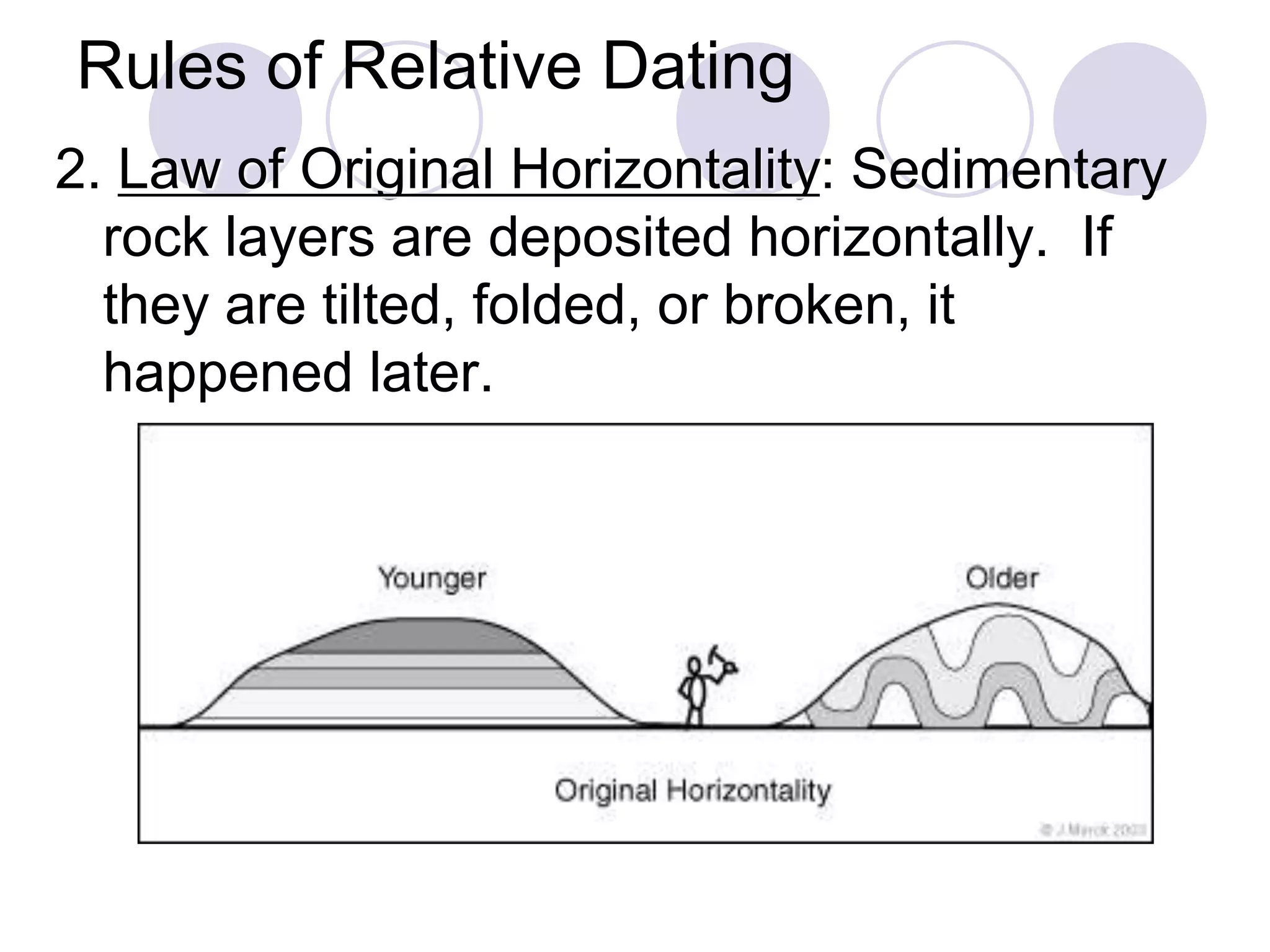
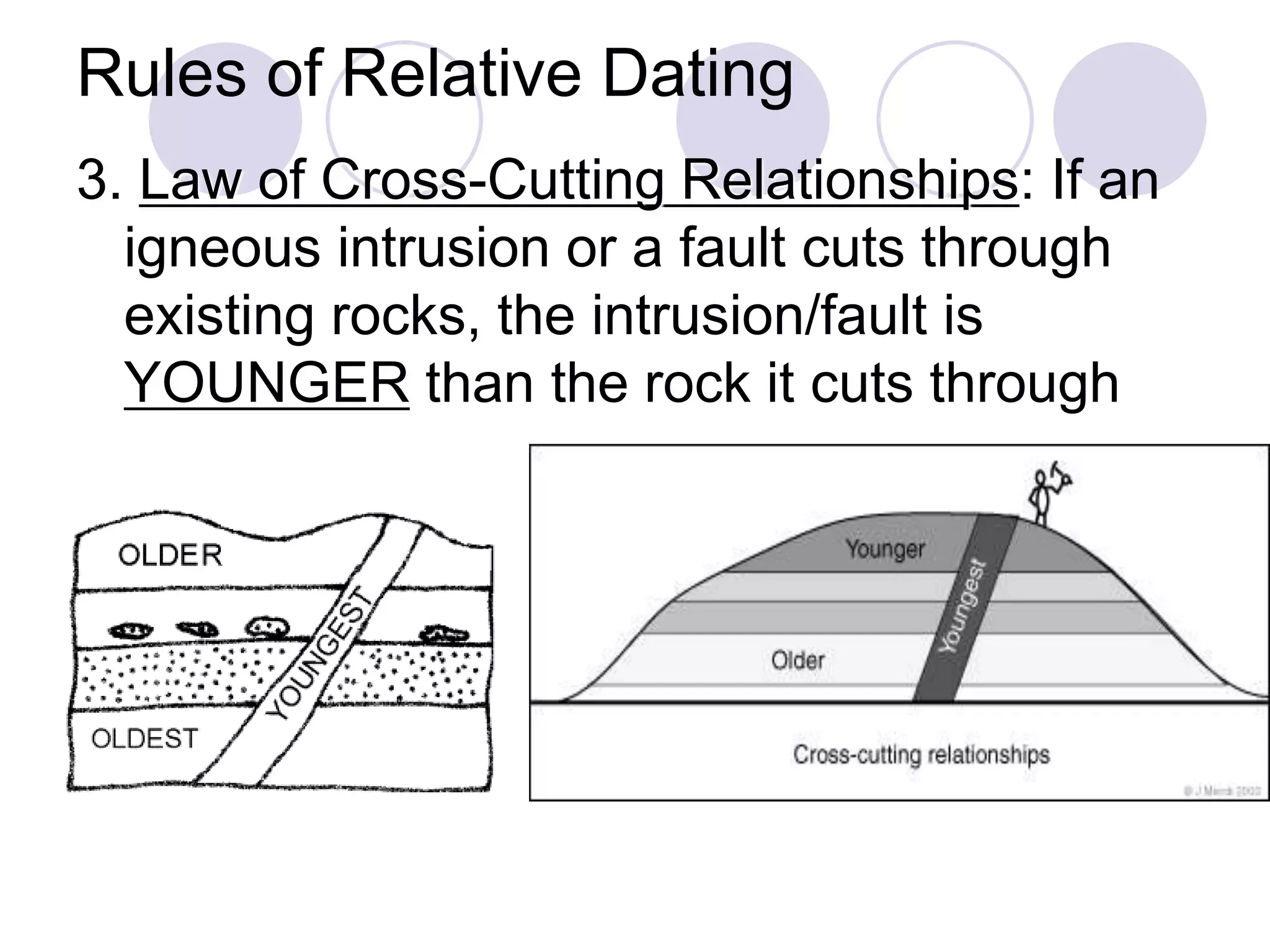
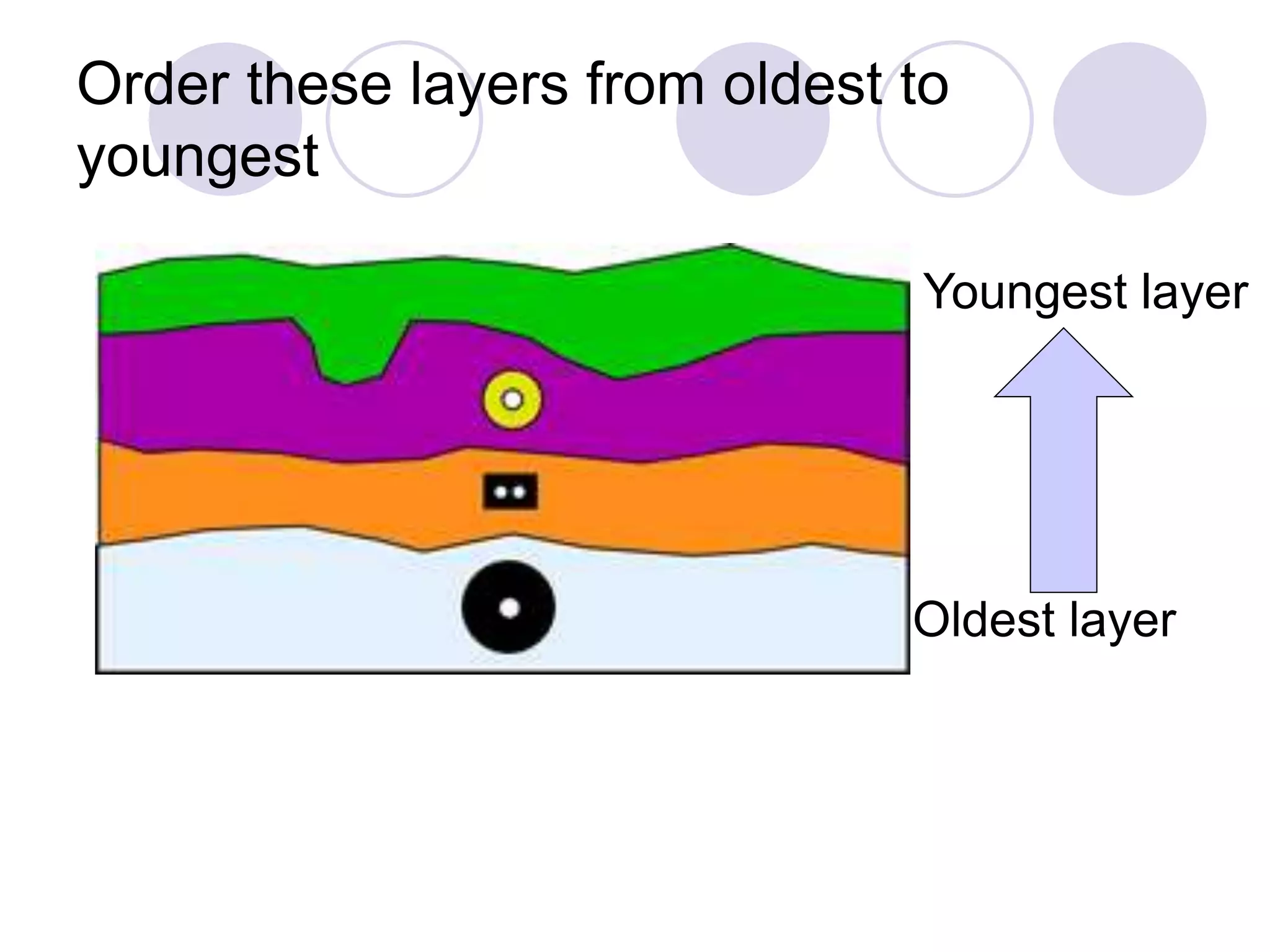
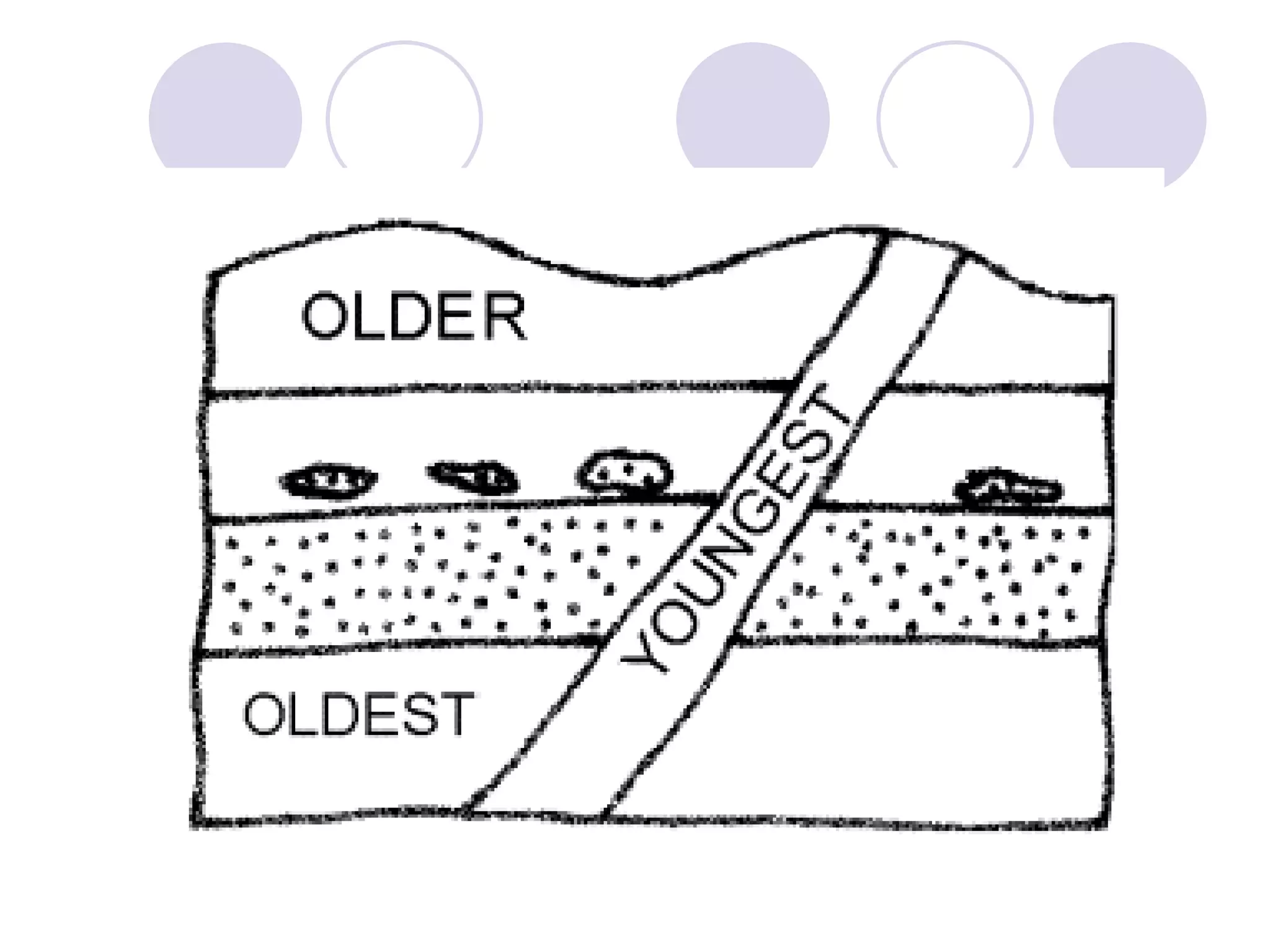
