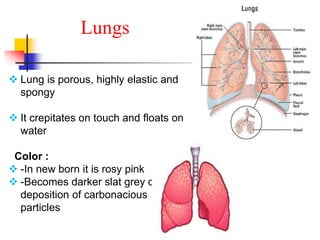
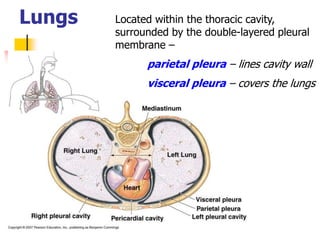
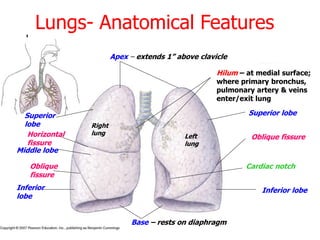
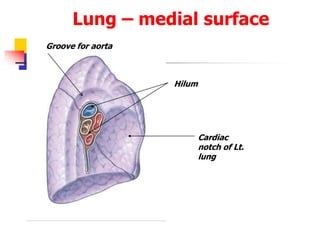
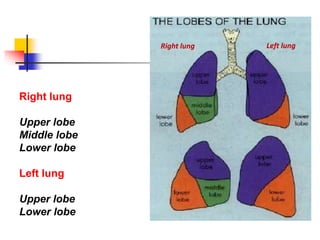
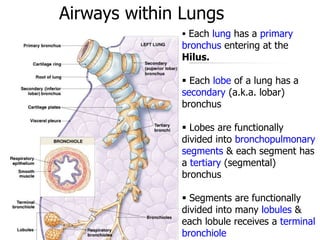
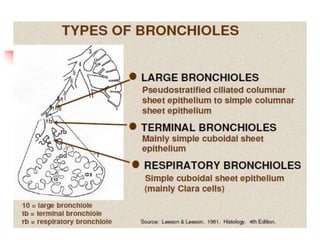
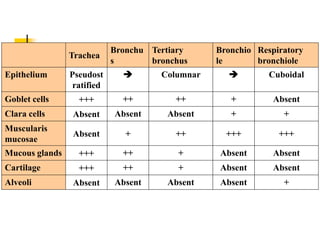
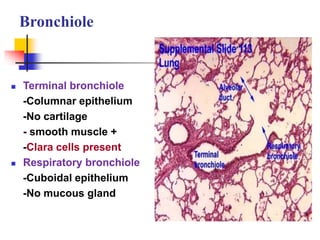
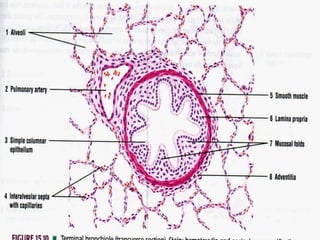
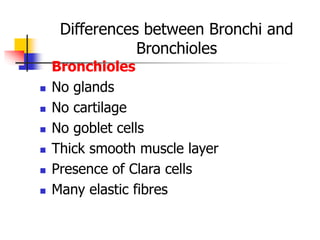
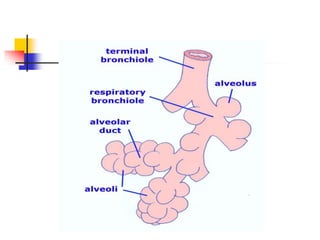
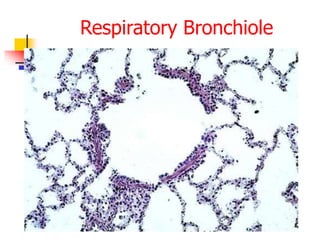
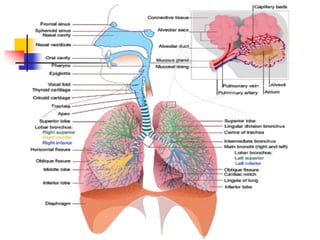
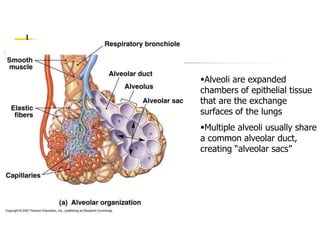
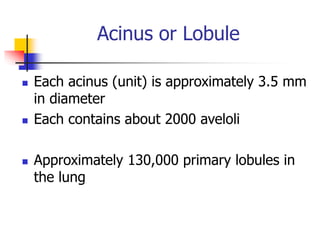
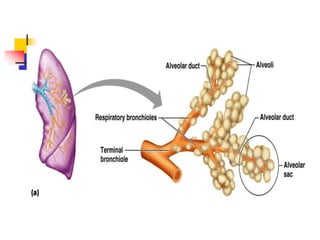
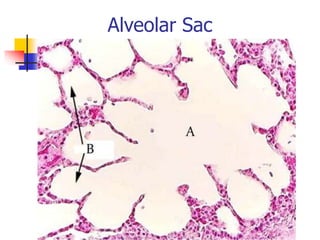
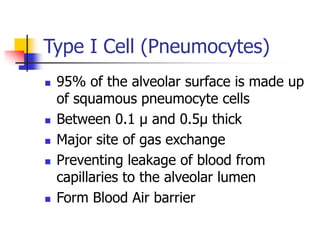
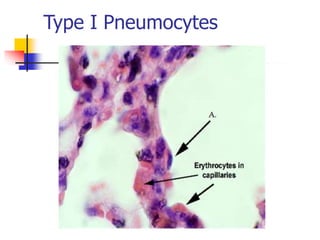
