Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times
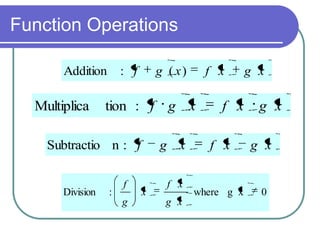
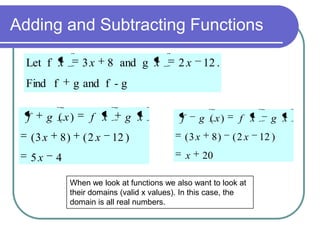
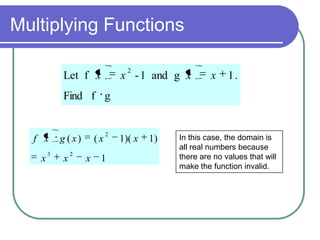
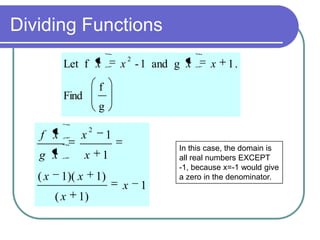
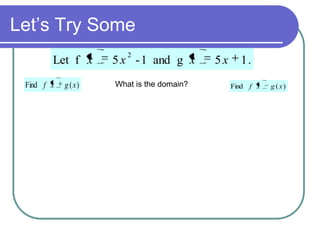
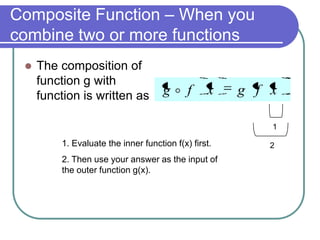
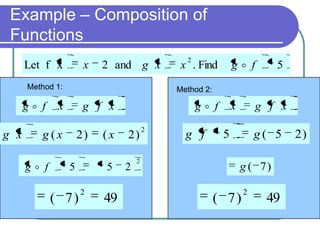
This document discusses various function operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition of functions. It provides examples of applying each operation to sample functions, noting that the domain of the results depends on the individual functions and operations to avoid undefined values. Composition of functions is defined as applying the outer function to the result of the inner function, and an example demonstrates evaluating a composite function in two steps.








