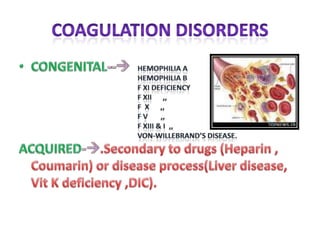
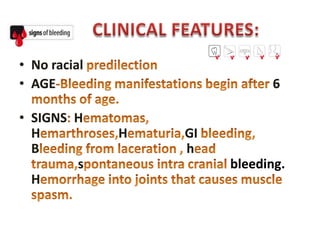
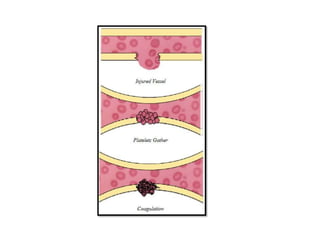
Dental procedures can have serious consequences for patients with bleeding disorders, possibly resulting in severe hemorrhage or death. Laboratory tests help evaluate coagulation disorders and bleeding risks, including platelet count, bleeding time, PT/INR, aPTT, and tests for factors, fibrin degradation products, and capillary fragility. Treatment depends on the specific disorder or condition, and may include replacement of platelets, coagulation factors, cryotherapy, laser ablation, or medications like tranexamic acid, desmopressin, corticosteroids, or thrombopoietin agents.










![fibrinolysis
(tPA)
PLASMINOGEN PLASMIN.
[FDPs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bleedingclottingdisorders-111121084102-phpapp02/85/Bleeding-clotting-disorders-12-320.jpg)