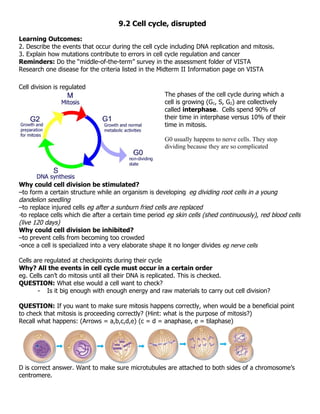
1. The cell cycle, which includes interphase and mitosis, is tightly regulated by checkpoints to ensure errors don't occur.
2. Mutations in genes that control the cell cycle, such as oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, can disrupt the checkpoints and allow cells to divide uncontrollably, potentially leading to cancer.
3. Viruses, carcinogens, and errors during DNA replication and mitosis can also introduce mutations that disrupt the cell cycle and contribute to cancer development if cells ignore checkpoints and divide excessively.