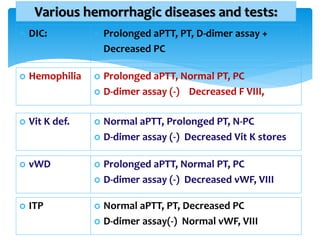
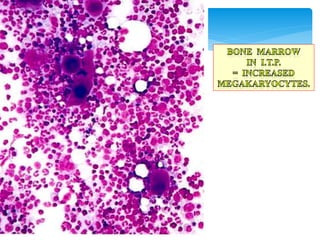
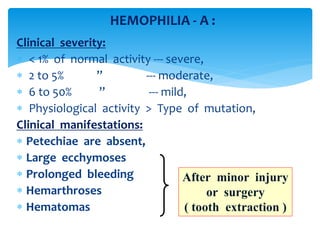
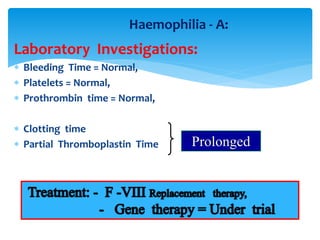
This document discusses various platelet and coagulation disorders. It covers quantitative and qualitative platelet disorders including thrombocytopenia and Glanzman's thrombasthenia. Congenital coagulation disorders discussed are hemophilia A, hemophilia B, and von Willebrand disease. Acquired coagulation disorders include vitamin K deficiency and liver disease. Tests covered are bleeding time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, and specific factor assays. Clinical manifestations of bleeding based on location and platelet versus coagulation origin are also summarized. Hemophilia A is then discussed in more detail including inheritance, clinical severity, manifestations, and laboratory findings.



![ Most common hereditary disease,
Cause:
... Factor - VIII deficiency [ Procoagulant]
Inheritance Pattern:
… X - linked recessive trait,
[ Sufferers - Invariably males,
Females - homozygous,
- unfavourable lionization,
… 30% no family history [ new mutations ]
HAEMOPHILIA – A:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150304102010-conversion-gate01/85/3-bleeding-disorders-dr-sinhasan-mdzah-8-320.jpg)
![CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS:
Clinically indistinguishable from
Haemophilia - A
DIAGNOSIS:
Factor Assay only;
HAEMOPHILIA - B
[ CHRISTMAS DISEASE, FACTOR - IX DEFICIENCY ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150304102010-conversion-gate01/85/3-bleeding-disorders-dr-sinhasan-mdzah-11-320.jpg)