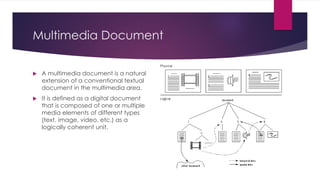
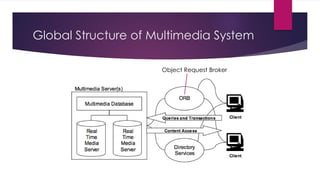
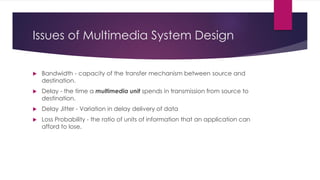
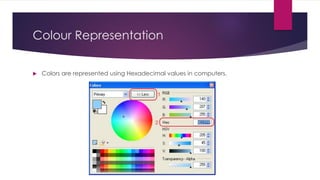
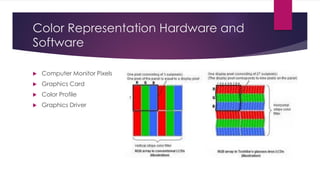
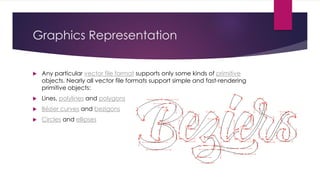
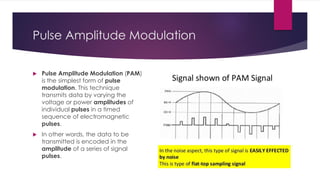
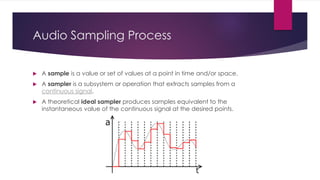
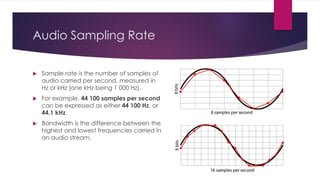
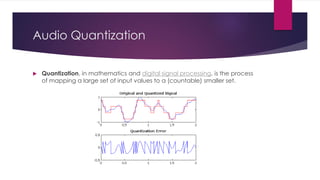
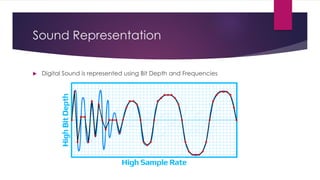
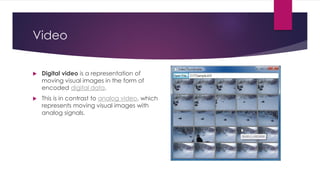
Chapter 3 covers multimedia system design, focusing on the processing, storage, and manipulation of multimedia data and applications. It addresses multimedia documentation, architecture, and key properties, while also outlining challenges and issues in multimedia system design such as bandwidth and latency. Additionally, it details digital representation across audio, video, and image formats, and discusses hardware and software requirements for effective multimedia processing.