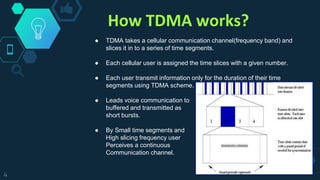
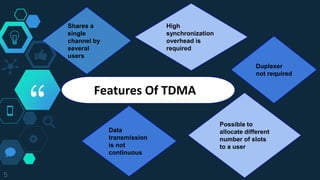
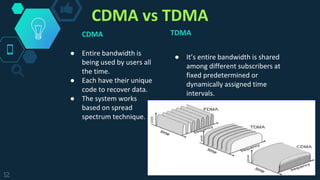
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) is a digital cellular communication technology that allows multiple users to share the same frequency by dividing a signal into time slots, increasing data capacity. The technology has evolved from first-generation analog systems to advanced digital standards like GSM and PDC. While TDMA offers advantages such as efficient spectrum use and lower operational costs, it also requires significant network planning and can be affected by multipath interference.