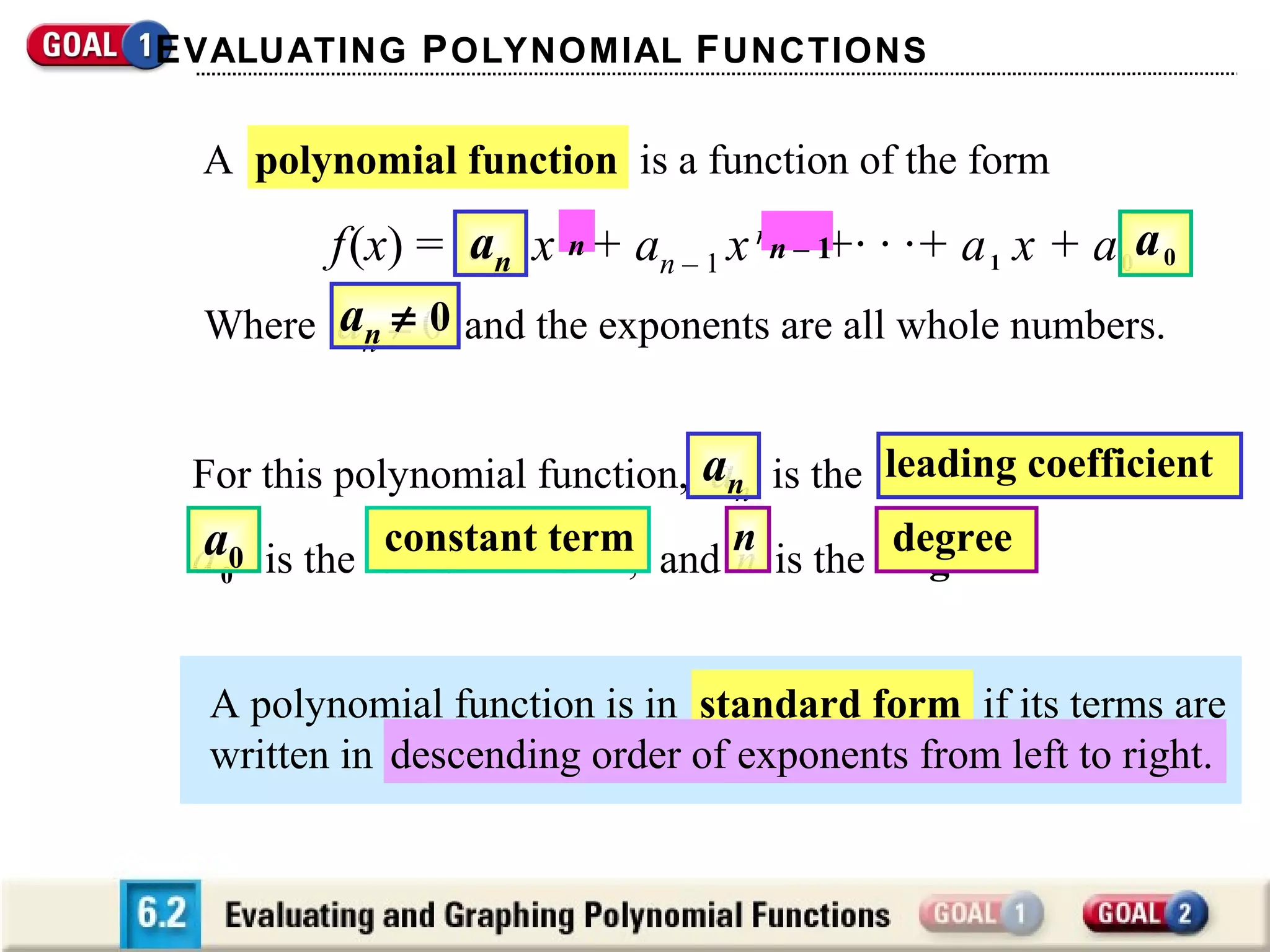
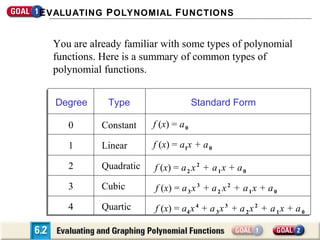
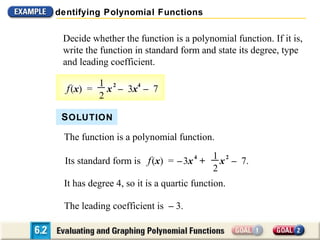
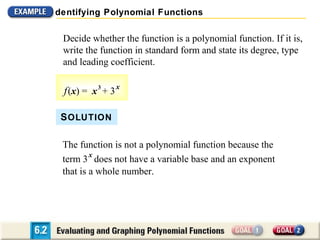
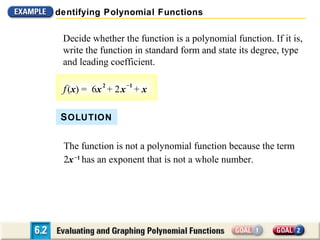
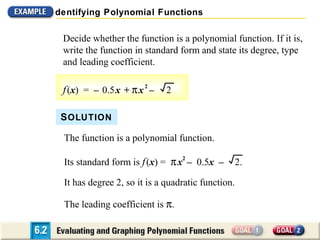
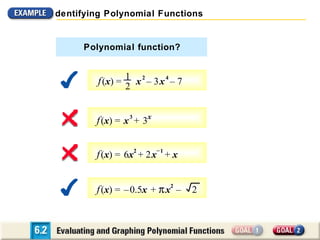
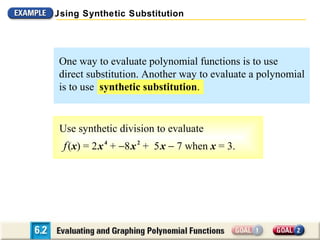
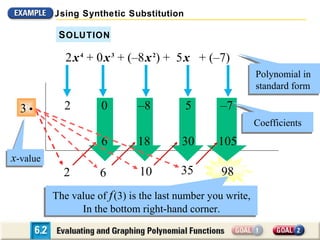
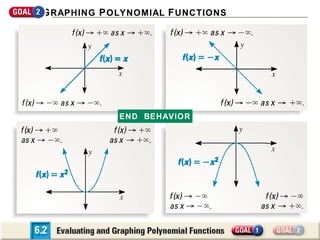
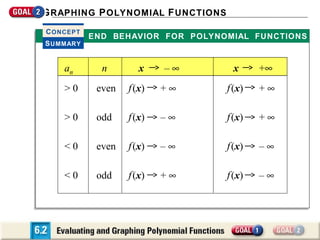
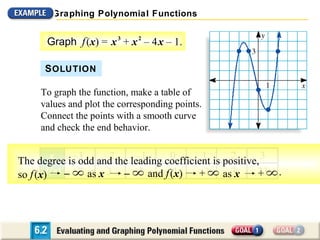
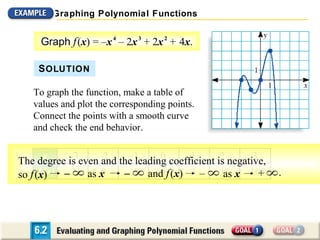
The document discusses evaluating and graphing polynomial functions, which are functions of the form f(x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a1x + a0, where the exponents are whole numbers. It provides information on identifying polynomial functions, evaluating them using synthetic substitution, and graphing them by examining end behavior as x approaches positive or negative infinity. Common types of polynomial functions include constant, linear, quadratic, and cubic functions.