Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times

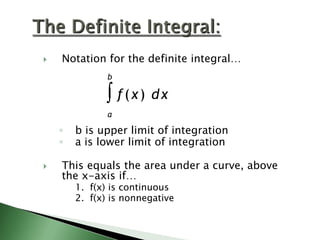
![If f ( x )
c on [a ,b ], th e n
b
c d x = c(b -a )
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-140109060547-phpapp02/85/4-3-The-Definite-Integral-4-320.jpg)


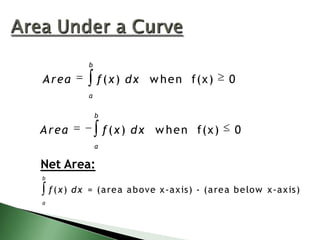
![4. Sum and Difference
b
b
[ f(x)
a
g ( x )] d x
b
f(x) dx
a
g( x ) d x
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-140109060547-phpapp02/85/4-3-The-Definite-Integral-9-320.jpg)
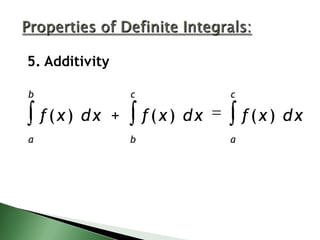
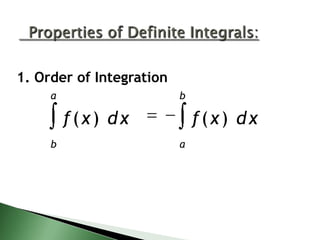
![a
b
1. Order of Integration
f(x) dx
f(x) dx
b
a
a
2. Zero
f(x) dx = 0
a
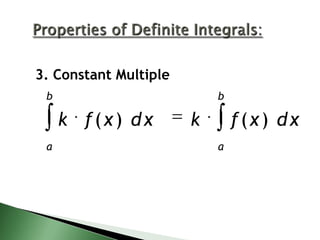
b
b
3. Constant Multiple
k f(x) dx
k
a
f (x ) dx
a
b
4. Sum and Difference
b
[ f(x)
g ( x )] d x
a
b
f(x) dx
a
b
5. Additivity
c
f(x) dx +
a
a
c
f(x) dx
b
g( x ) d x
f (x) dx
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-140109060547-phpapp02/85/4-3-The-Definite-Integral-11-320.jpg)

The document discusses notation and properties for definite integrals. It defines the definite integral from a to b of f(x) dx as the area under the curve of f(x) between the x-axis and the limits of a and b. It lists five properties of definite integrals: 1) the order of integration does not matter, 2) the integral from a to a of any function f(x) is equal to zero, 3) a constant can be pulled out of the integral, 4) integrals can be added or subtracted, and 5) a definite integral over an interval can be broken into a sum of integrals over subintervals.



![If f ( x )
c on [a ,b ], th e n
b
c d x = c(b -a )
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-140109060547-phpapp02/85/4-3-The-Definite-Integral-4-320.jpg)




![4. Sum and Difference
b
b
[ f(x)
a
g ( x )] d x
b
f(x) dx
a
g( x ) d x
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-140109060547-phpapp02/85/4-3-The-Definite-Integral-9-320.jpg)

![a
b
1. Order of Integration
f(x) dx
f(x) dx
b
a
a
2. Zero
f(x) dx = 0
a
b
b
3. Constant Multiple
k f(x) dx
k
a
f (x ) dx
a
b
4. Sum and Difference
b
[ f(x)
g ( x )] d x
a
b
f(x) dx
a
b
5. Additivity
c
f(x) dx +
a
a
c
f(x) dx
b
g( x ) d x
f (x) dx
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-140109060547-phpapp02/85/4-3-The-Definite-Integral-11-320.jpg)