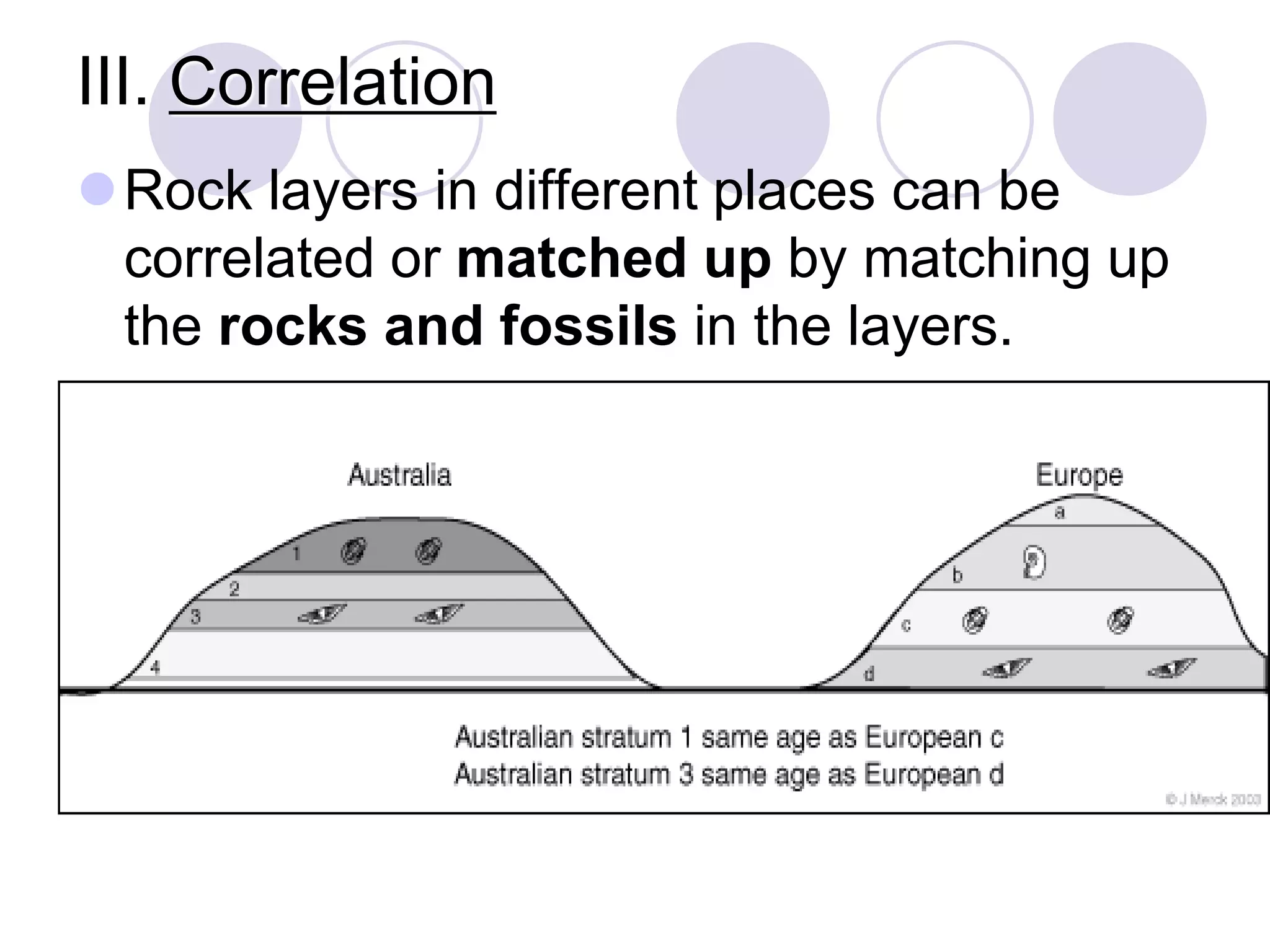
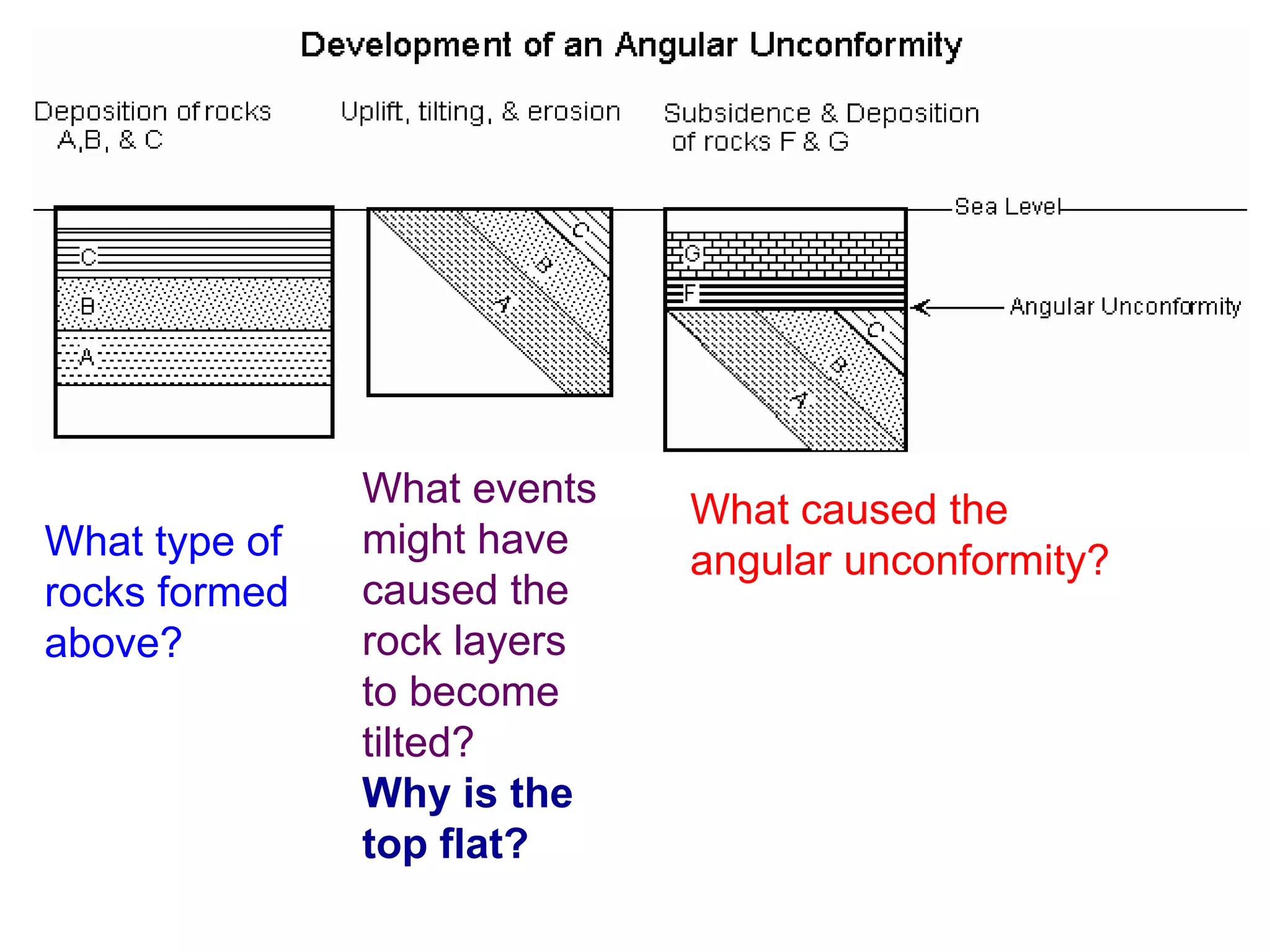
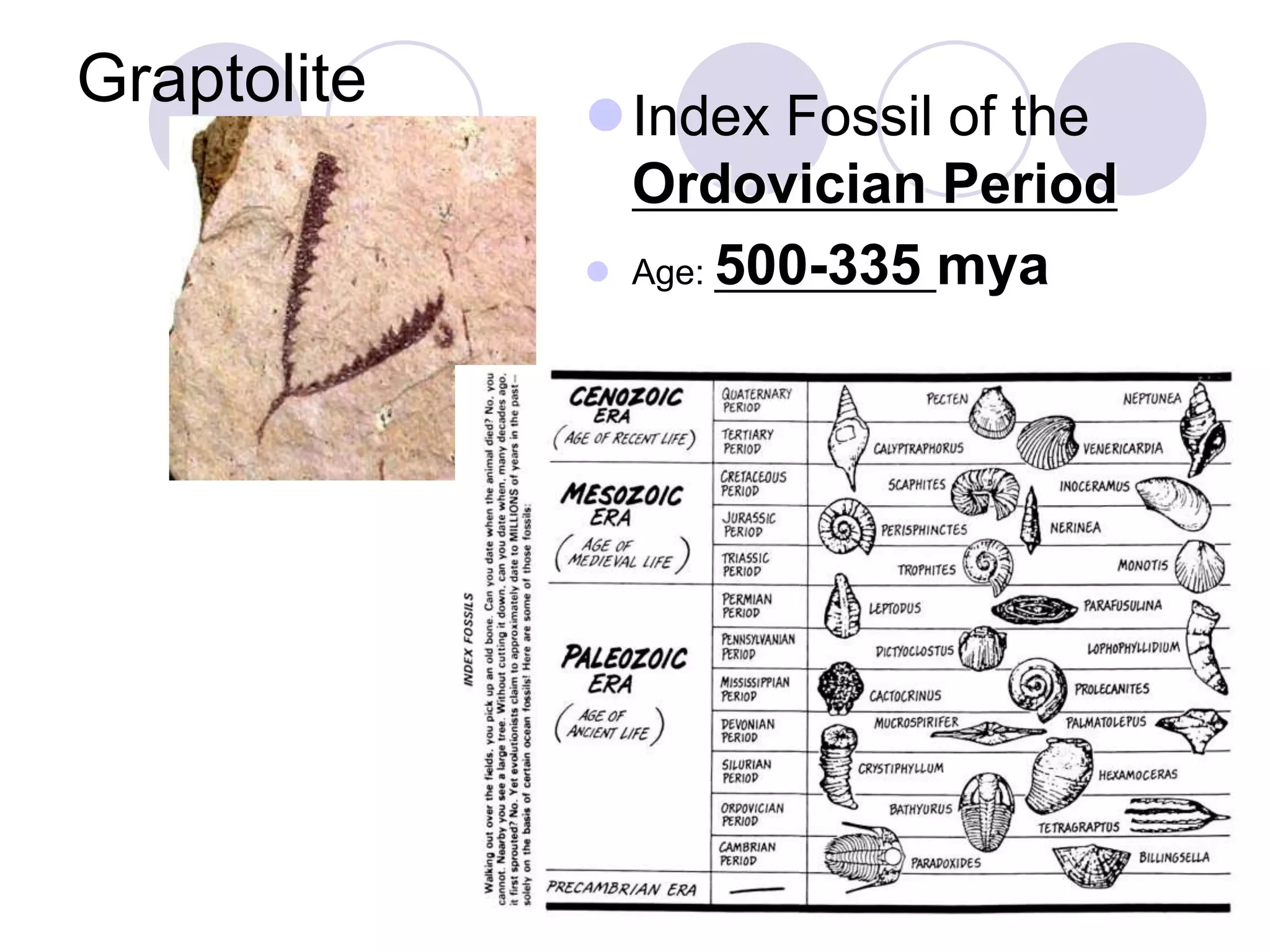
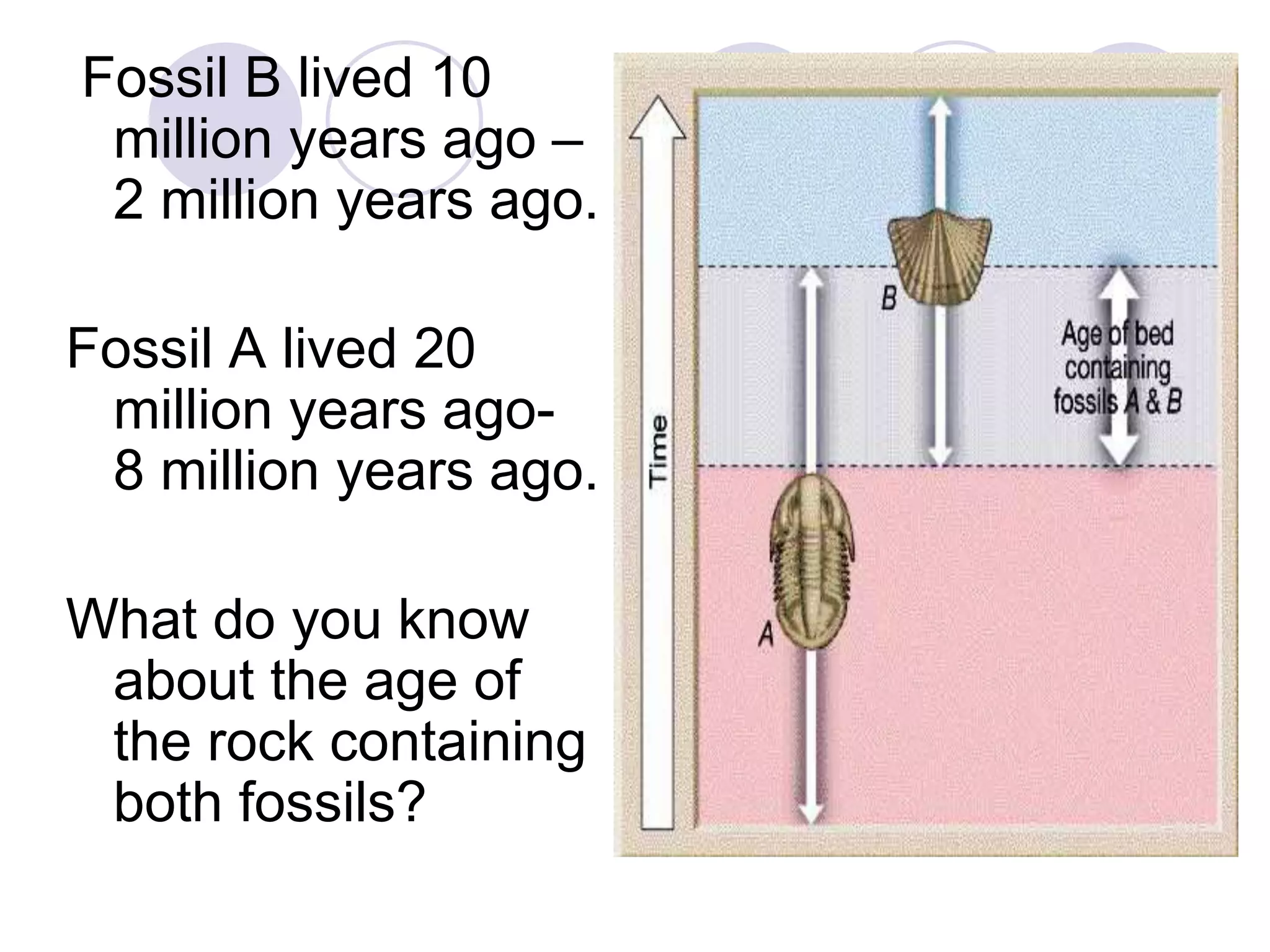
