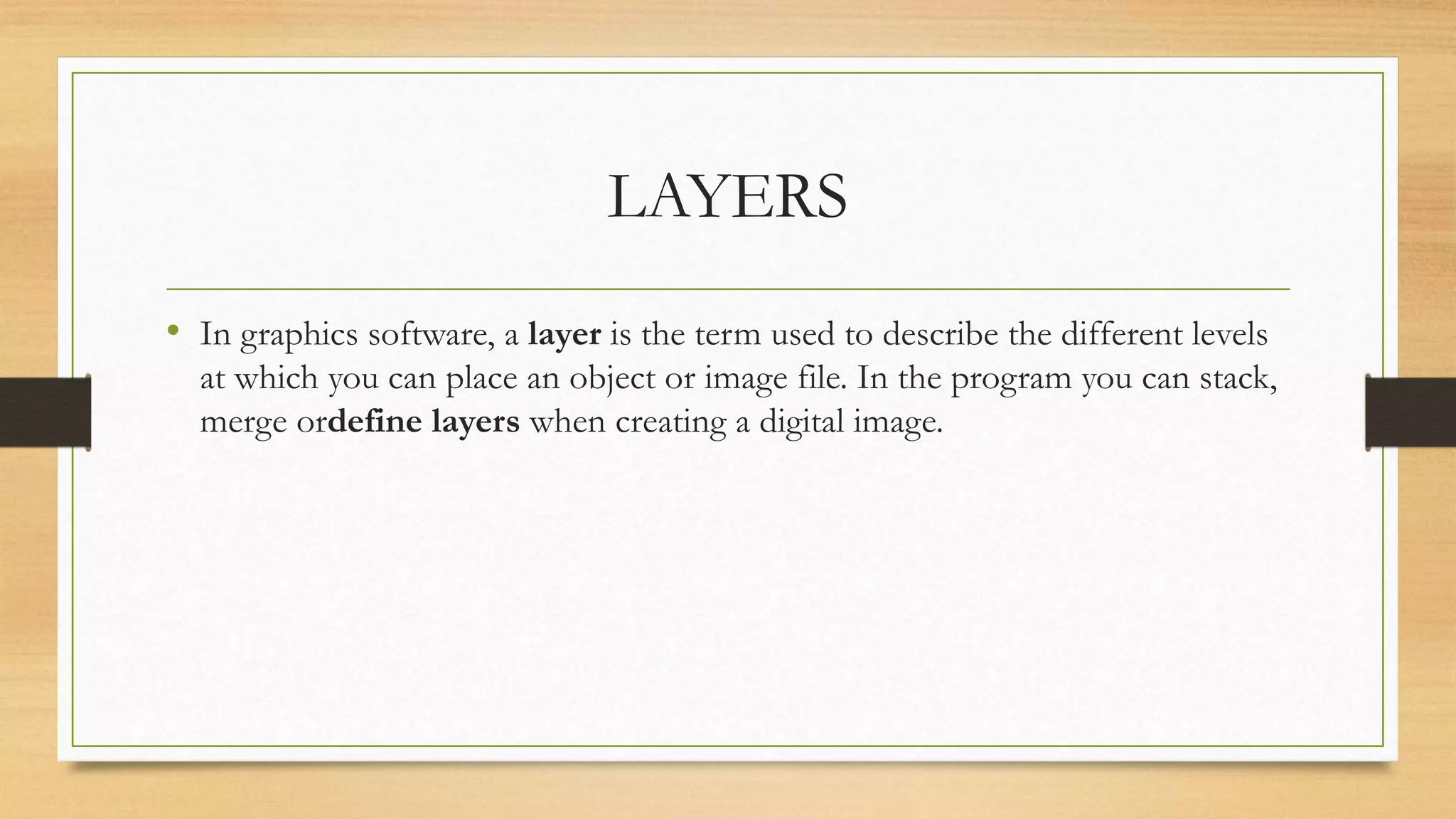
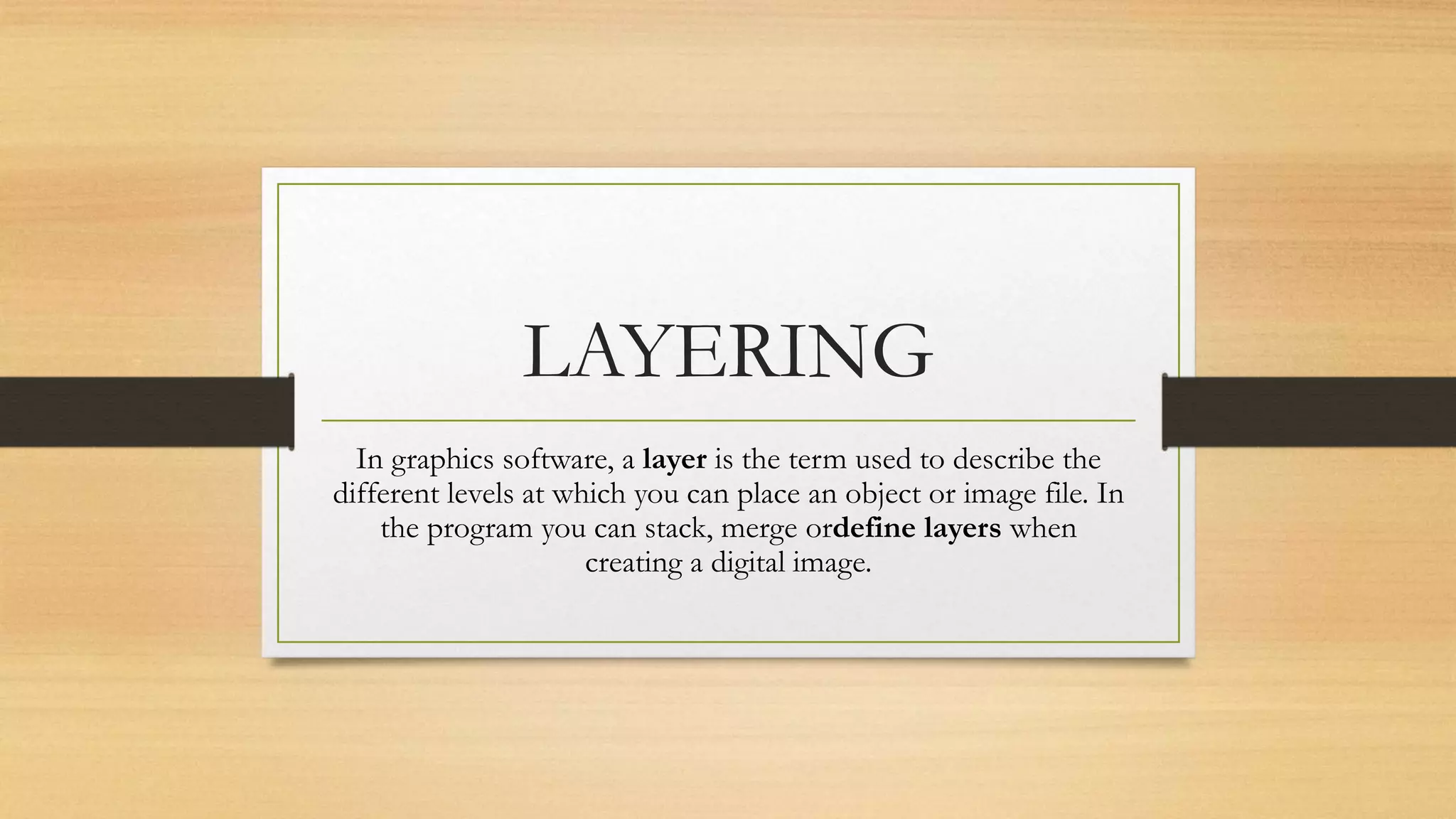
Image editing applications allow users to crop, touch up, and organize digital photos into albums and slideshows, though they typically have fewer filters than professional programs like Photoshop. Cropping removes outer parts to improve framing or change aspect ratios. Resizing and compressing optimize file sizes for intended uses after editing. Correcting and sharpening or softening are global corrections often applied to digital images. Layers, selections, resolution, image size, and color mode are key terms related to editing digital images.