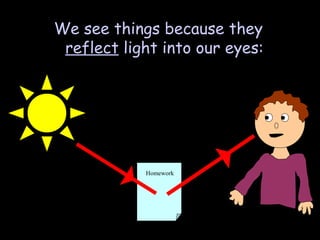
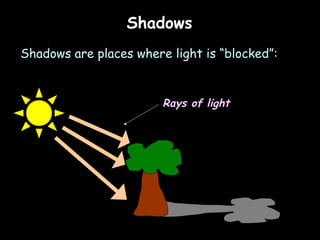
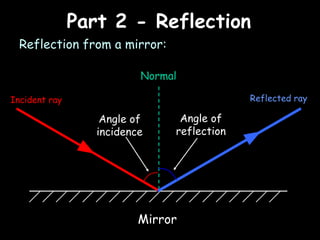
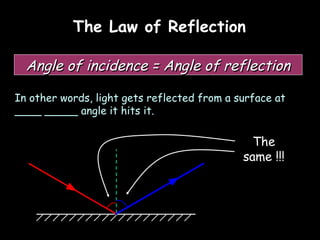
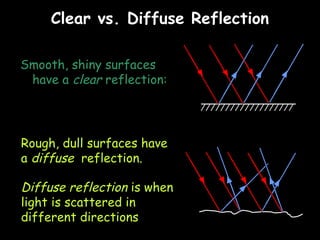
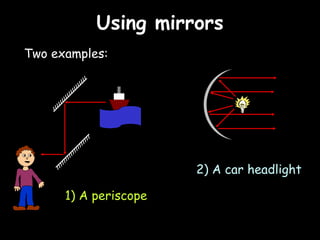
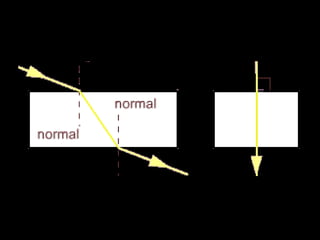
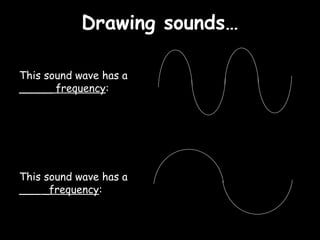
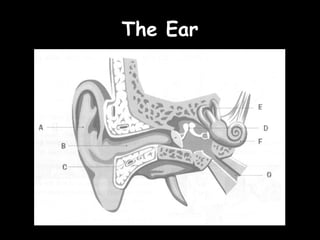
Here is a labeled diagram of the ear:
Outer Ear
- This part "picks up" the vibrations
Ear Canal
- This part "channels" the sound towards the ear drum
Ear Drum
- This part is vibrated by the sound waves
Hammer
- One of the bones vibrated by the eardrum
Anvil
- One of the bones vibrated by the eardrum
Stirrup
- One of the bones vibrated by the eardrum
Cochlea
- This part of the ear contains many small hairs with turn vibrations into an electrical signal
Semicircular Canals
- This