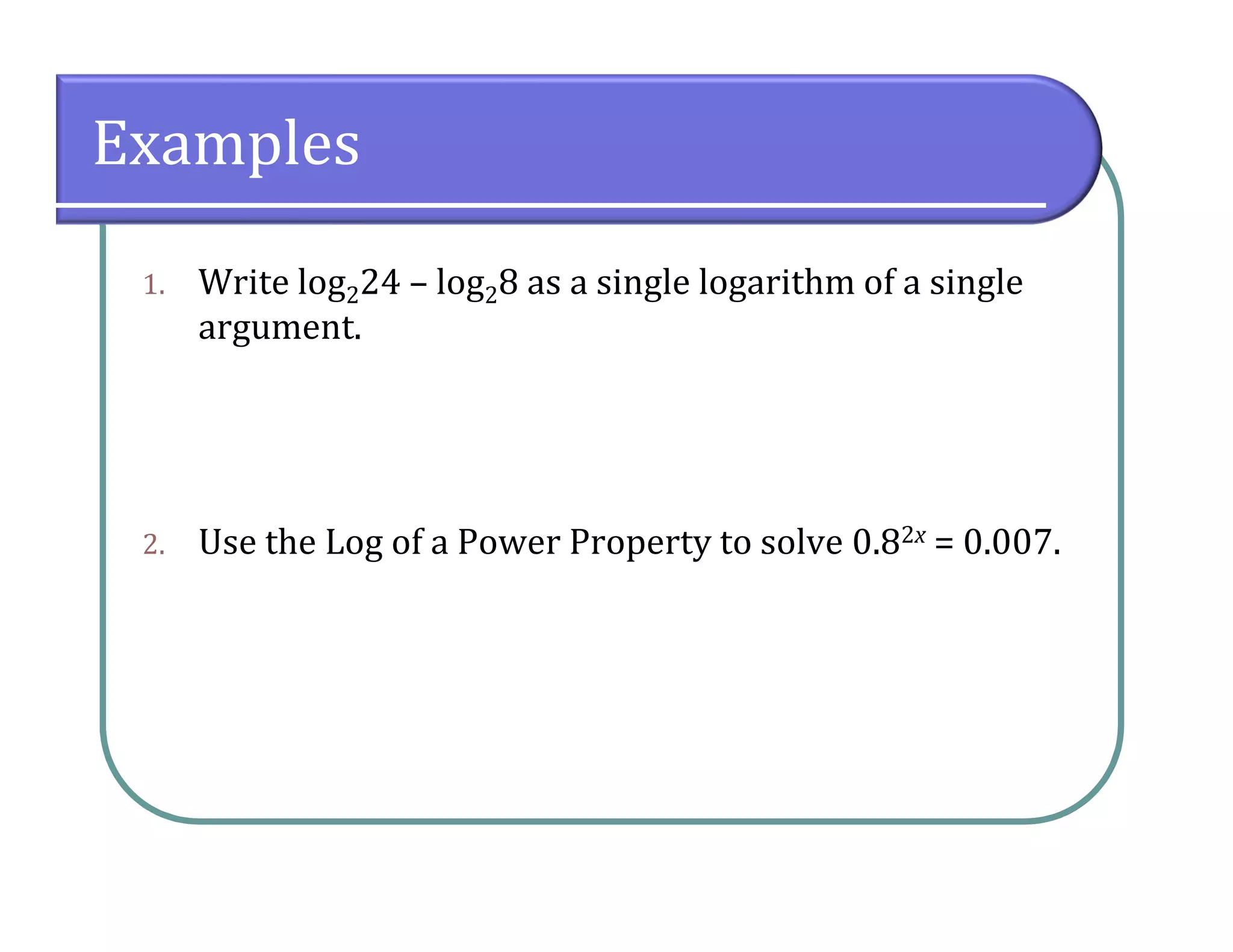
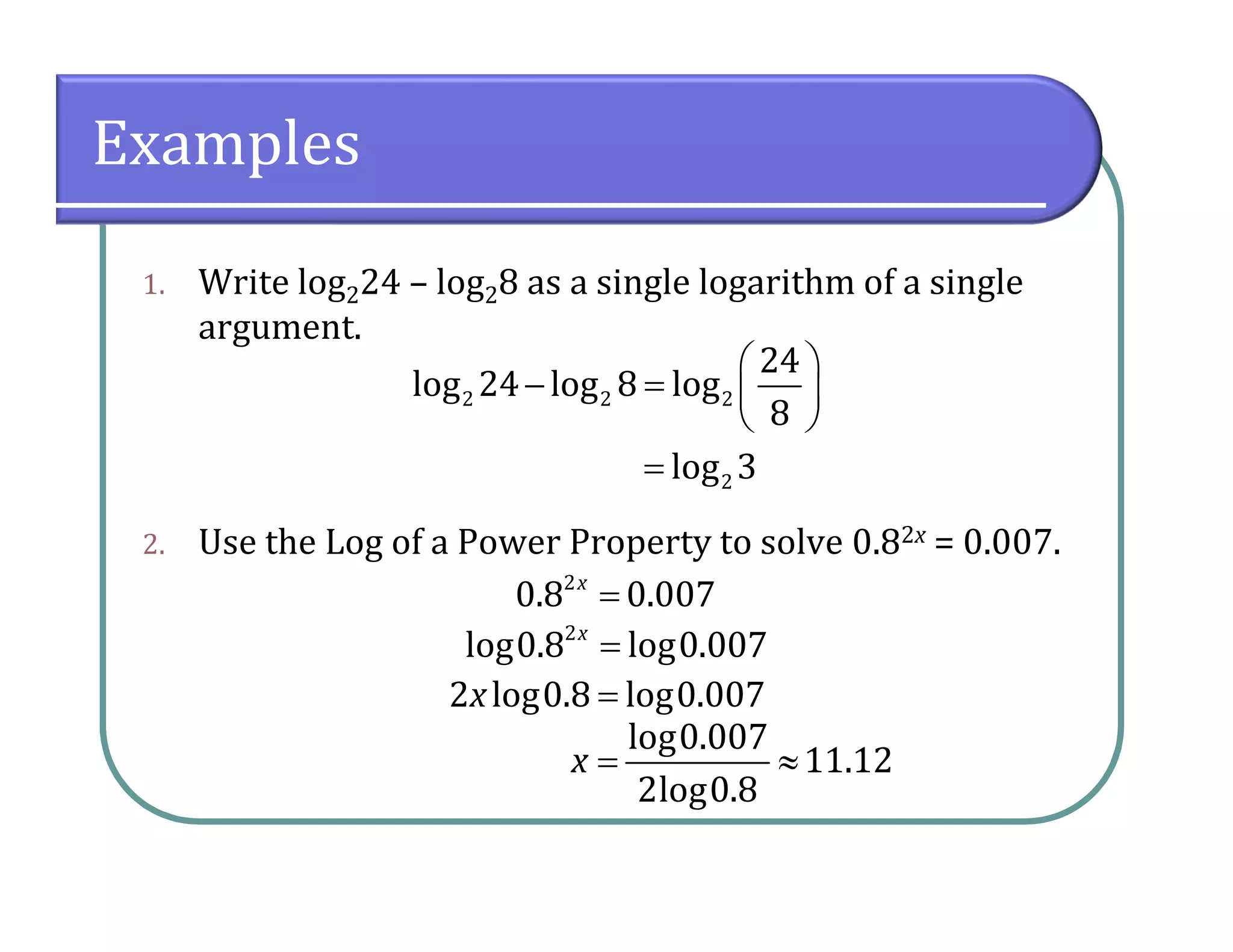
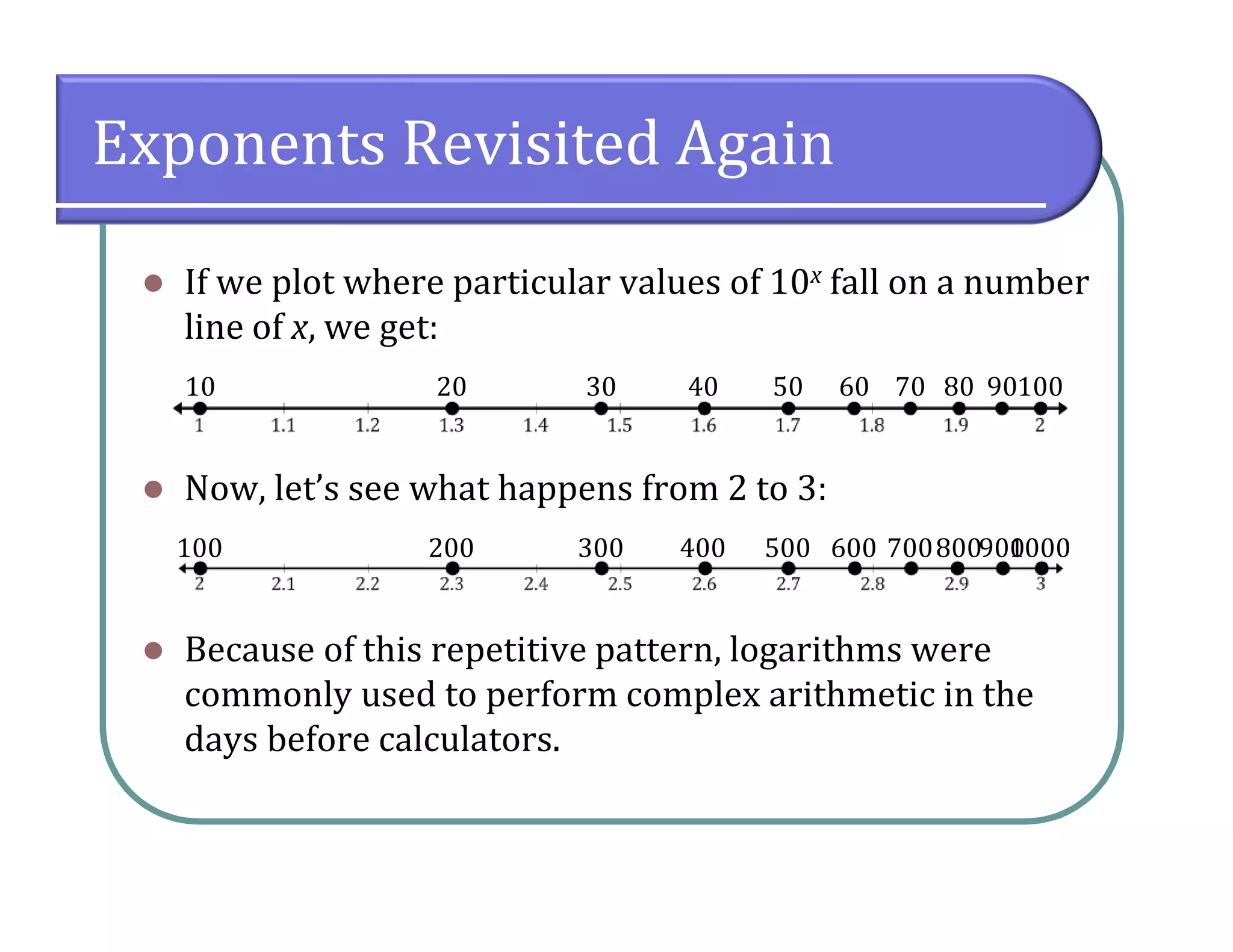
This document provides an overview of logarithmic functions. It defines logarithms as the inverse of exponents, where the logarithm of a number is the exponent that the base must be raised to to produce that number. It presents examples of solving logarithmic equations by rewriting them as exponential equations. The key properties of logarithms - that they satisfy the same properties as exponents - are described. The document works through multiple examples of evaluating logarithms and using their properties to simplify expressions and solve equations.