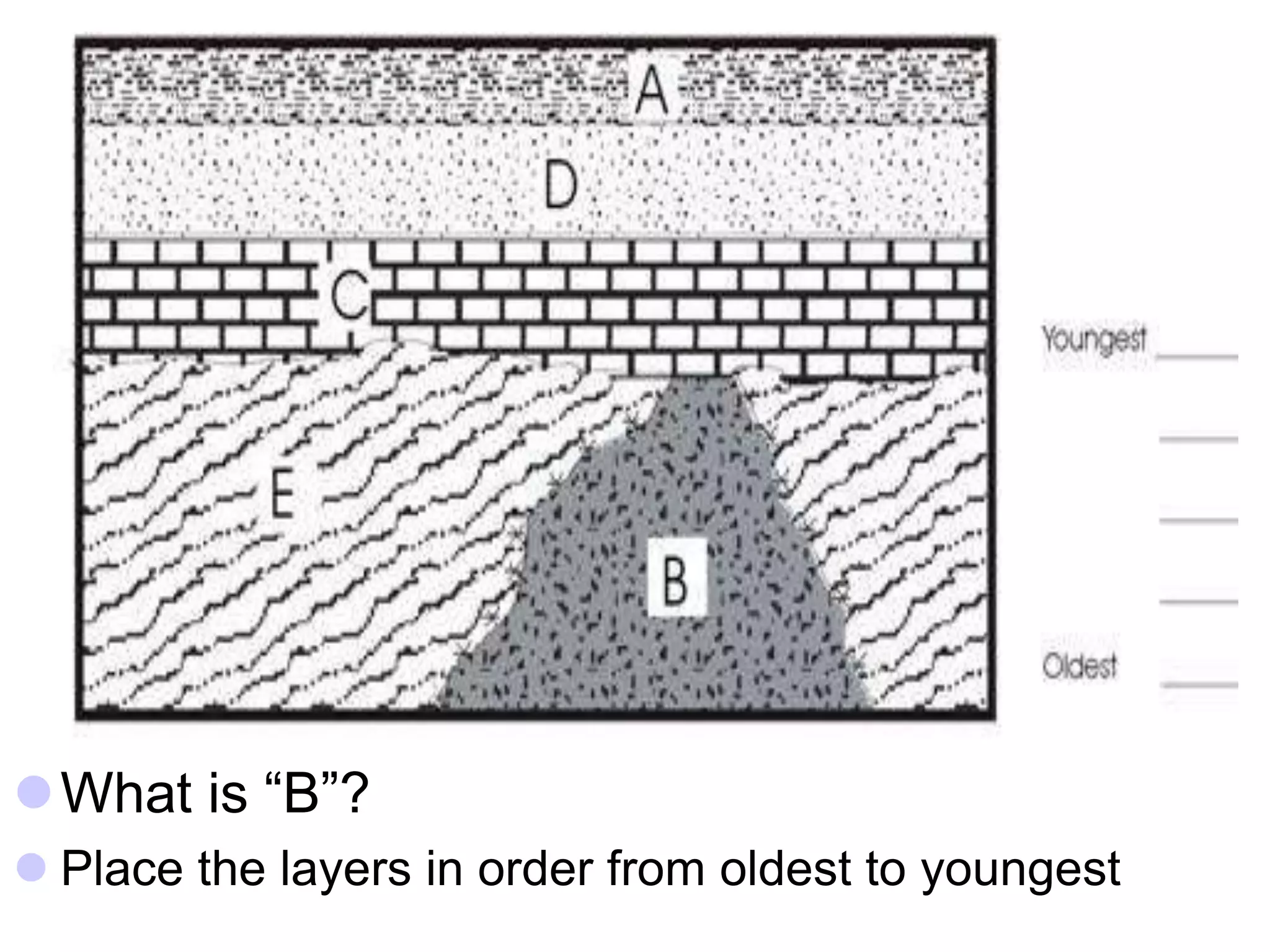
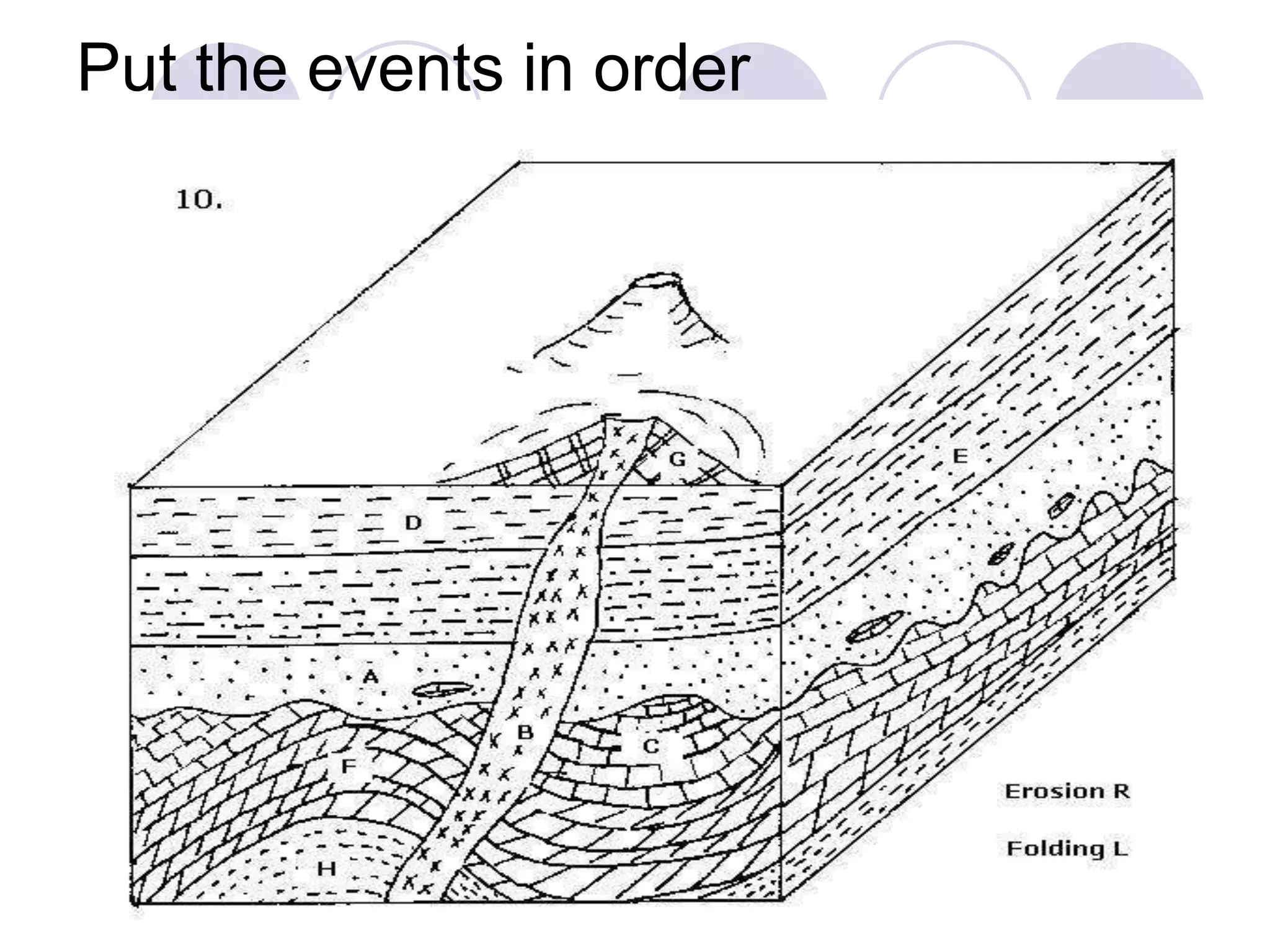
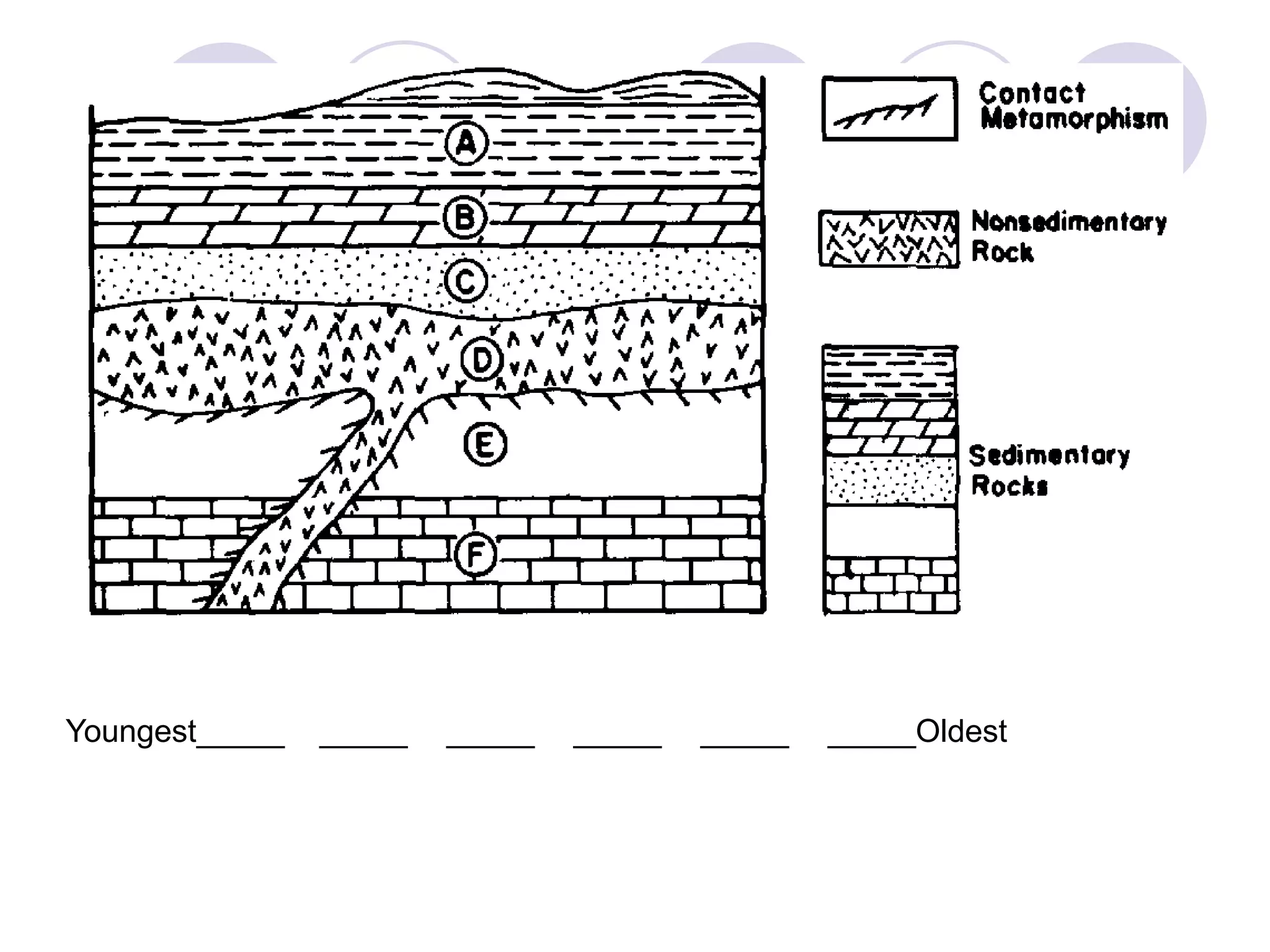
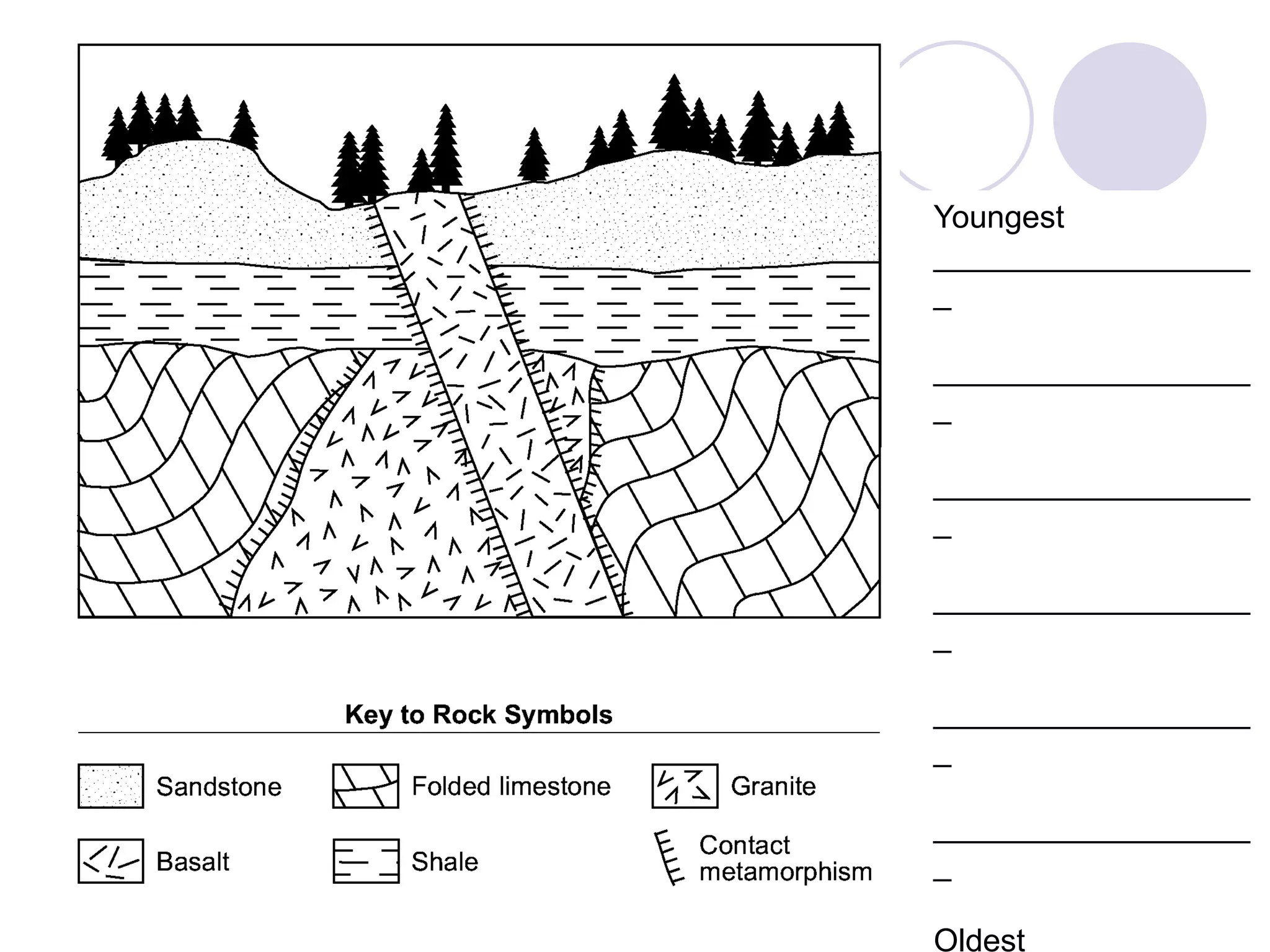
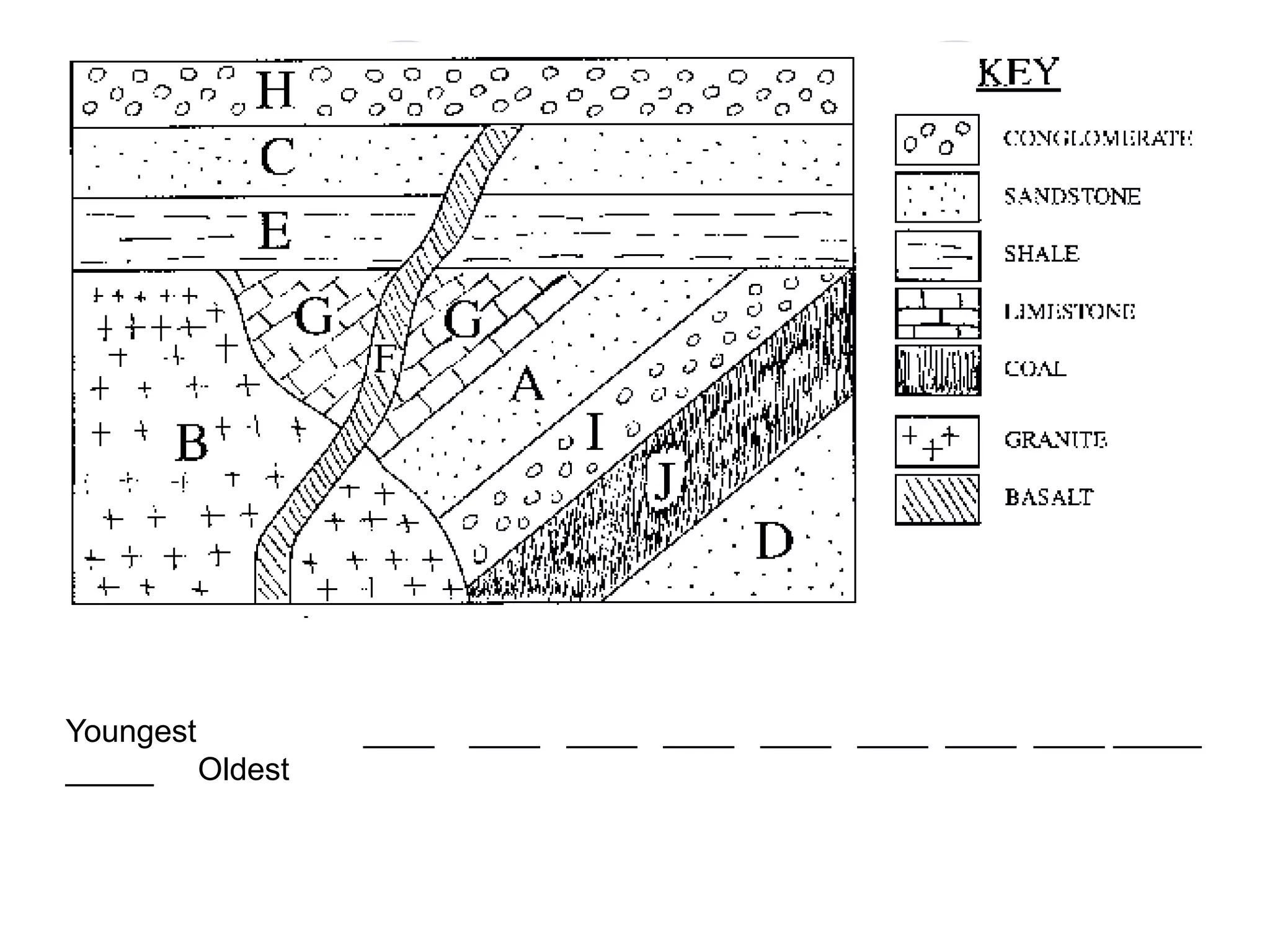
