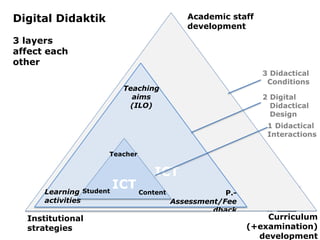
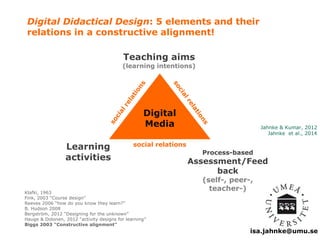
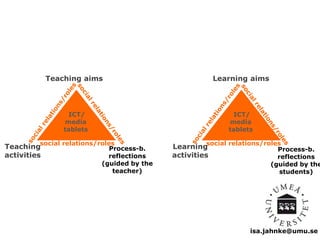
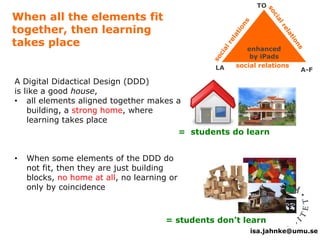
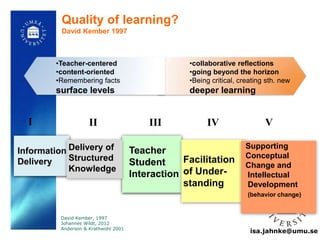
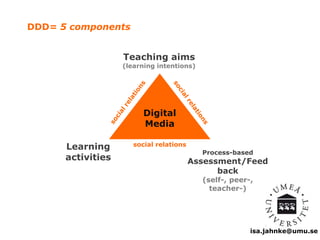
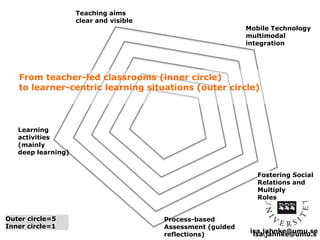
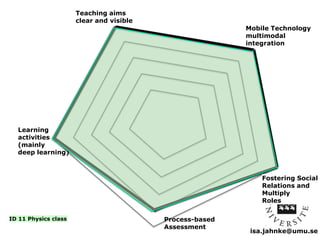
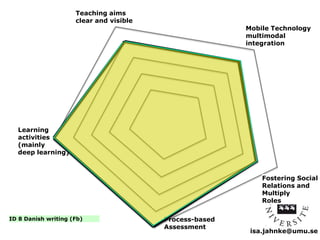
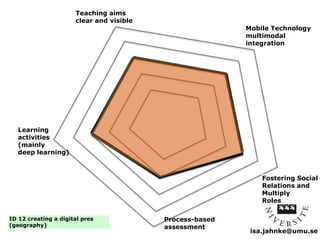
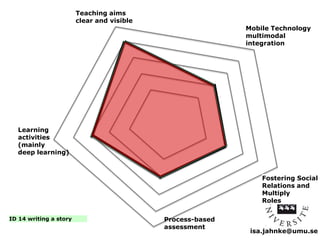
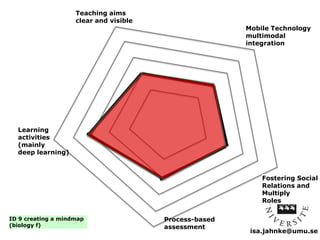
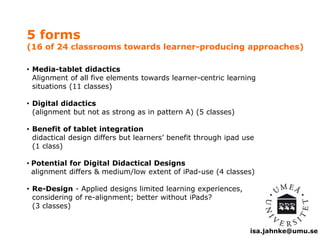
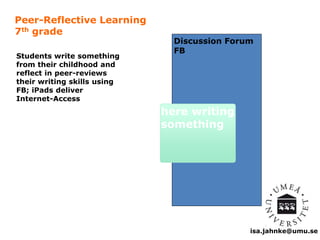
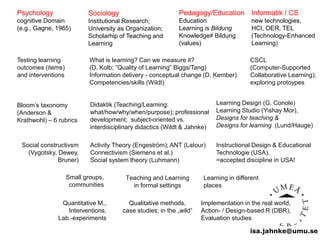
The document explores the integration of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in education, focusing on the impact of digital media on teaching and learning. It discusses the necessity of research on digital didactical designs that promote deeper learning and the evolving role of universities in fostering such educational environments. The content highlights various theoretical frameworks, technological trends, and the importance of constructive alignment in educational design for effective learning outcomes.


















![Characteristics of Web 2.0, Social Media and Co.
e.g., Jahnke & Koch, 2009
isa.jahnke@umu.se
Beliefs
Partizipation
„Architecture of Participation“
„Everyone can be a publisher“
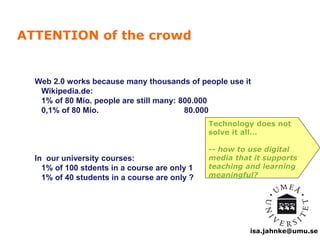
“Wisdom of the Crowds”
Software systems that support
human collaboration
finding other people – building of social relations and
networks
Me-Centricity, Human interaction via human-computer-interaction (HCI; CHI)
Easy to use, Interactive systems
Fun and Flow experience
Degree of freedom to act: informal [less rules, only few roles, no standardized
behavior, still not formal – but on the way to become more formal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-ict-in-educ-v2ij-web-141007055237-conversion-gate02/85/2014-ICT-in-education-24-320.jpg)