Embed presentation
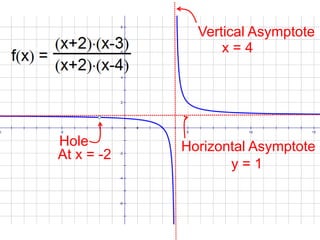




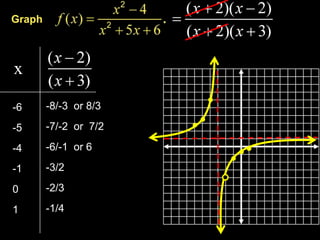



This document discusses key concepts for graphing rational functions: 1) Vertical and horizontal asymptotes are determined by factors in the denominator that do or do not cancel out. A vertical asymptote is indicated at x = -3 and there is a hole at x = -2. 2) The horizontal asymptote is the line y = 1. 3) Examples are provided to demonstrate graphing rational functions based on identifying discontinuities and asymptotes.