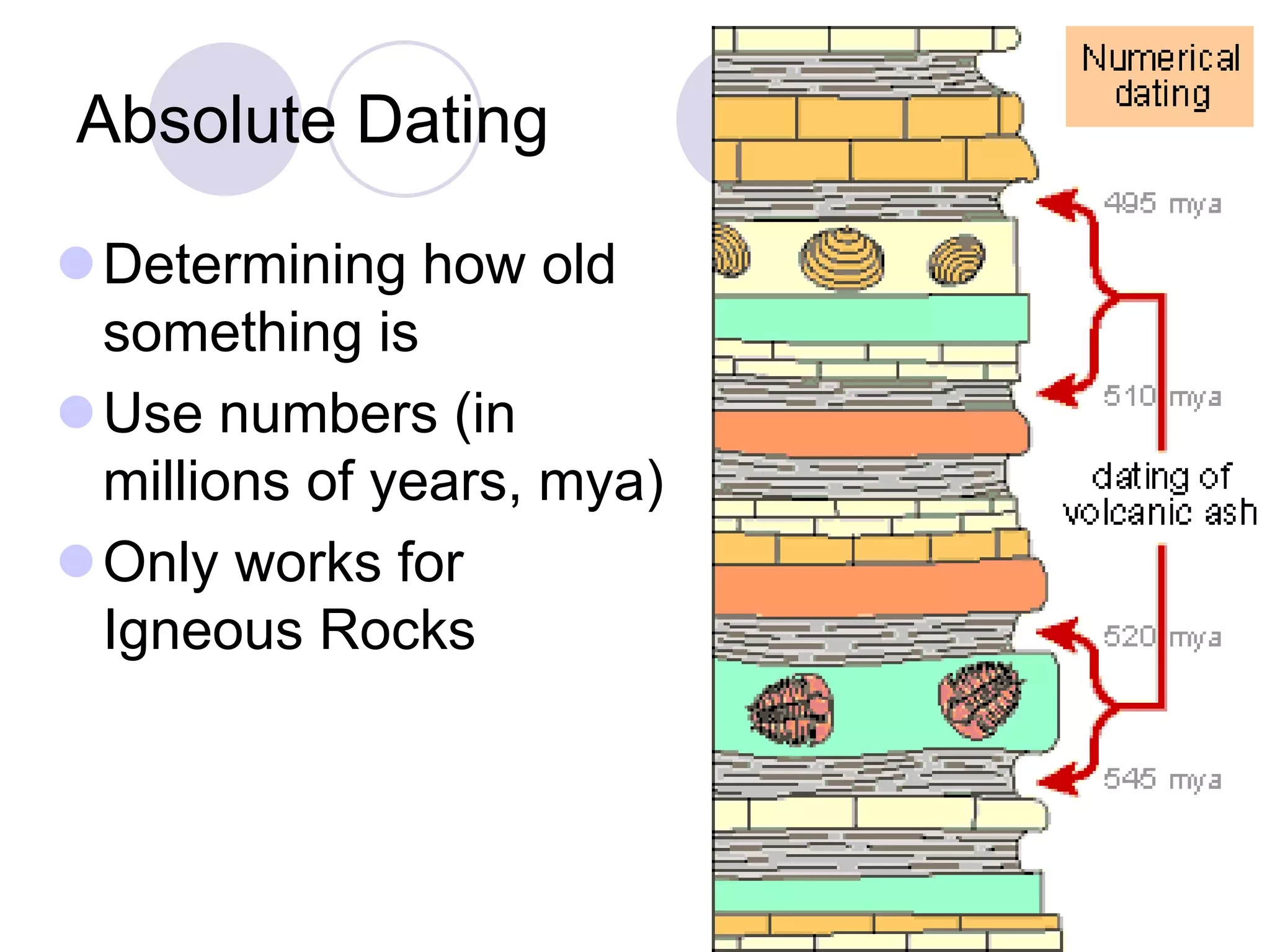
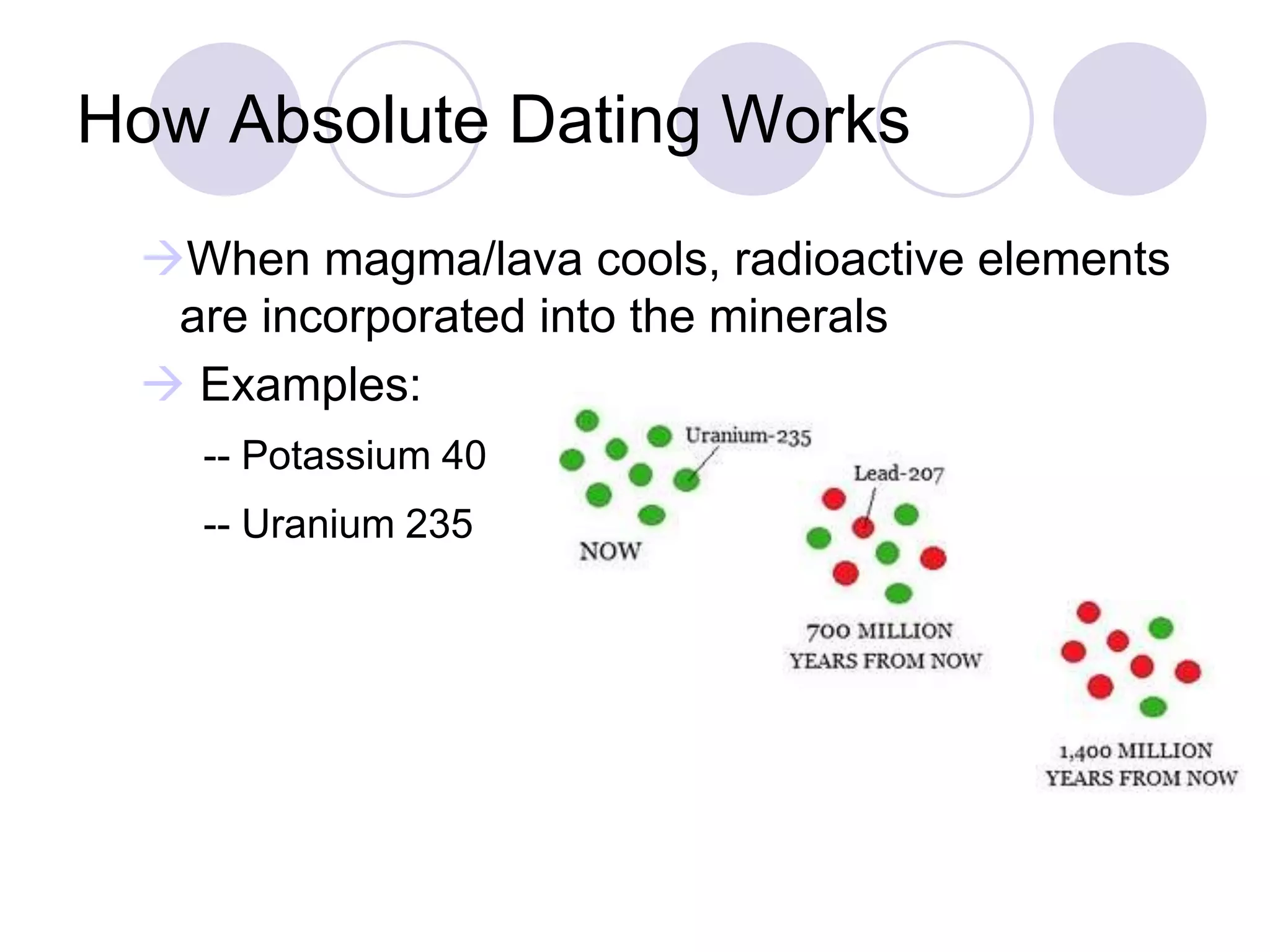
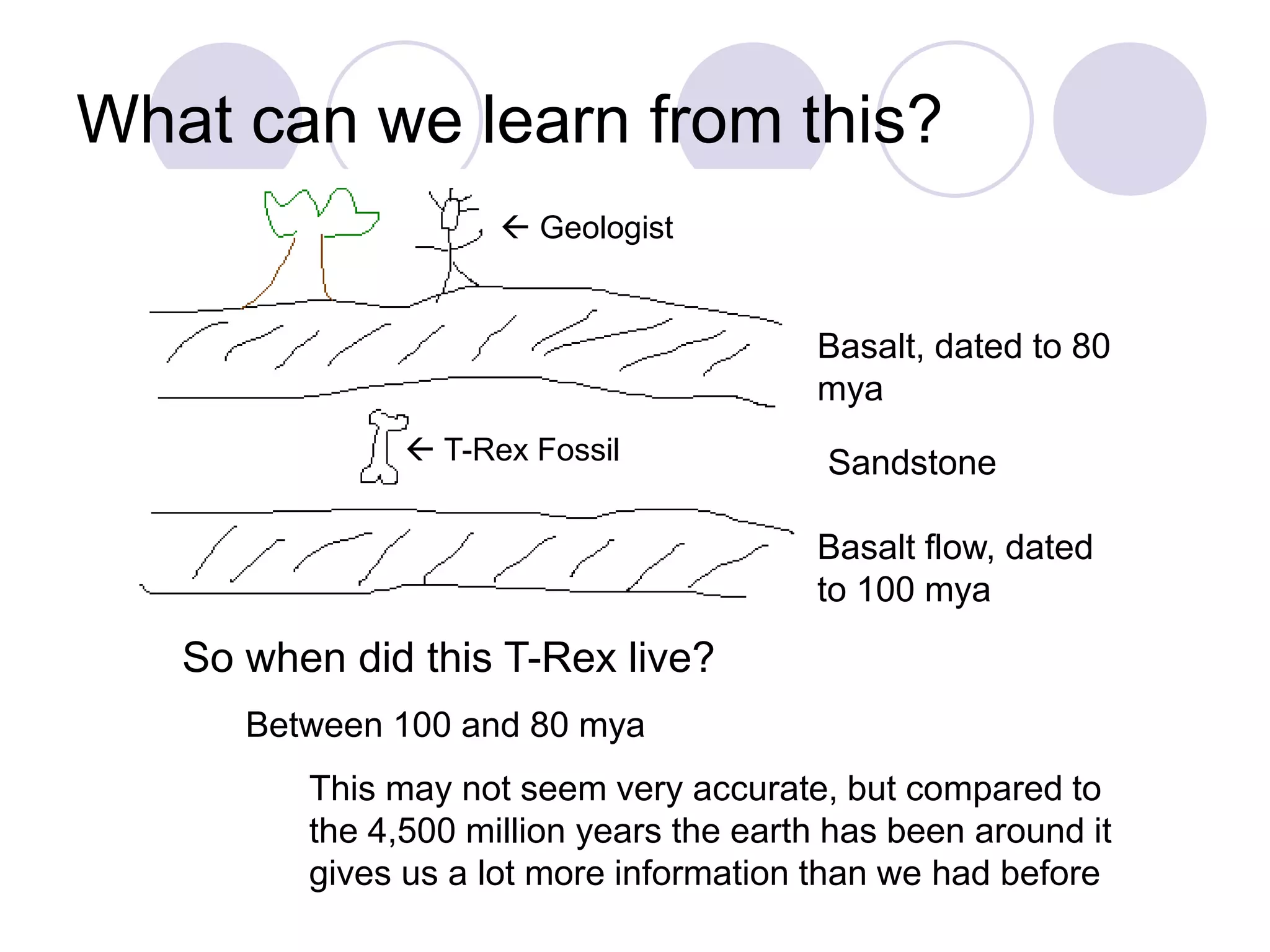
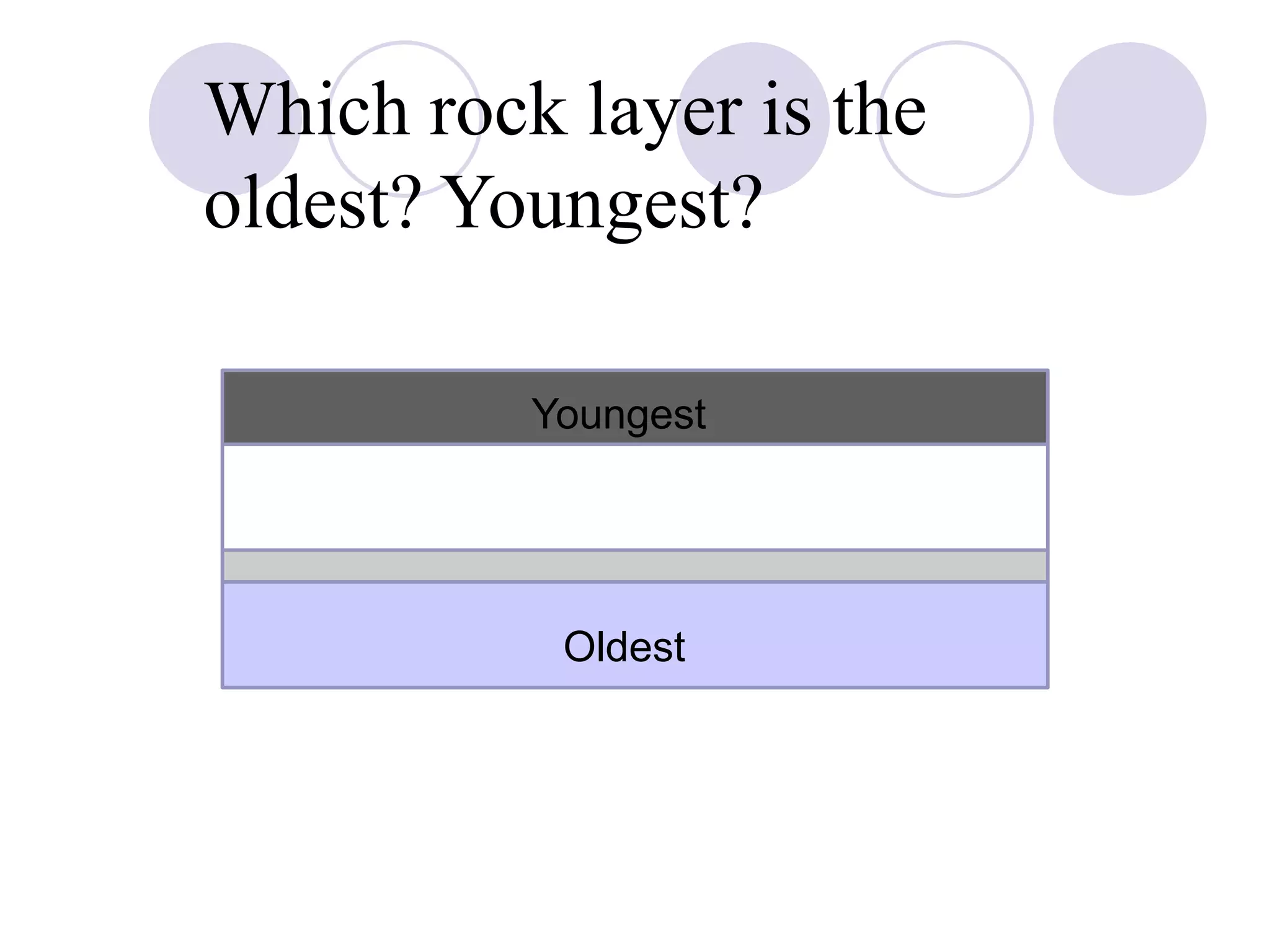
This document discusses methods for dating fossils and rocks. It describes two main dating methods: relative dating and absolute dating. Relative dating involves determining the relative ages of rocks or fossils compared to one another, using principles like superposition. Absolute dating determines precise ages in years using radiometric dating techniques like carbon-14 dating or potassium-argon dating. Radiometric dating works by measuring the decay of radioactive elements that were present when rocks formed. Together, relative and absolute dating provide scientists with tools to reconstruct sequences of geological events and better understand the age of fossils and rocks.