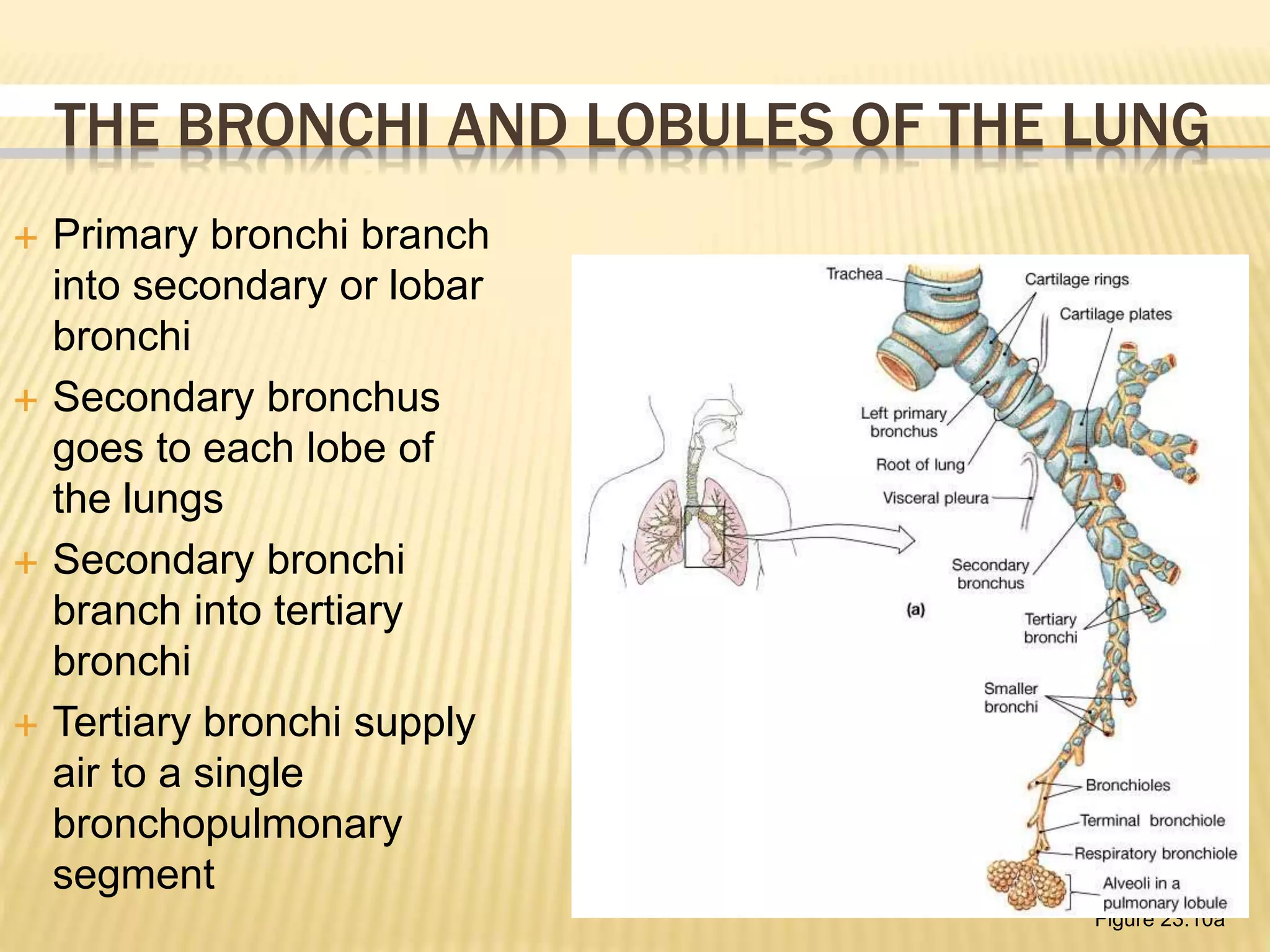
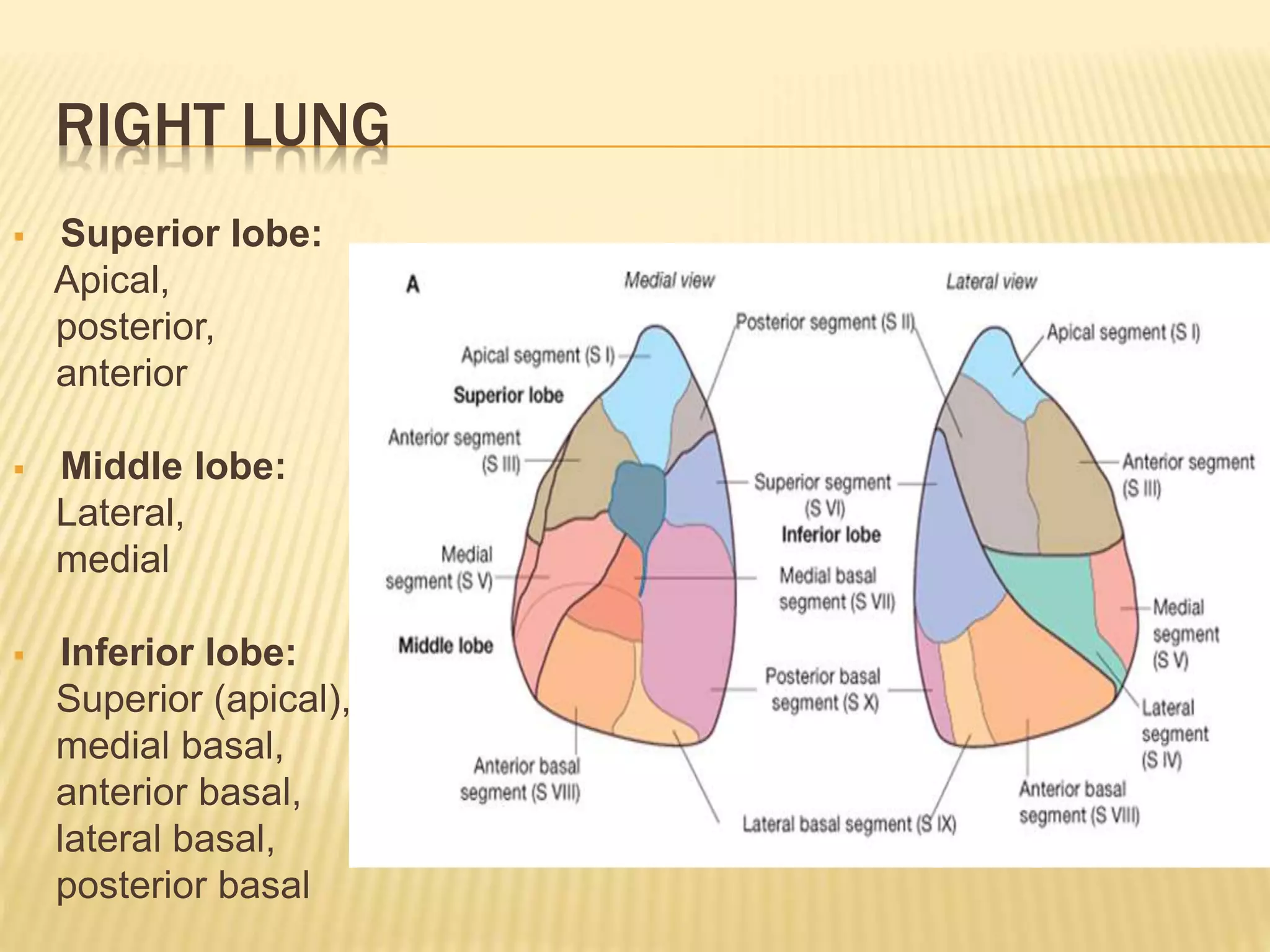
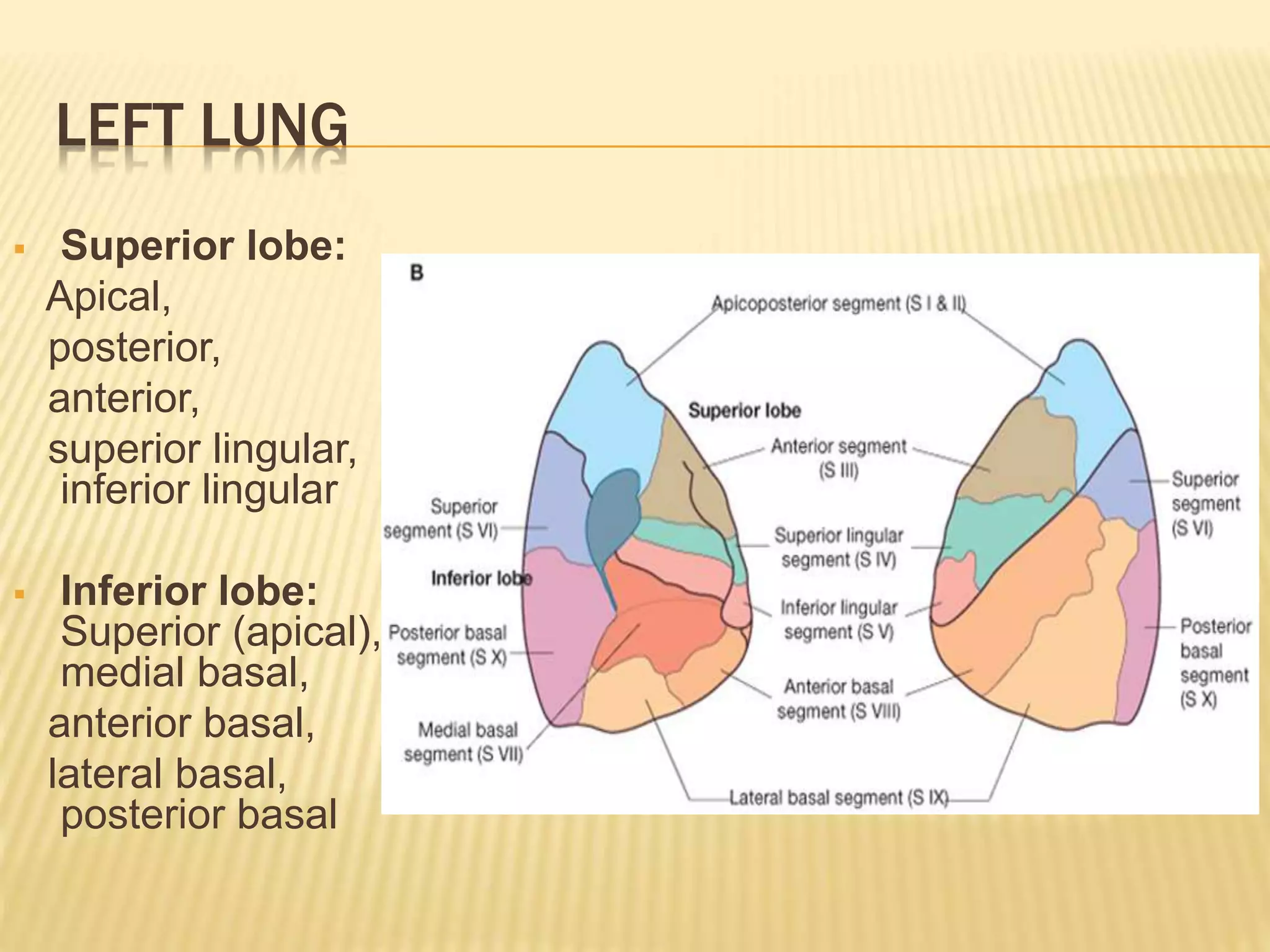
The lungs are a pair of respiratory organs located in the thoracic cavity. Each lung has a cone shape and is divided into lobes and segments. The right lung has three lobes while the left has two. The lobes are further divided into bronchopulmonary segments, which are the basic functional units of the lung, each served by its own segmental bronchus, artery, veins, lymphatics and nerves. There are approximately 10 segments in each lung.