Embed presentation
Download to read offline


![MedNotes [ www.mednotes.in ]
Full MedNotes : mednotesebooks.company.site
App Available on PlayStore
laboratory Diagnosis :
( is
Transport media - YR ( Venkatraman Ramakrishnan
)
Media
-
Cary - Blair Medium
ciii Enrichment Media -
Alkaline
Peptone water .
ciii, selective media -
T CBs ( Green to Yellow )
Treatment :
ii. Fluid
replacement
cii, Antibiotics (minor role)
Is
Doc = Macrolides ( Azithromycin or
Erythromycin )
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-230131071956-31dc8a25/85/4-Cholera-pdf-4-320.jpg)
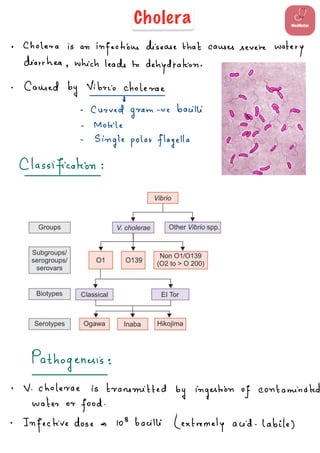
Cholera is an infectious disease caused by Vibrio cholerae bacteria that leads to severe watery diarrhea and dehydration. The bacteria is transmitted by ingesting contaminated water or food. Cholera toxins produced by the bacteria cause increased cyclic AMP levels that inhibit sodium absorption and activate chloride secretion in the intestines, resulting in a massive loss of fluid and electrolytes from rice water stools. Treatment involves oral rehydration and antibiotics which play a minor role in treating the infection.



![MedNotes [ www.mednotes.in ]
Full MedNotes : mednotesebooks.company.site
App Available on PlayStore
laboratory Diagnosis :
( is
Transport media - YR ( Venkatraman Ramakrishnan
)
Media
-
Cary - Blair Medium
ciii Enrichment Media -
Alkaline
Peptone water .
ciii, selective media -
T CBs ( Green to Yellow )
Treatment :
ii. Fluid
replacement
cii, Antibiotics (minor role)
Is
Doc = Macrolides ( Azithromycin or
Erythromycin )
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-230131071956-31dc8a25/85/4-Cholera-pdf-4-320.jpg)