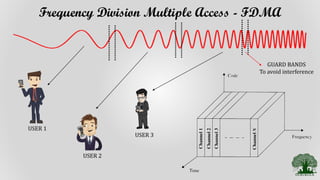
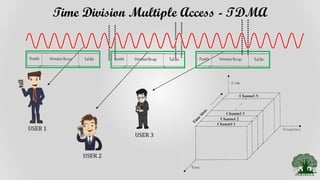
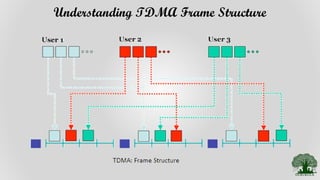
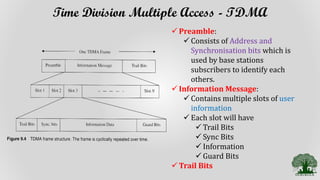
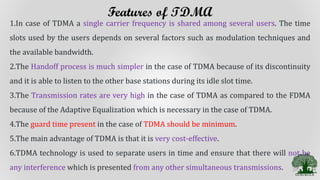
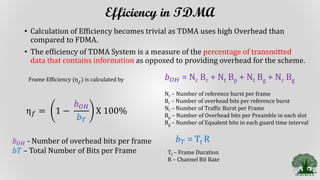
TDMA divides the radio spectrum into time slots and allows only one user to transmit or receive data during each time slot. It uses a buffer-and-burst transmission method, making it well-suited for digital systems. TDMA systems employ TDMA/TDD or TDMA/FDD for duplexing and multiple access. A TDMA frame includes a preamble for identification and synchronization, and multiple time slots containing user data, trail bits, and guard bits between slots. TDMA provides high transmission rates, simpler handoff, and is more cost-effective than FDMA, though it requires minimum guard times between slots to avoid interference.