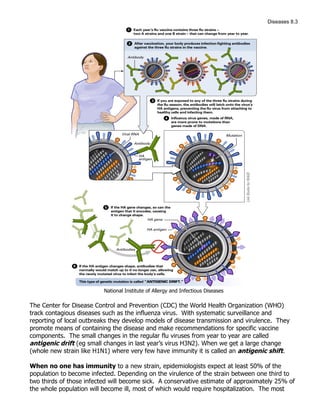
The most likely reason we get sick when the virus mutates is because we do not have a large pool of memory cells and antibodies which recognize the new shapes (antigens) on the surface of the mutated virus. When the virus mutates, it changes the shape of proteins on its surface like hemagglutinin. Our immune system has memory of previous shapes it has encountered, but not the new mutated shapes. Therefore, we are susceptible to infection by the new virus strain.