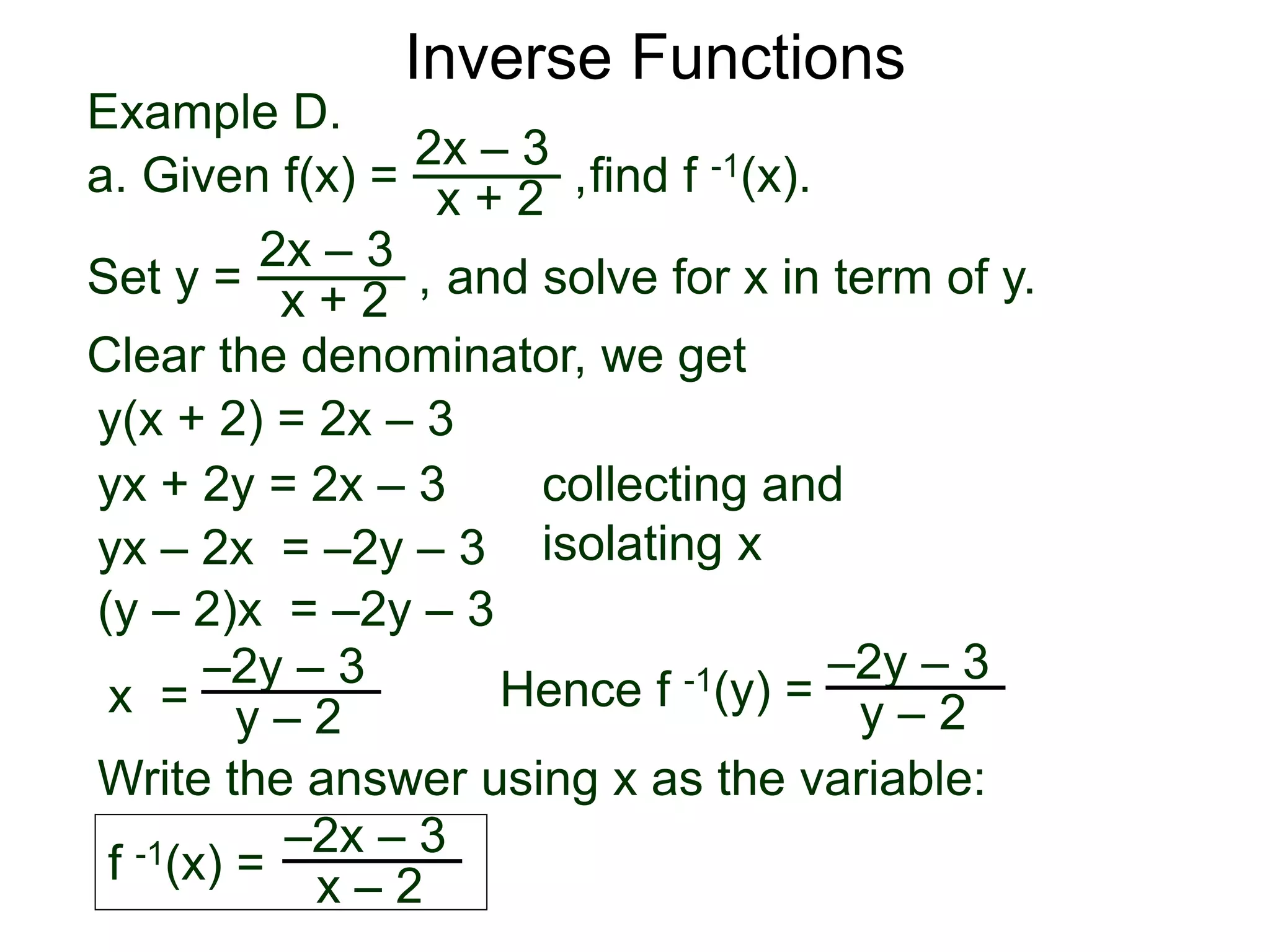
This document provides examples and exercises on inverse functions. It first shows an example of finding the inverse of the function f(x) = 2x-3/(x+2). It gives the steps to solve for x in terms of y and obtain the inverse function f^-1(x) = -2x-3/(x-2). It then asks the reader to verify that f(f^-1(x)) = x. The exercises provide 20 functions and ask the reader to find their inverses and verify the inverses are correct. It also gives graphs of 8 functions and asks the reader to determine properties of the inverse graphs, including their domains and ranges and any fixed or end points.
![Inverse Functions
b. Verify that f(f -1(x)) = x
We've f(x) = and
2x – 3
x + 2 , f -1(x) =
–2x – 3
x – 2
f(f -1(x)) = f( )–2x – 3
x – 2
=
–2x – 3
x – 2
– 3
–2x – 3
x – 2
+ 2
( )2[
[ ]
](x – 2)
(x – 2)
=
2(-2x – 3) – 3(x – 2)
(-2x – 3) + 2(x – 2)
=
-4x – 6 – 3x + 6
-2x – 3 + 2x – 4
=
-7x
-7
= x
Your turn. Verify that f -1(f(x)) = x
Use the LCD to simplify
the complex fraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-190616052903/75/4-1-inverse-functions-t-2-2048.jpg)




![Exercise C.
Inverse Functions
(4, 3)
y = x
(-1, -3)
1. domain: [-1, 4]
range: [-3, 3]
(–5, –2)
(3,4)
3. domain: [-5, 3]
range: [-2, 4]
(–2, –4)
(7,5)
5. domain: [-2, 7]
range: [-4, 5]
(3, –4)
7. domain: [-1, 3], range: [-4,2]
(–1, 2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-190616052903/75/4-1-inverse-functions-t-7-2048.jpg)