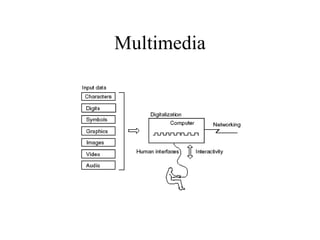
Multimedia involves four key factors: digitization of audio and visual content, networking to exchange information over communication lines, interactivity through two-way communication, and diverse human interfaces. It is a collection of technologies used to manipulate text, graphics, audio, and video. Multimedia applications accept user input and perform actions in response through interactive links.