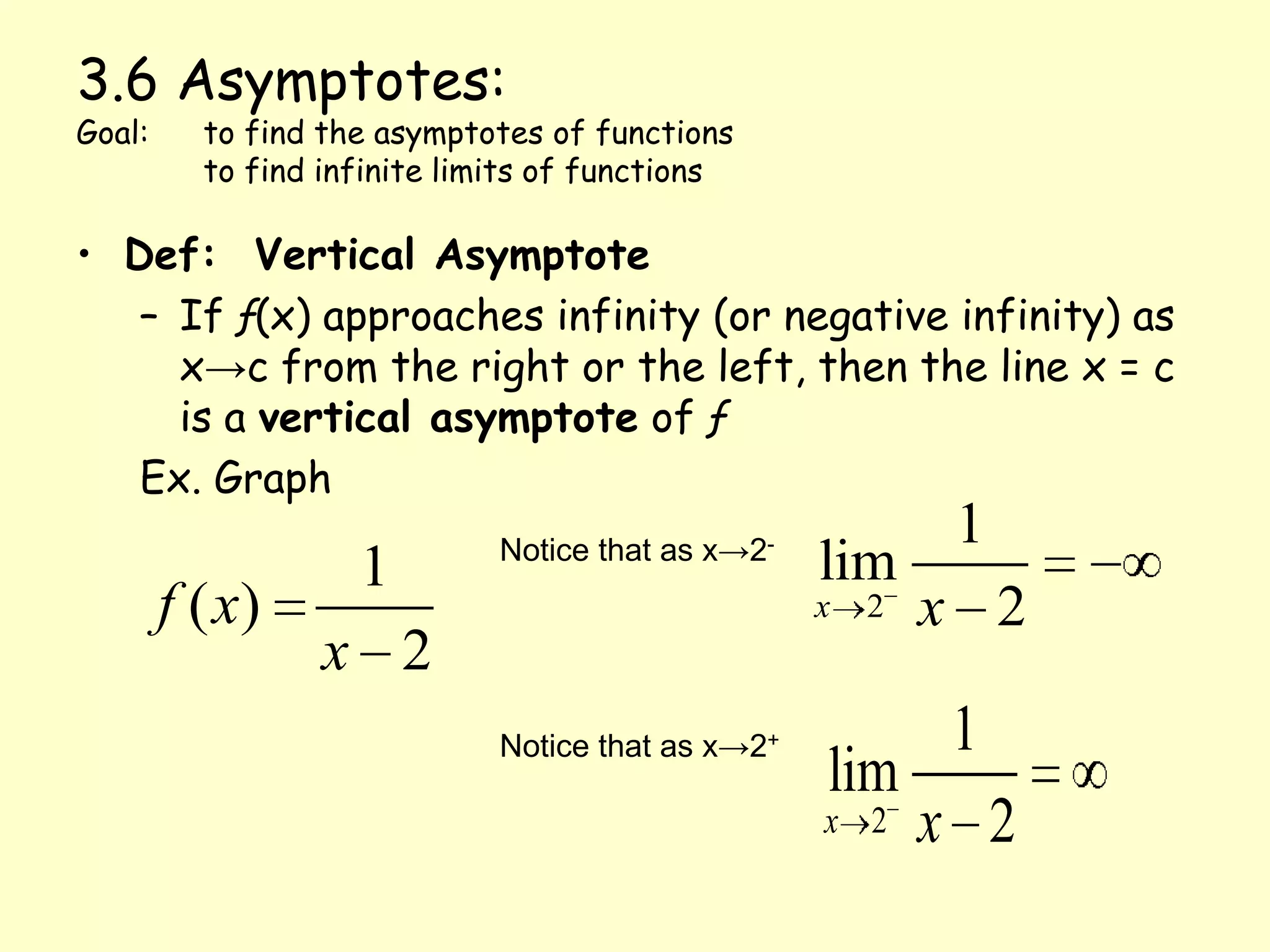
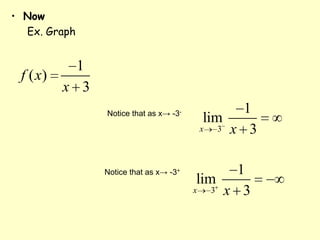
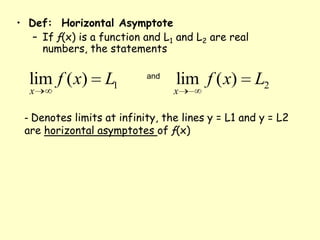
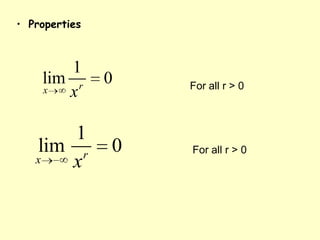
This document defines and provides examples of vertical and horizontal asymptotes of functions. It states that a vertical asymptote occurs when the function approaches infinity as x approaches a particular value, making that x-value an asymptote. A horizontal asymptote occurs when the limit of the function is a real number L as x approaches positive or negative infinity, making the lines y=L asymptotes. It provides properties and examples of determining horizontal asymptotes of rational functions based on the degrees of the numerator and denominator.