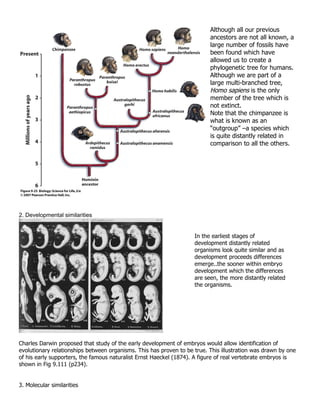
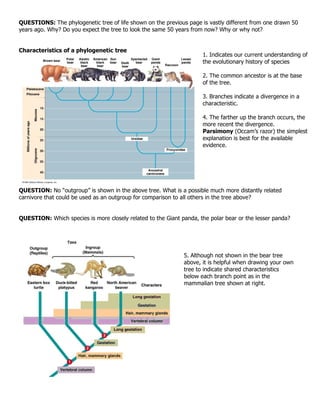
1. Phylogenetic trees illustrate the evolutionary relationships and degree of relatedness between organisms. They are based on Darwin's idea that all life shares a common ancestor.
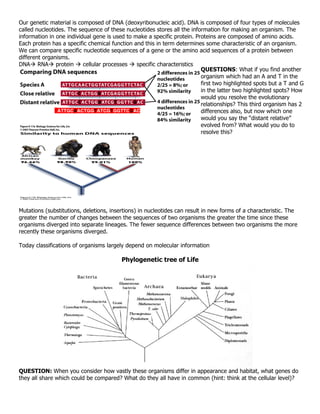
2. Characteristics used to construct phylogenetic trees include morphological similarities, fossil evidence, developmental patterns, and molecular sequences. Comparisons are made to determine shared derived characteristics versus analogous structures.
3. Phylogenetic trees are constantly revised as new evidence emerges from fossils, genetics and other data. Earlier trees may look quite different than current understanding.