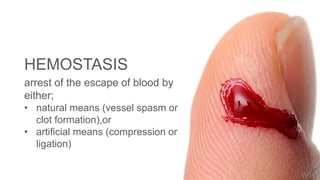
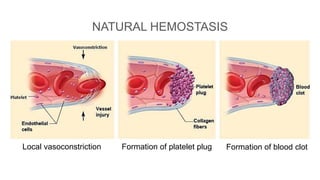
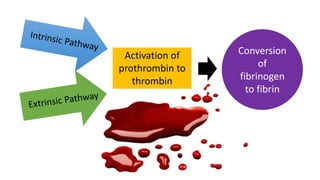
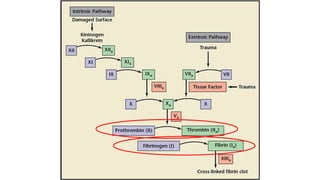
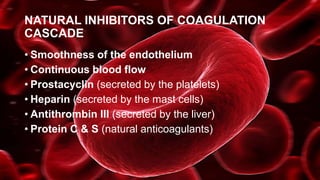
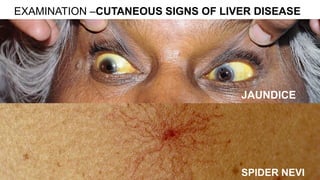
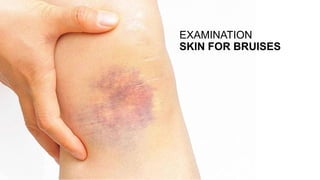
This document discusses surgical hemostasis. It begins by outlining the learning objectives, which are to understand what hemostasis is, the causes of excessive bleeding during or after surgery, and how to evaluate a patient's hemostasis before surgery. It then defines hemostasis as the arrest of blood escape through natural or artificial means. It describes the natural hemostasis process involving vasoconstriction, platelet plug formation, and blood clot formation. It lists the 12 clotting factors and the intrinsic and extrinsic clotting pathways. The document concludes by discussing causes of bleeding during or after surgery, including defects of hemostasis, and the steps of pre-operative evaluation of a patient's hemost