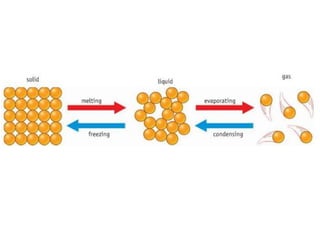
This document describes changes of state between solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that:
- Solids melt when heated and particles gain enough energy to overcome bonding forces, becoming a liquid. Different substances have different melting points depending on bonding strength.
- Gases condense when cooled, as slower particle motion allows intermolecular forces to attract particles together into a liquid.
- Liquids evaporate when heated, as faster particle motion overcomes bonding forces and particles escape as a gas. Evaporation leads to boiling when it occurs throughout the liquid.
- The boiling point of a liquid depends on surrounding air pressure, with lower pressure resulting in a lower boiling point.