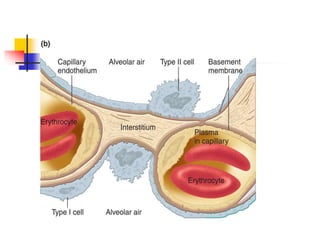
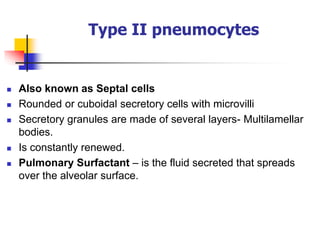
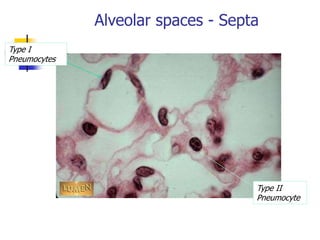
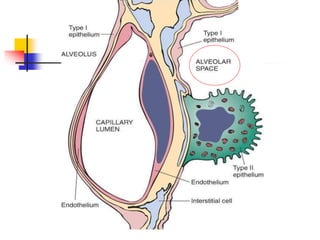
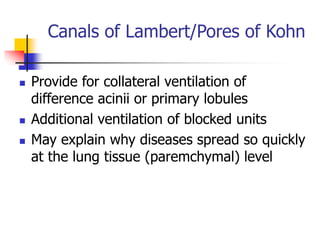
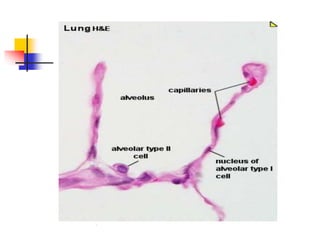
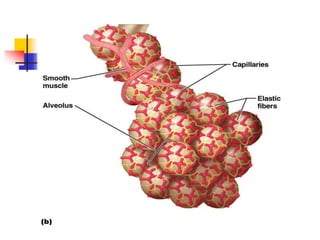
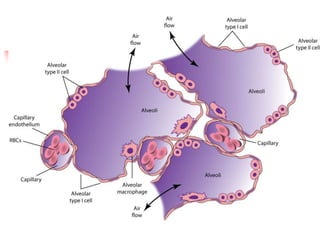
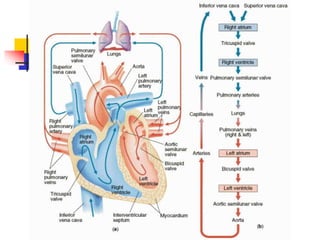
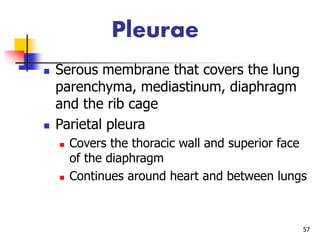
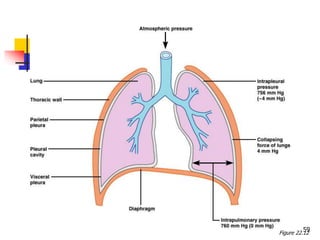
The lungs are located within the thoracic cavity and are surrounded by the pleural membranes. Each lung has a conical shape with an apex and base. The right lung is divided into three lobes and the left lung into two lobes by fissures. Over 300 million alveoli within the lungs provide a vast surface area for gas exchange to occur between the air in the alveoli and blood in the pulmonary capillaries.