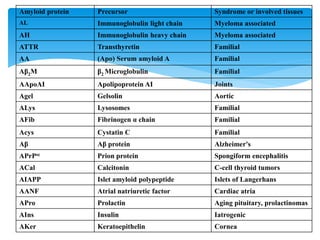
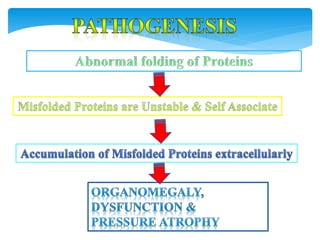
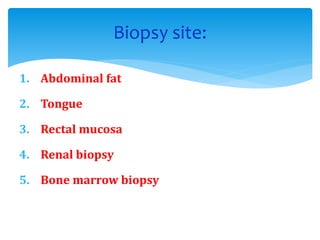
Amyloid is an abnormal protein that aggregates into unbranched fibrils. It is caused by misfolding of normal or mutant proteins. There are different types classified by the precursor protein such as AL, AA, and Aβ. Amyloidosis involves deposition of amyloid fibrils in tissues and organs which can cause organ dysfunction. Diagnosis involves staining methods like Congo red that show apple-green birefringence under polarized light. Biopsies of affected tissues may be needed to confirm amyloidosis.