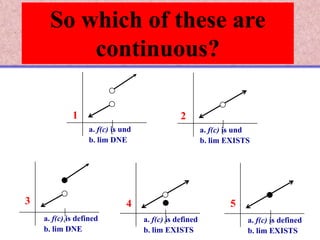
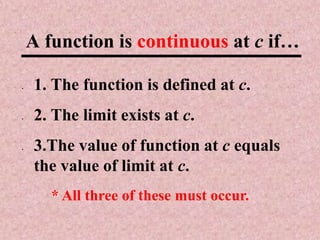
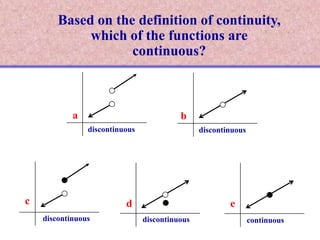
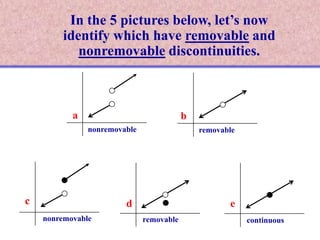
The document discusses continuity of functions at a point c. It defines continuity as a function being defined at c, the limit existing at c, and the function value at c equaling the limit value. Five examples are given and categorized as continuous, discontinuous with removable discontinuities, or discontinuous with nonremovable discontinuities. Removable discontinuities can be resolved by redefining the function value at c, while nonremovable discontinuities cannot be resolved.