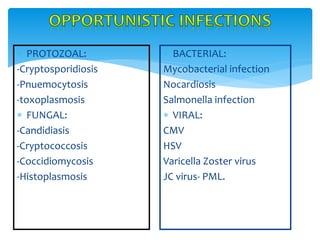
HIV is a retrovirus that causes AIDS by profoundly weakening the immune system through depletion of CD4+ T cells. It is transmitted via bodily fluids and can be passed from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding. While HIV infection may not cause symptoms for years, it can ultimately lead to AIDS if left untreated. Common opportunistic infections associated with AIDS include Pneumocystis pneumonia, toxoplasmosis, and various fungal and bacterial infections.